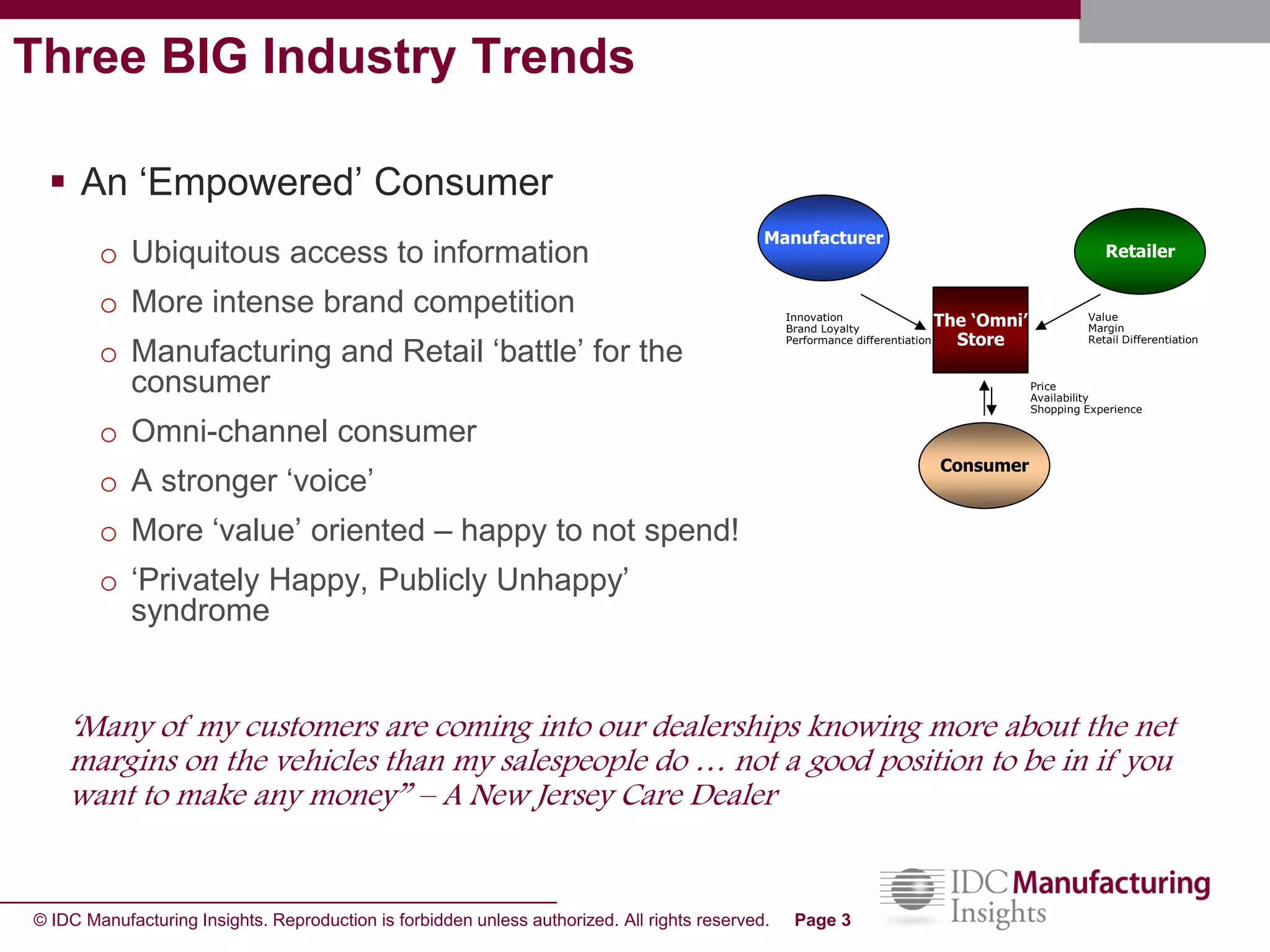
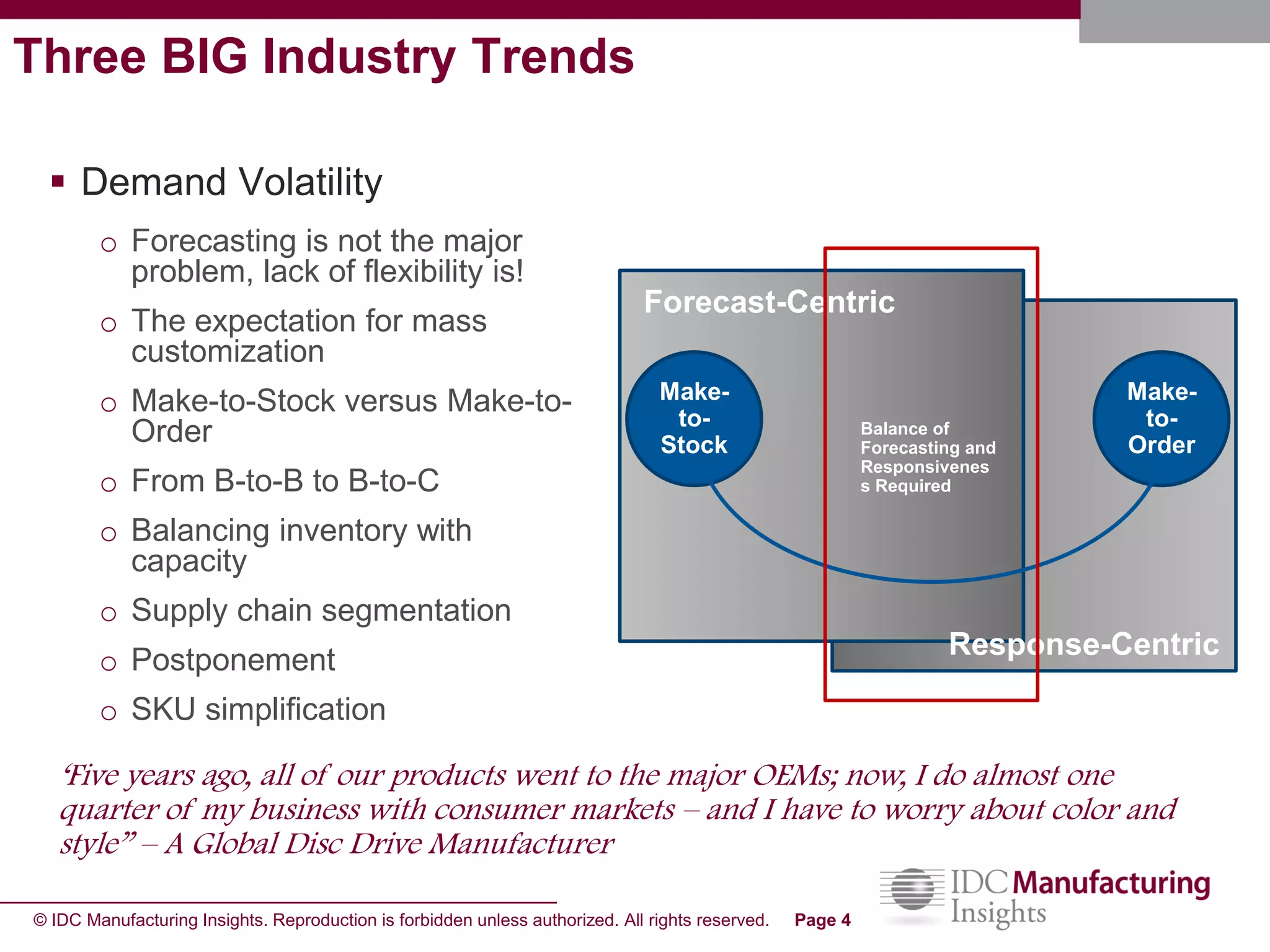
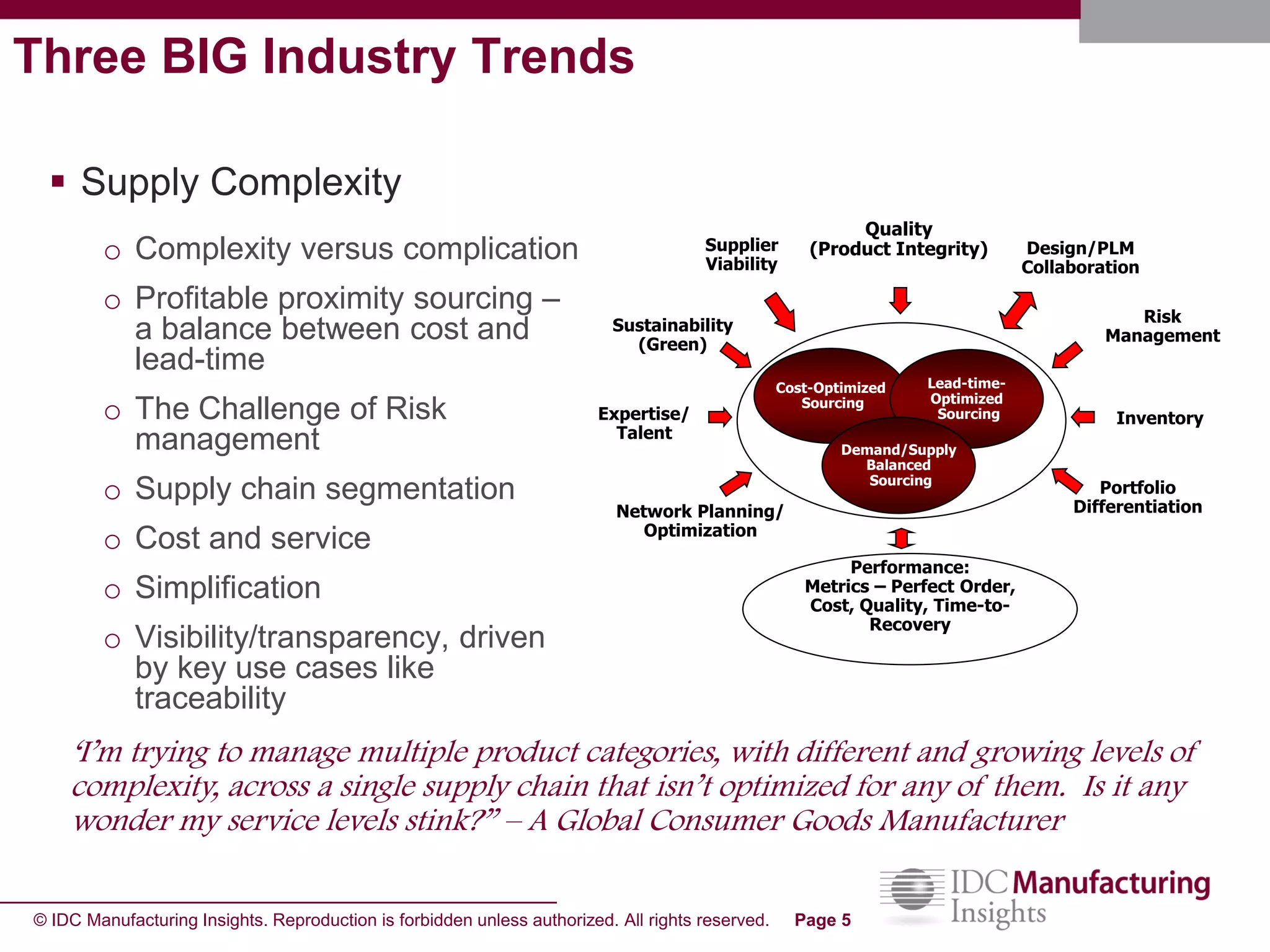
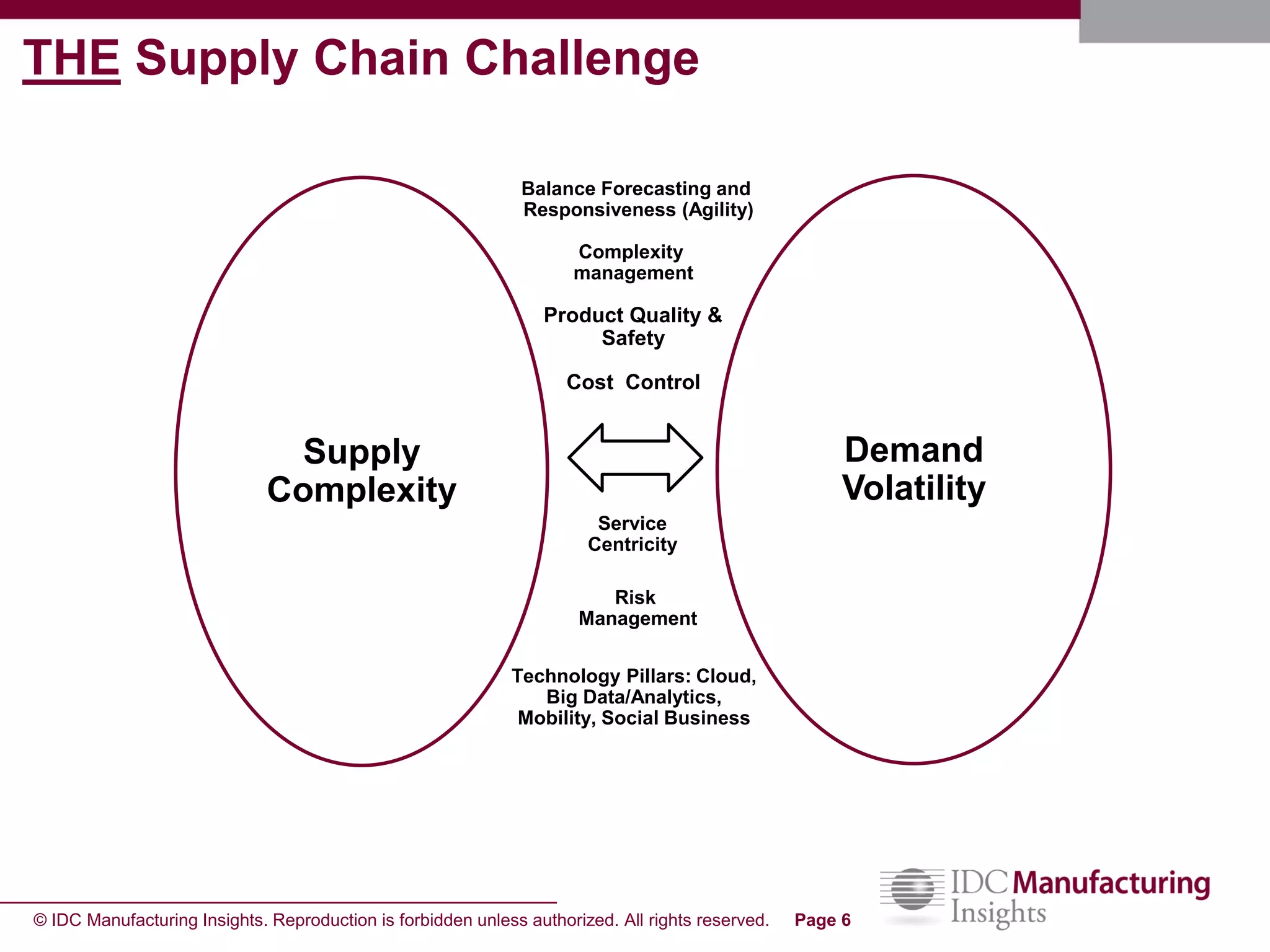
