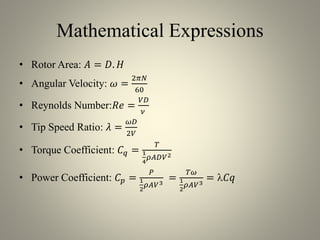
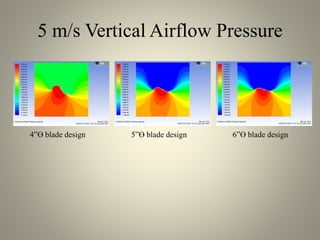
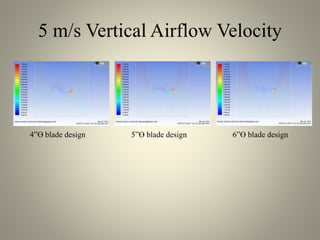
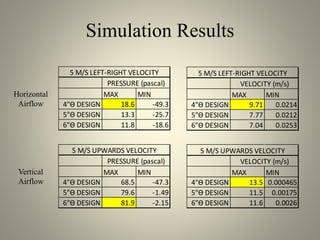
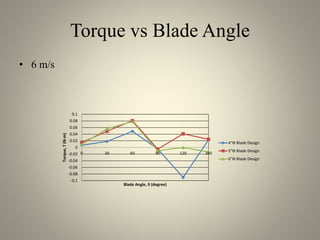
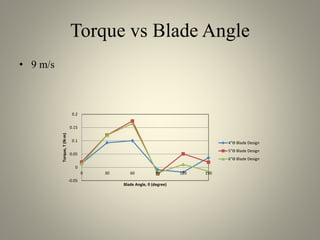
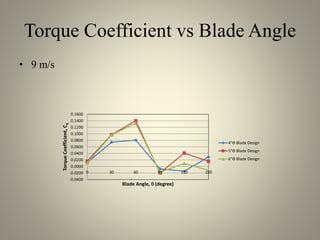
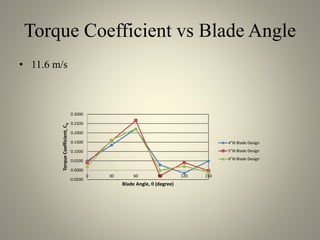
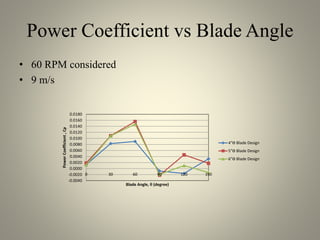
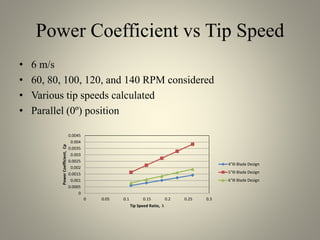
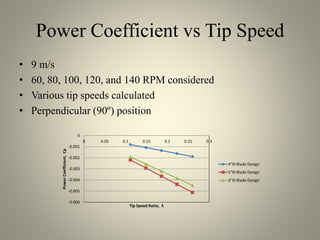
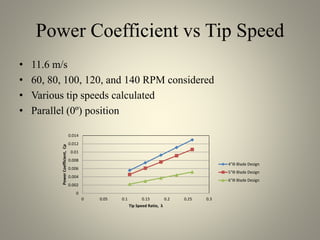
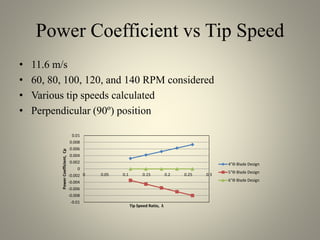
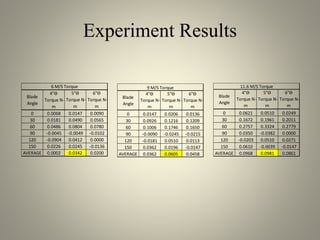
This document analyzes the static torque of various two-bladed Savonius wind turbine models through computational fluid dynamics simulations and wind tunnel experiments. It finds that a turbine with 5-inch diameter curved blades produced the highest average torque across wind speeds of 6, 9, and 11.6 m/s. Simulations were conducted in ANSYS Fluent to compare pressure and velocity fields, while experiments measured torque at varying blade angles and revolutions per minute to calculate torque, power, and tip speed ratios.