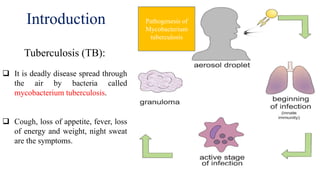
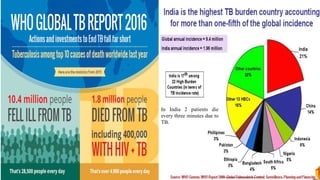
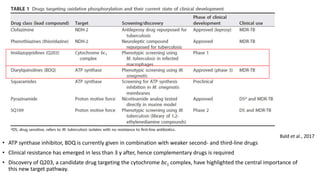
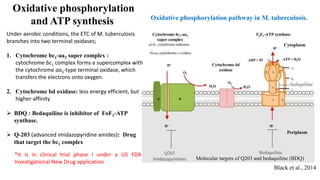
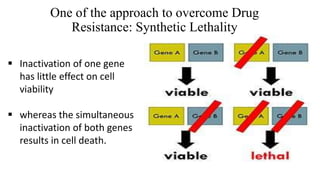
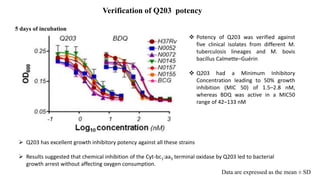
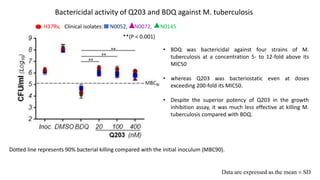
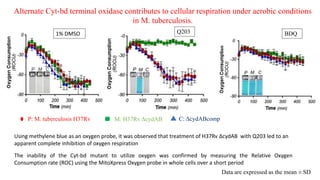
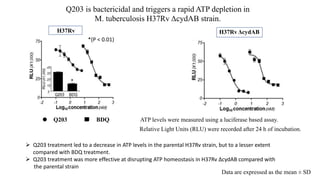
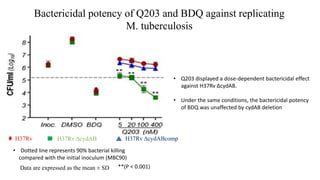
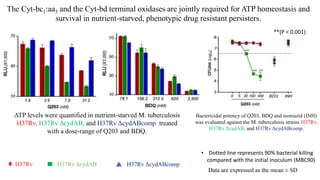
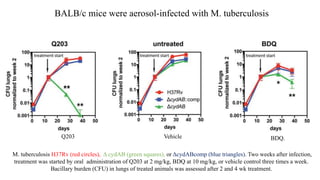
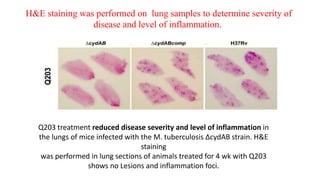
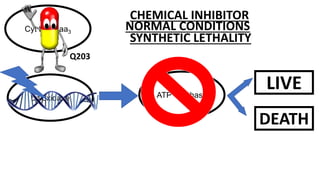
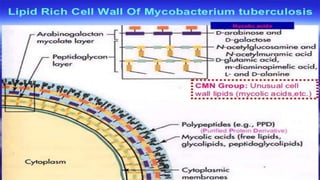
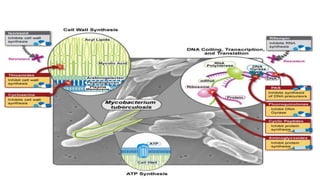
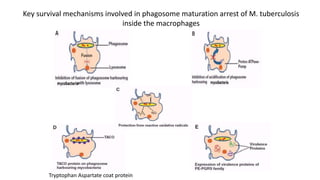
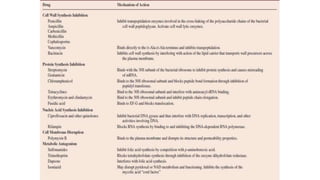
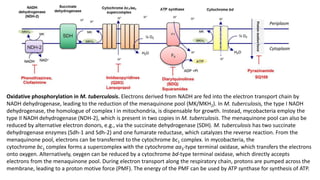
The document discusses a research study on exploiting synthetic lethality between terminal respiratory oxidases to combat multi-drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb). Key findings highlight the effectiveness of the drug candidates Q203 and Bedaquiline (BDQ) against M.tb and the role of different respiratory pathways in bacterial survival and drug resistance. The study concludes that simultaneous inactivation of both oxidases is crucial for causing cell death in drug-resistant M.tb strains.