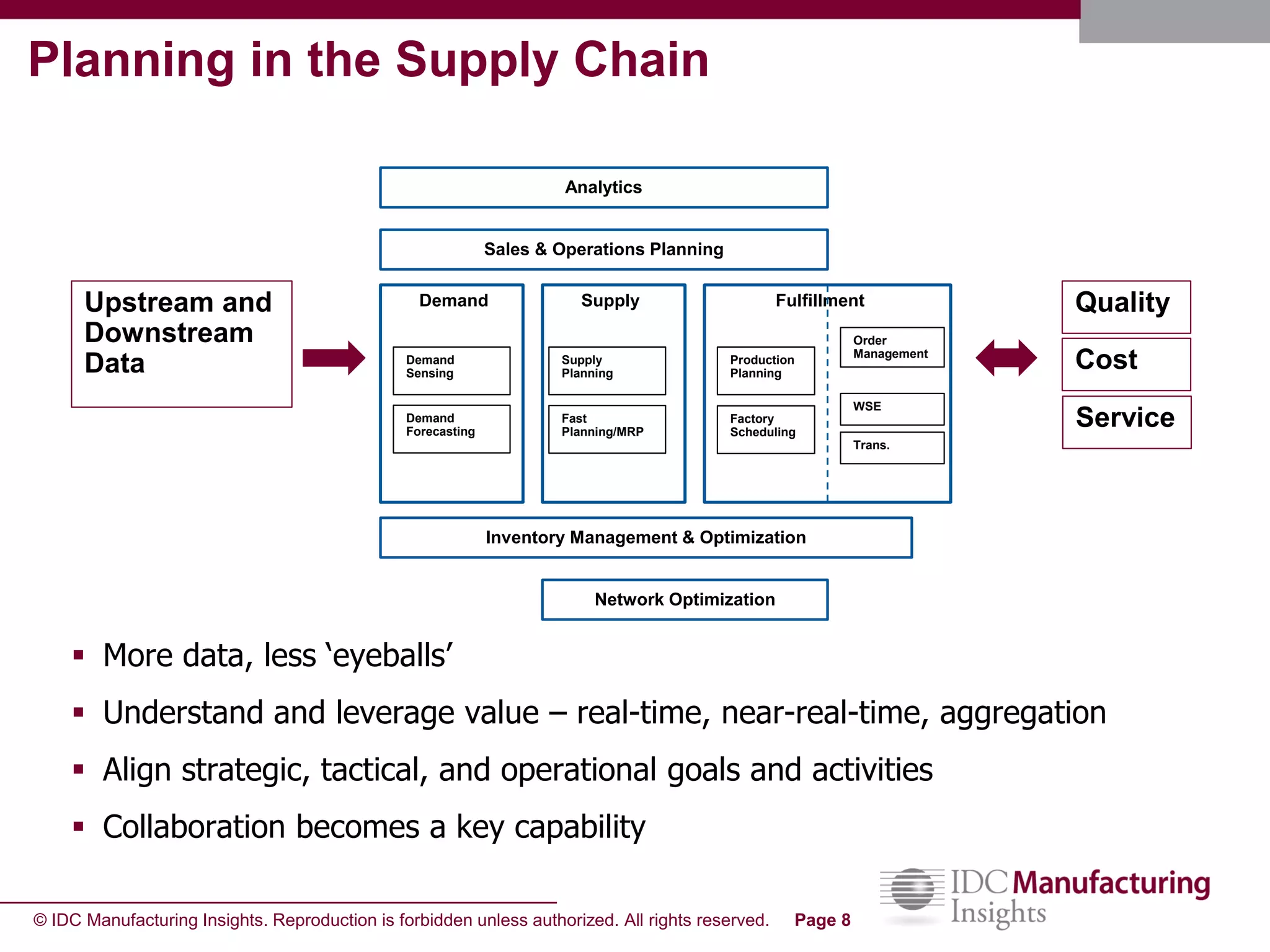
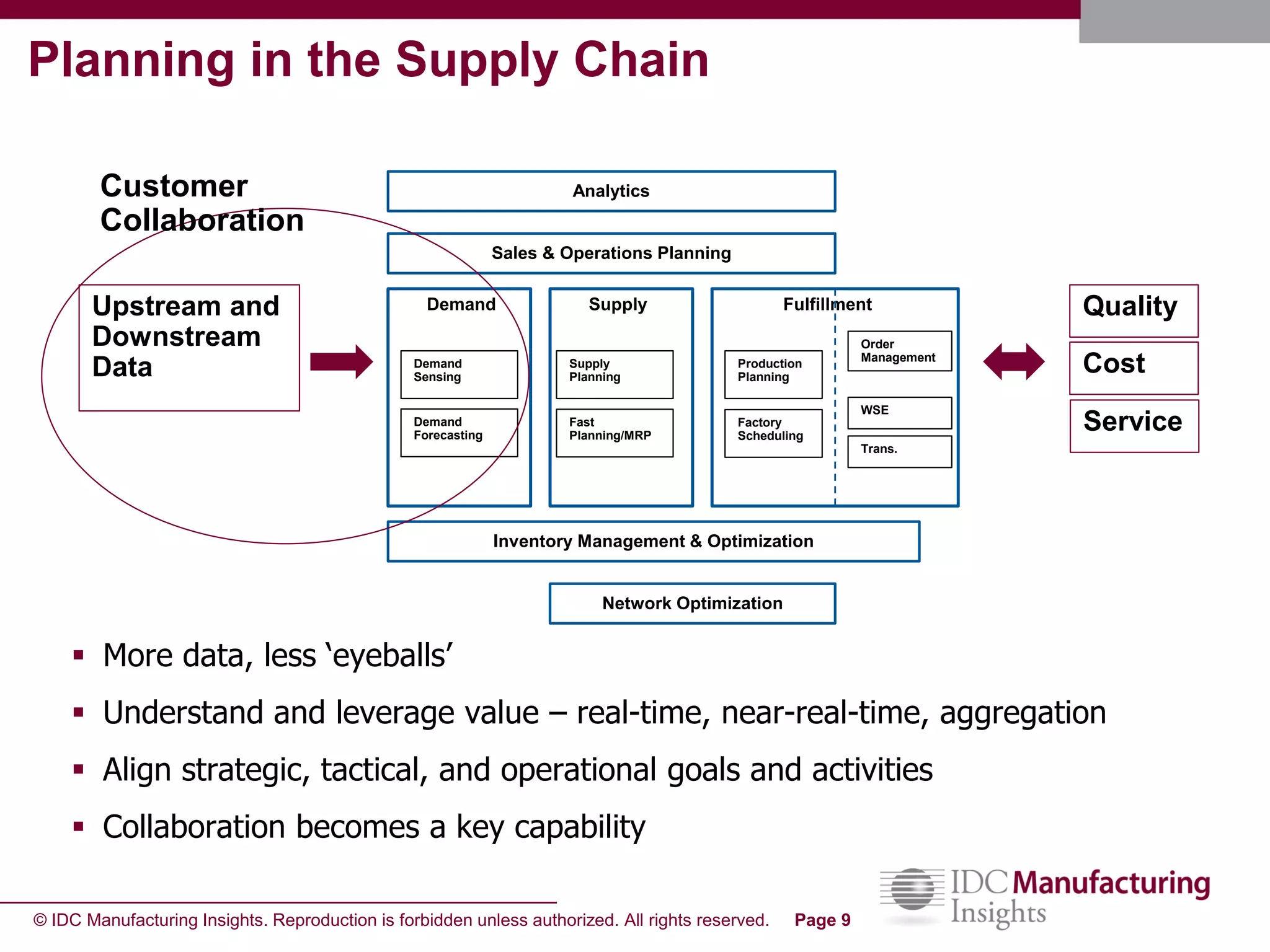
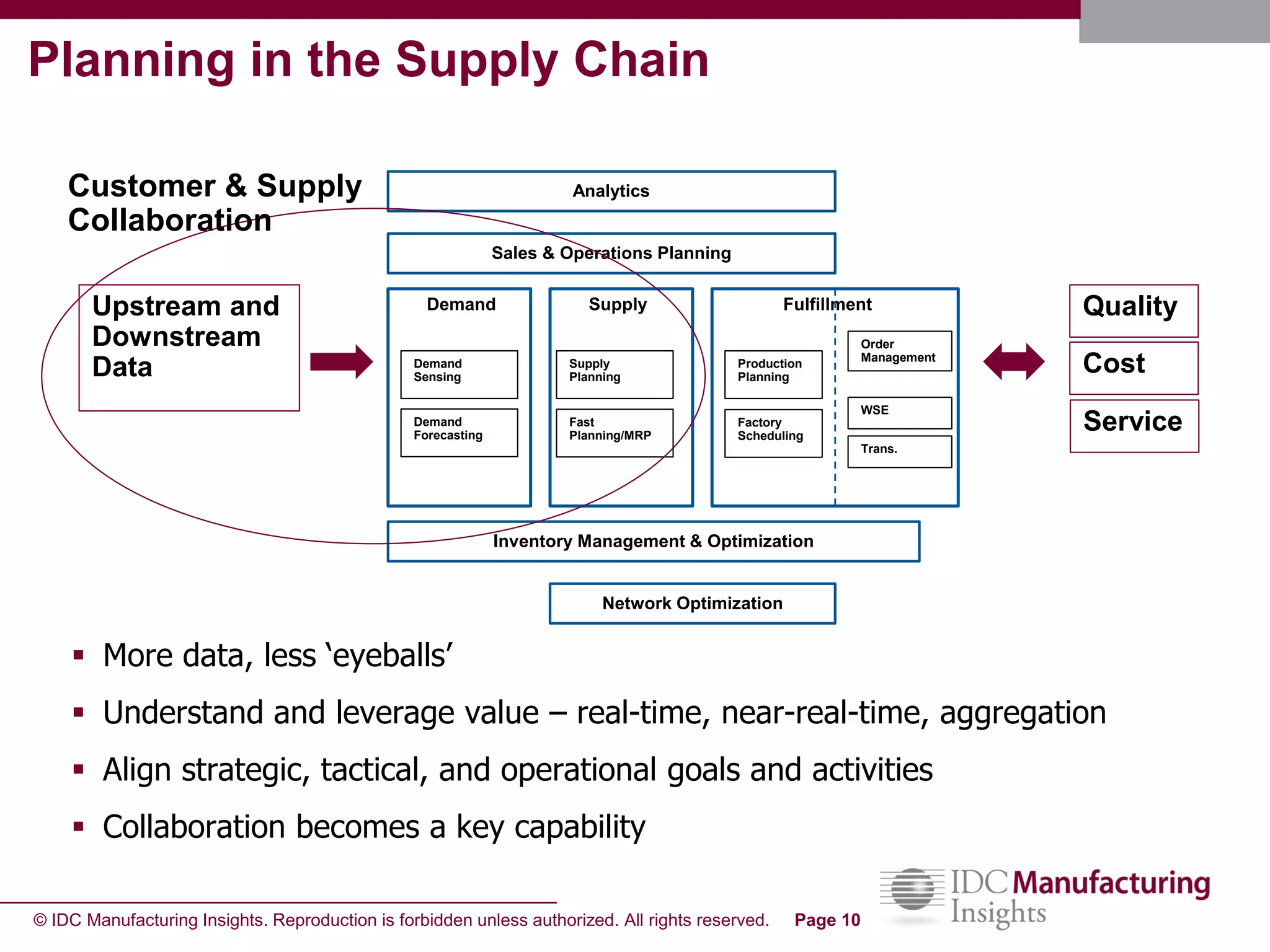
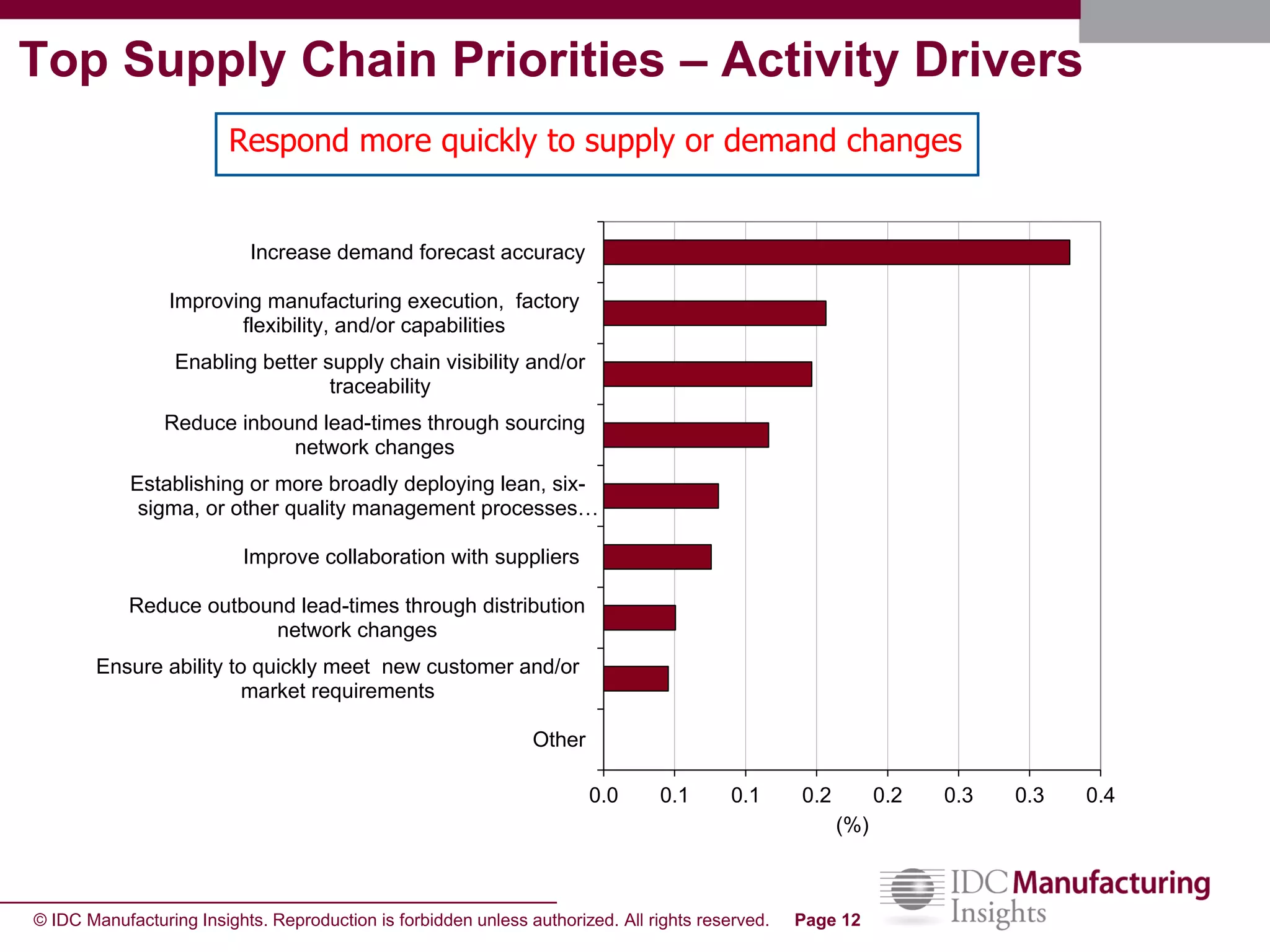
