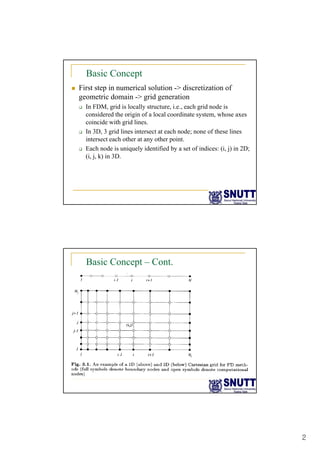
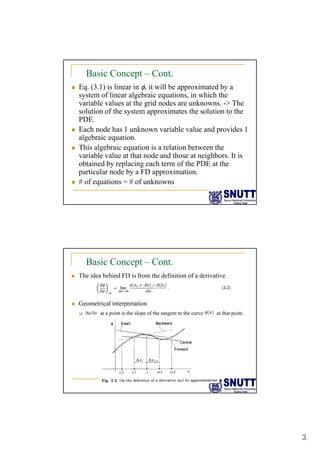
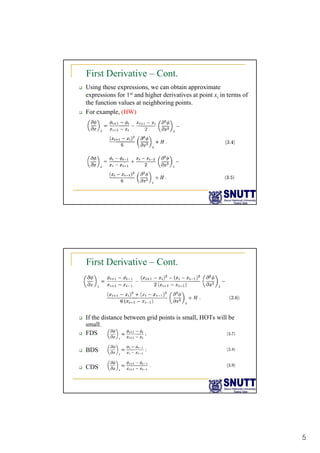
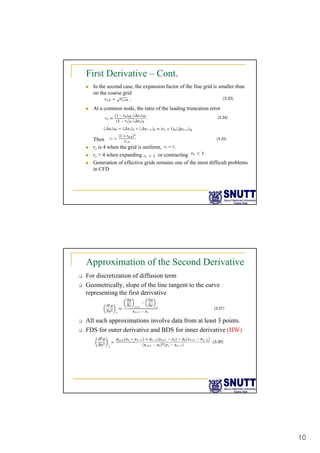
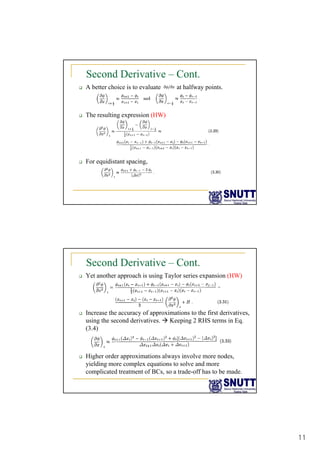
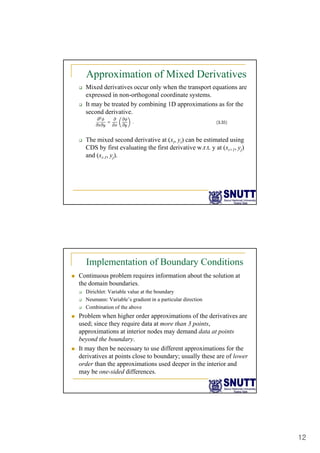
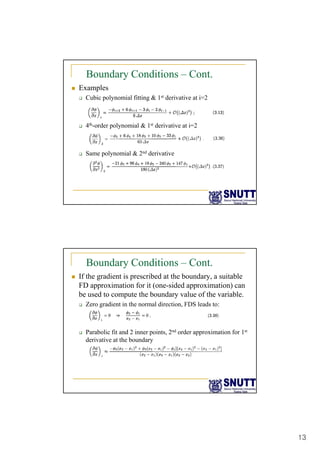
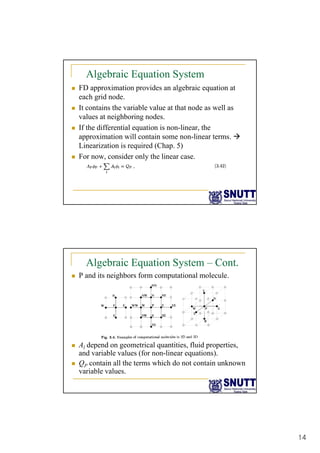
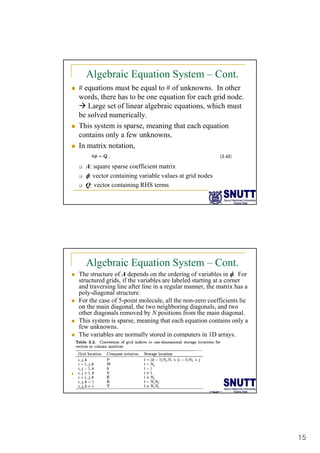
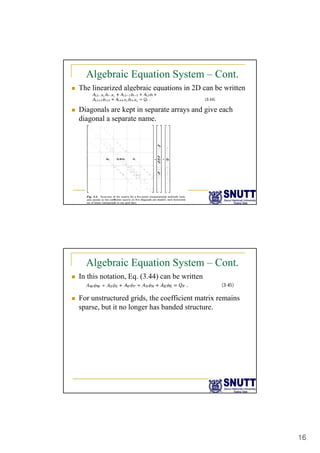
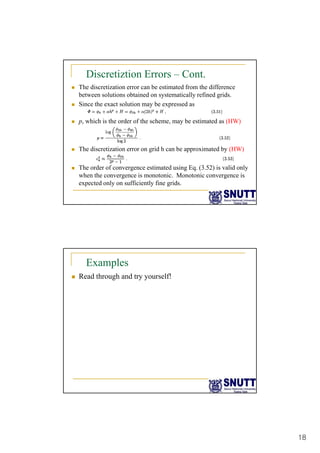
Finite difference methods discretize the domain into a grid and approximate derivatives as algebraic equations relating variable values at neighboring grid points. First and second derivatives can be approximated using forward, backward, or central differencing schemes of varying orders of accuracy. Boundary conditions require special treatment as higher-order approximations may require values outside the domain. Solving the resulting system of algebraic equations provides an approximate numerical solution to the partial differential equation over the discretized domain.