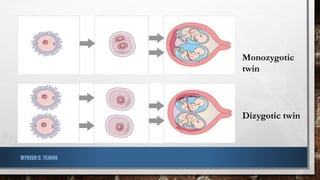
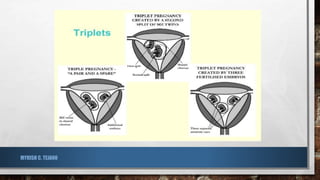
The document provides an overview of multiple births, including twins, triplets, and quintuplets. It explains the differences between monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins, as well as the formation of triplets and quintuplets, and discusses the risks associated with multiple pregnancies. The text notes that quintuplets are extremely rare, occurring naturally in approximately 1 in 55 million births.







![• Quintuplets occur naturally in 1 in 55,000,000 births.[10] the first quintuplets known to
survive infancy were the all-female Canadian Dionne quintuplets, born in 1934.
MYRISH C. TEJANO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tc4poweerpointtejano-160721182053/85/Twins-Triplets-and-Quintuplets-11-320.jpg)