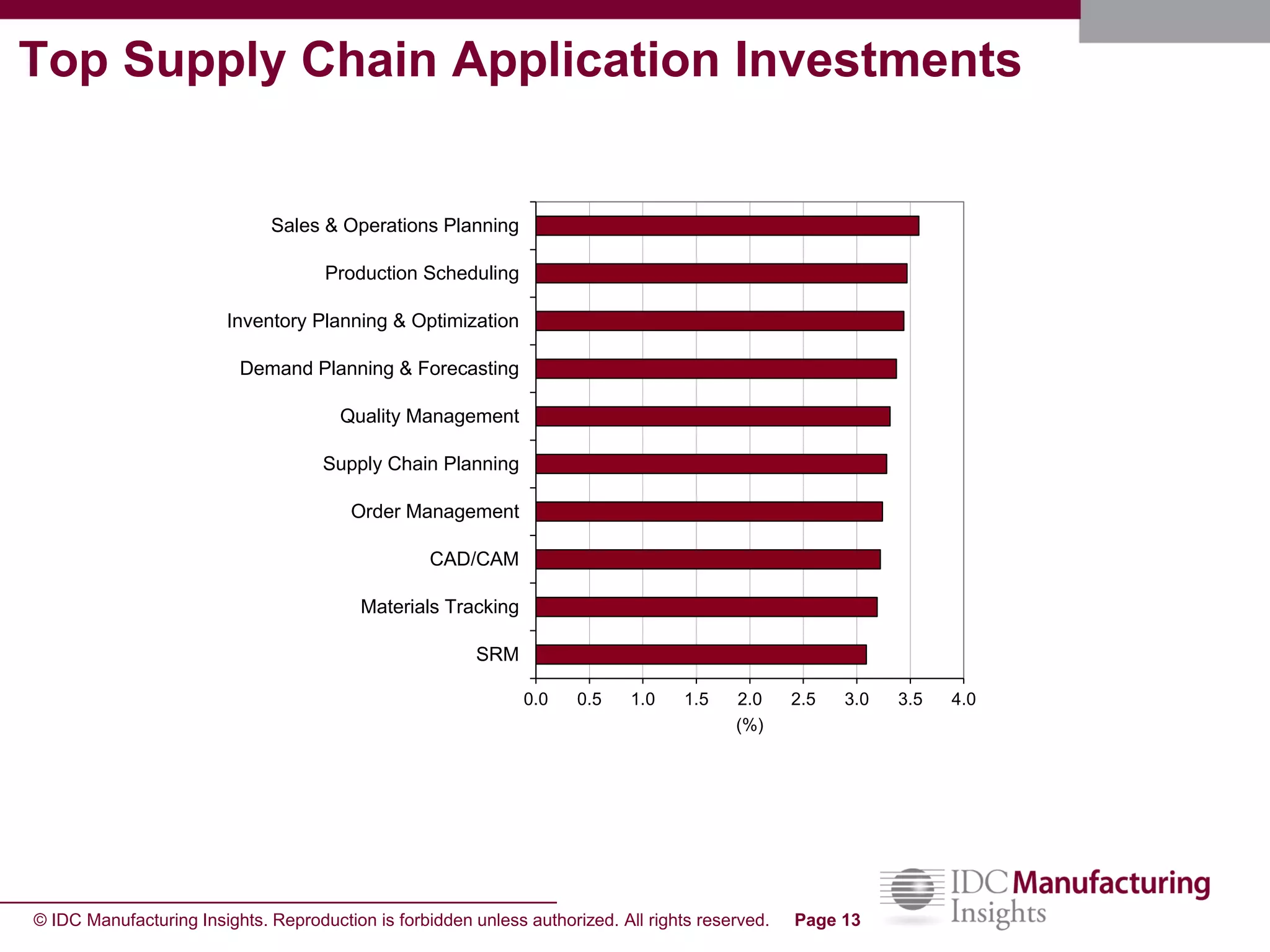
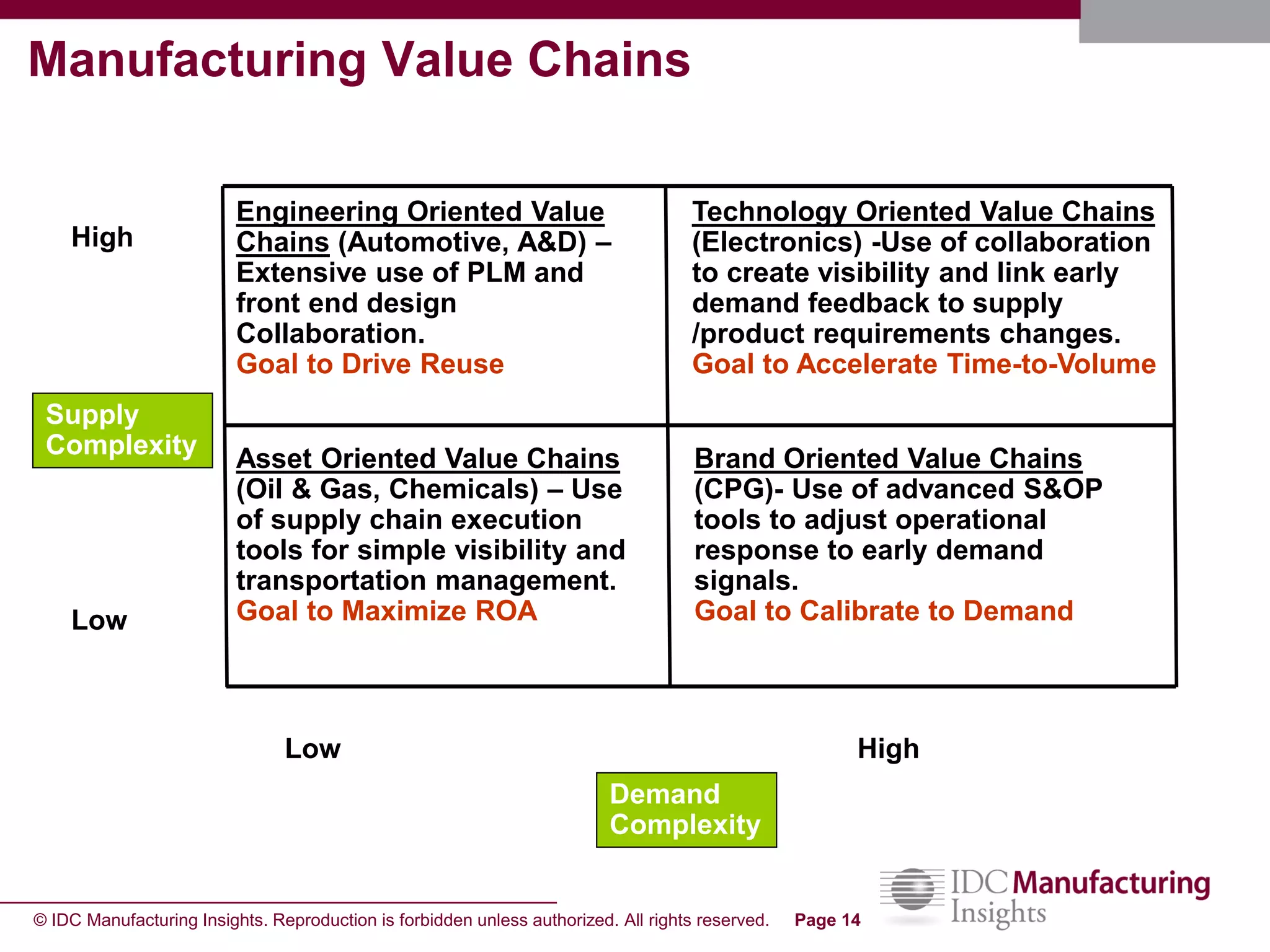
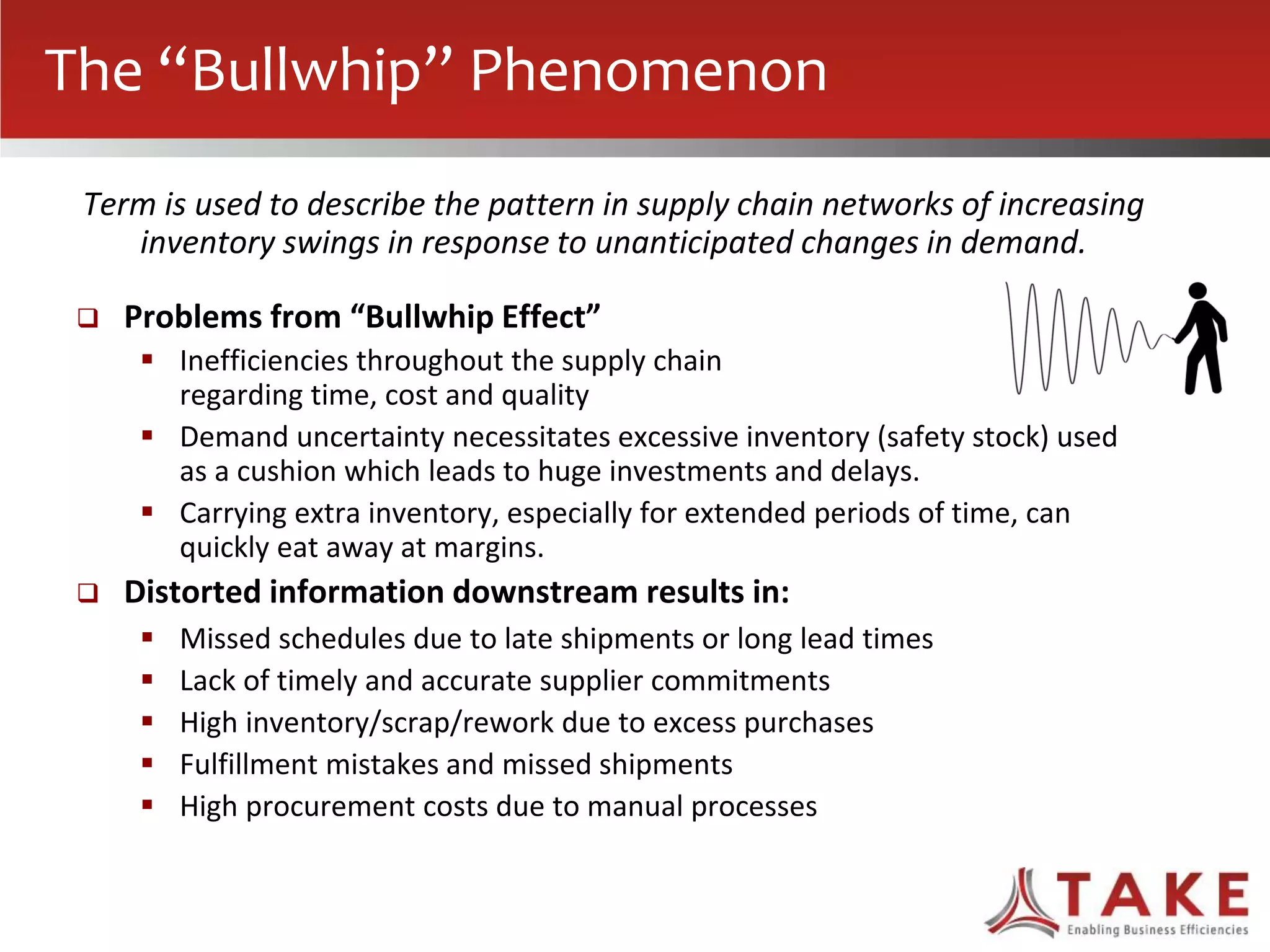
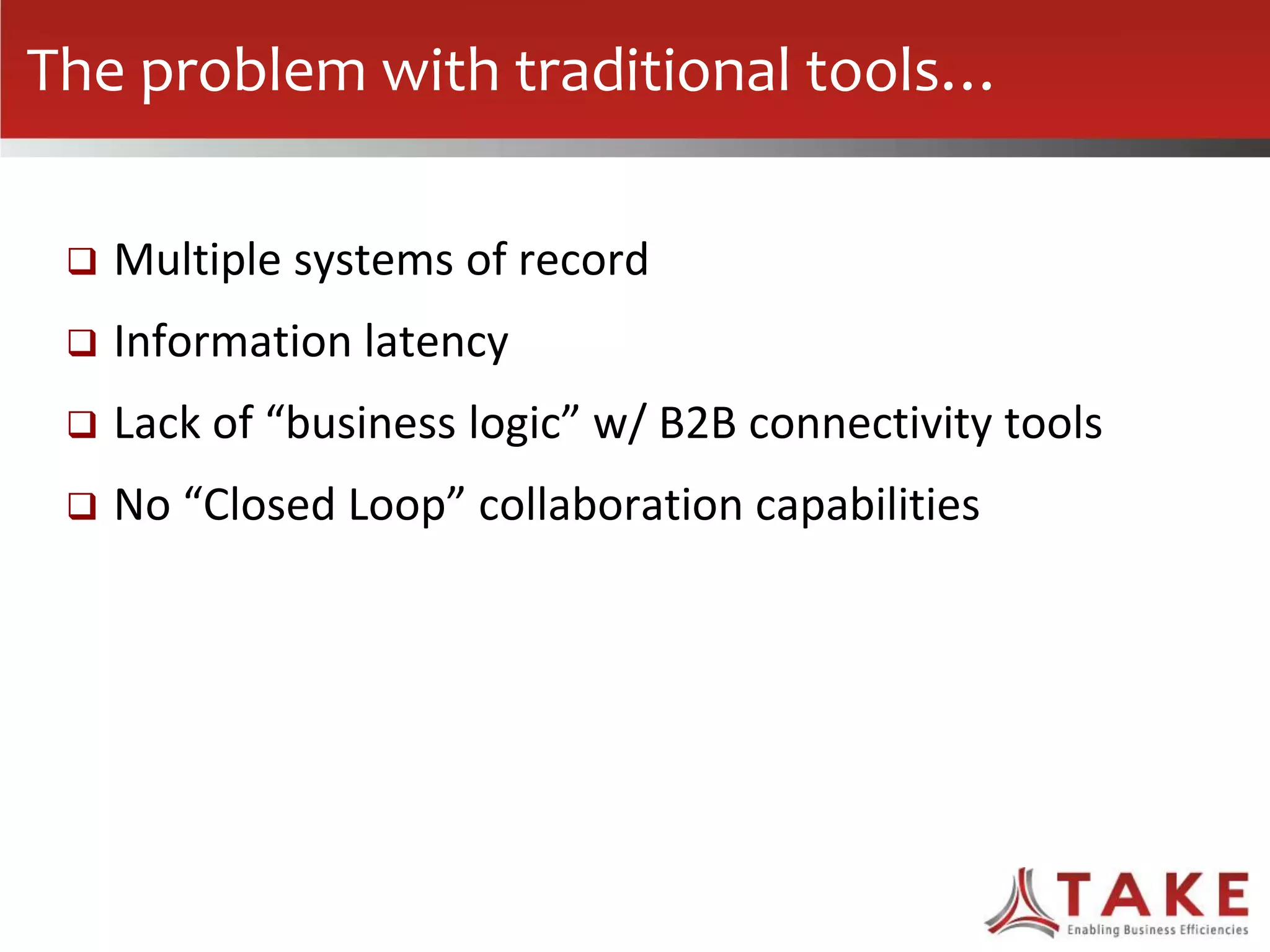
