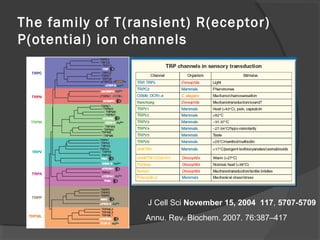
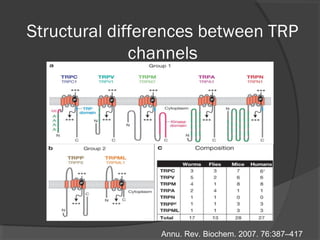
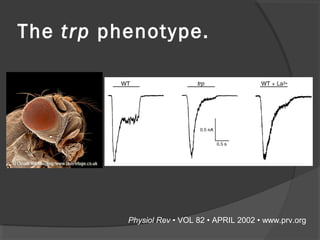
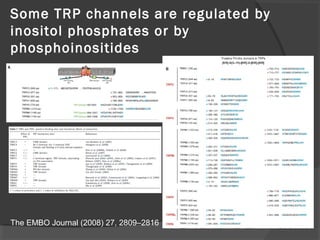
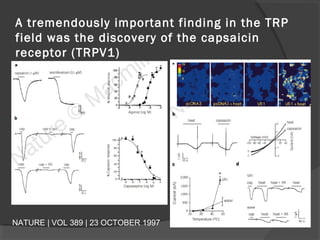
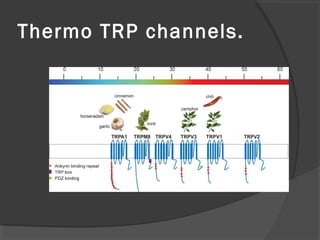
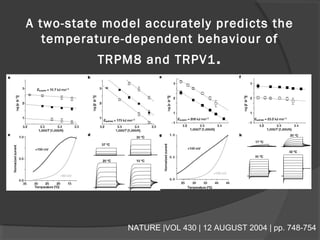
The document summarizes research on TRP (Transient Receptor Potential) ion channels. Key findings include: (1) TRP channels were initially identified in Drosophila and their function was unclear for 20 years, (2) Amino acid sequencing revealed TRP's structural similarity to ion channels, (3) Electrophysiology experiments showed reduced calcium influx in TRP mutants, confirming TRP is a calcium-permeable channel, (4) TRP channels function as global sensors across species, detecting sensory stimuli like temperature, taste, smell, and mechanosensation, and (5) Malfunctions in human TRP channels can underlie diseases.