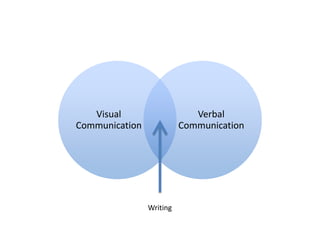
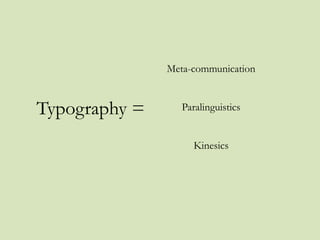
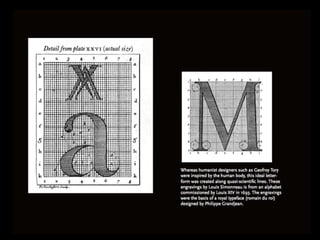
This document aims to provide a simple introduction to the history of typography by covering six main classifications of type, some famous typefaces and their connotations, the metalinguistic function of typography, and details about kerning and x-heights. It discusses type from Gutenberg's printing press to modern sans serif fonts. The document introduces humanist, old style, transitional, modern, slab serif, and sans serif type classifications and examples like Garamond, Bodoni, Gill Sans, and Times New Roman. It concludes by emphasizing the visual communication of type beyond just content.