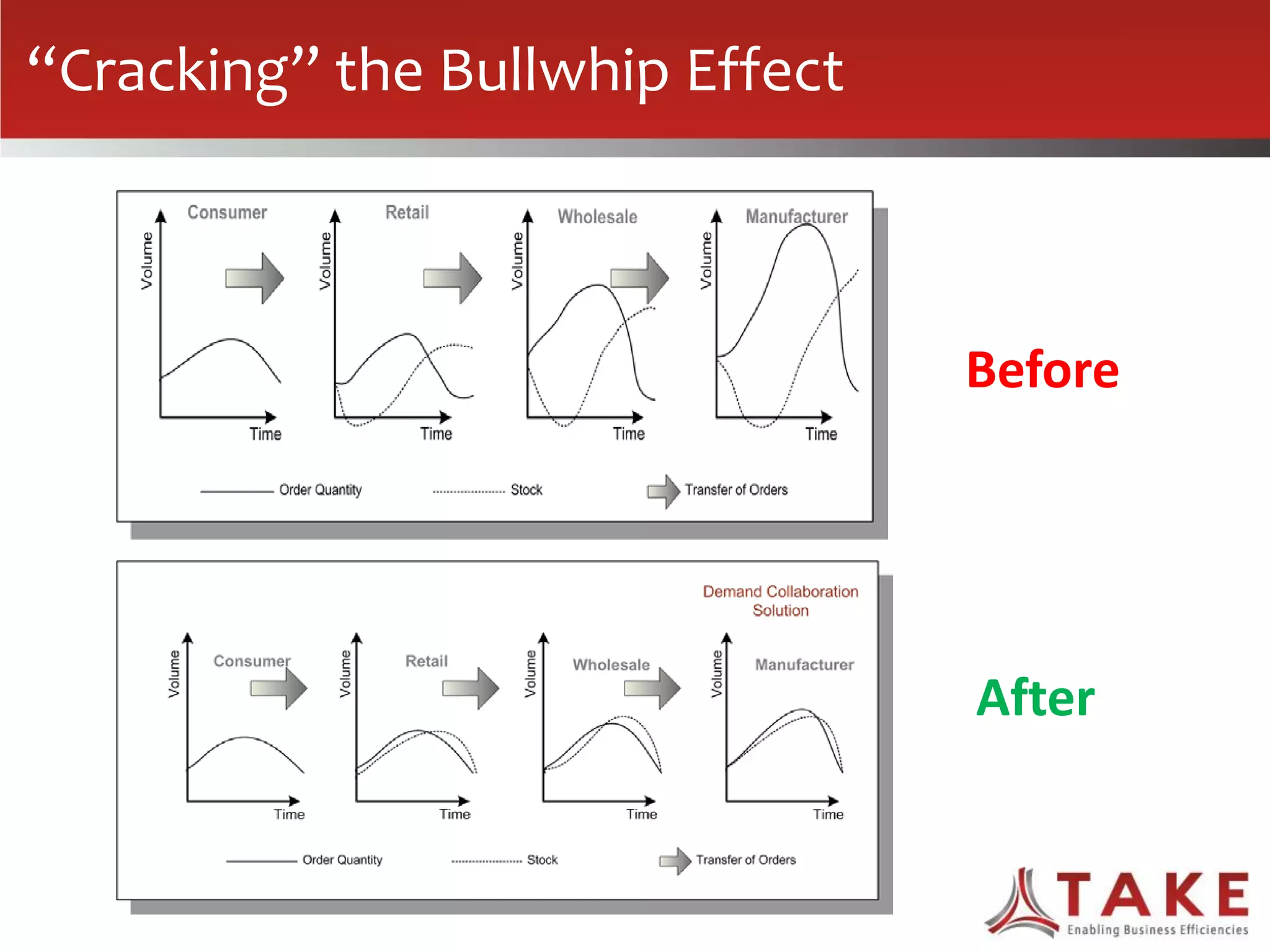
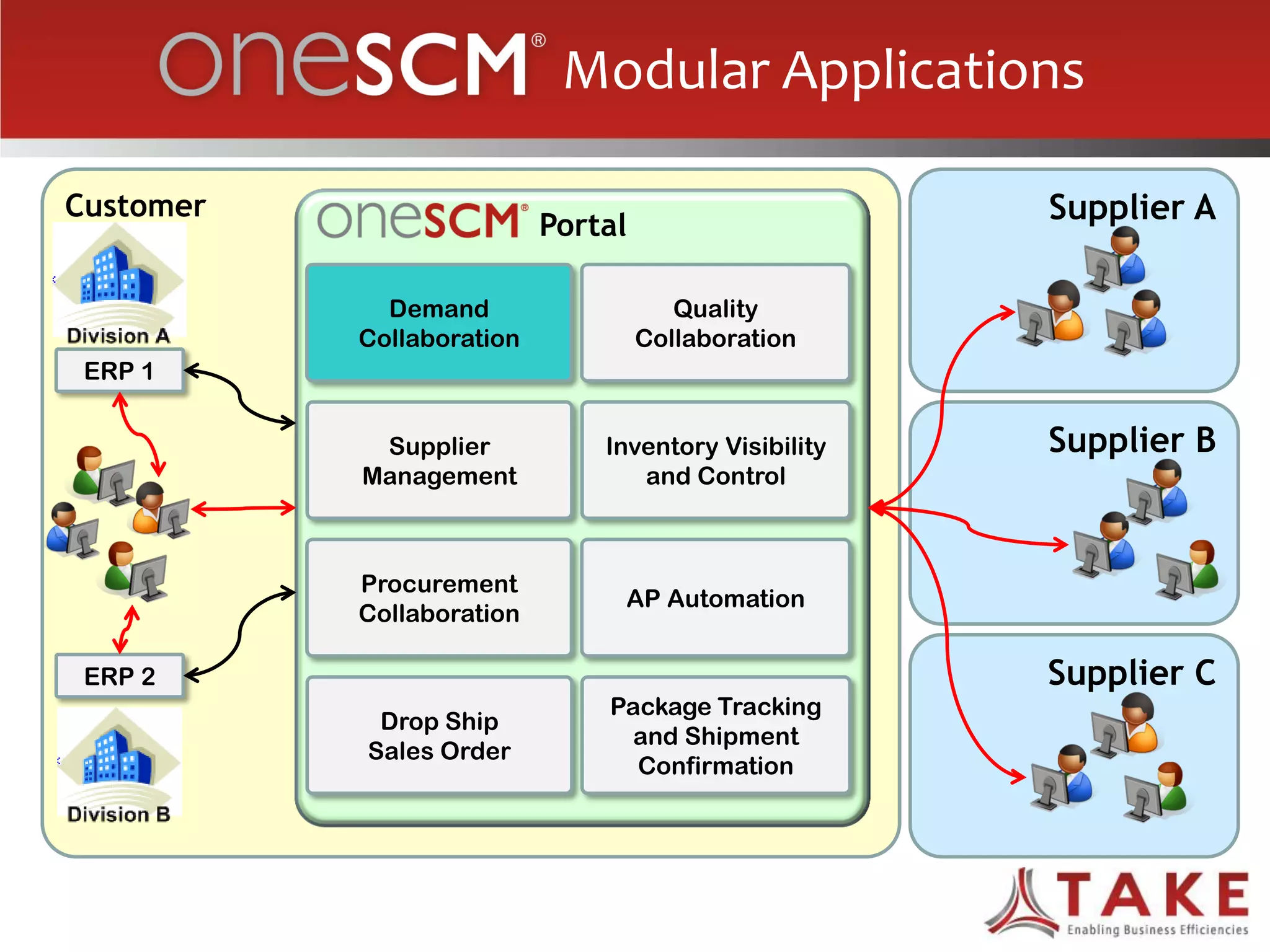
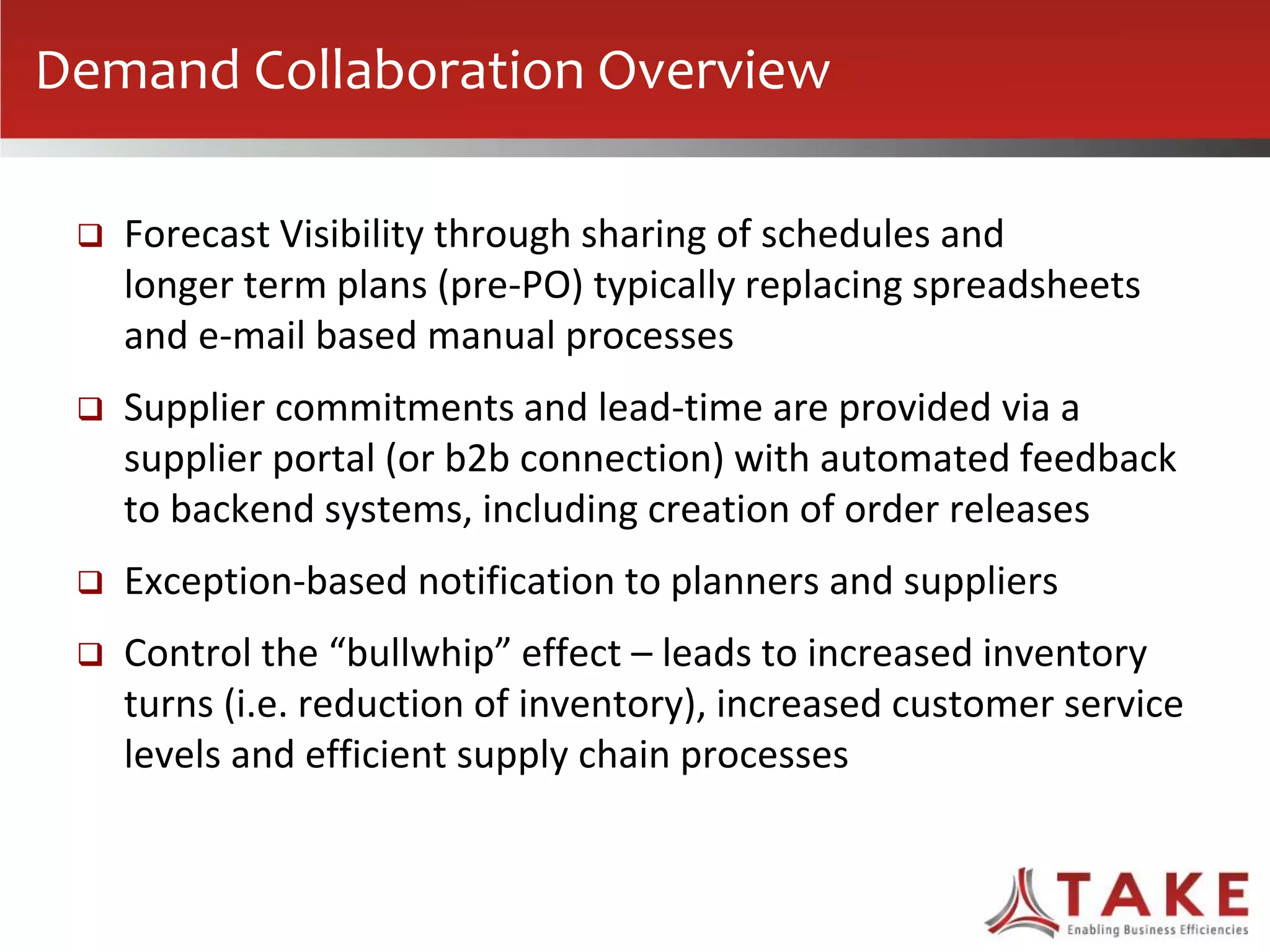
The document discusses how forecast collaboration tools can help align supply and demand in the supply chain. It notes that traditional planning tools have limitations that can exacerbate the "bullwhip effect" of increasing volatility as demand signals move up the supply chain. Effective demand collaboration using new modular applications for forecast visibility, supplier commitments, and automated feedback can reduce inventory levels, improve on-time delivery and cash flow by increasing accuracy and reducing latency in communication. The document provides examples of companies that achieved savings and efficiencies through implementing forecast collaboration solutions.