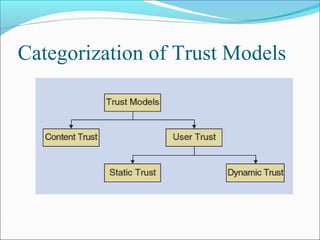
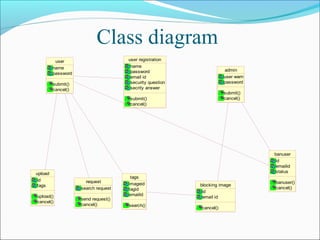
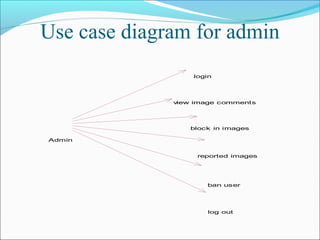
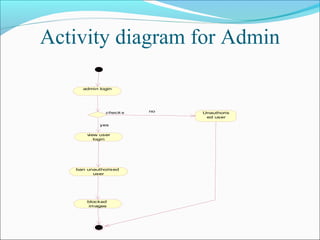
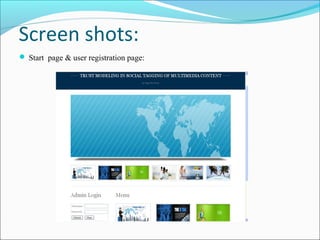
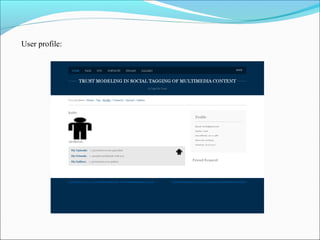
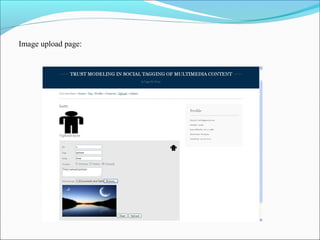
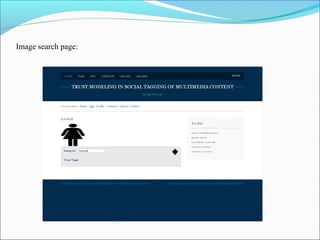
This document discusses trust modeling approaches for social tagging systems. It describes existing problems with noisy and spam tags that make search inefficient. The proposed system models trust at three levels: spam content, tag-content associations, and spammers. Trust modeling is categorized into content and user trust modeling, ranging from simple to advanced approaches. User trust modeling, which assesses a user's reliability over time, is more popular than content trust modeling. The document outlines requirements and provides UML diagrams to illustrate the system.