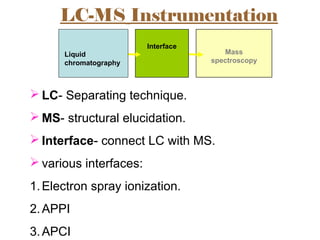
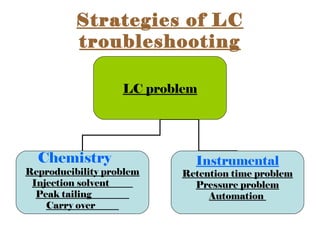
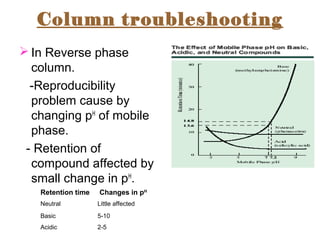
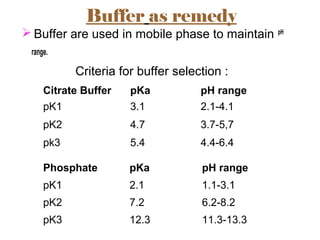
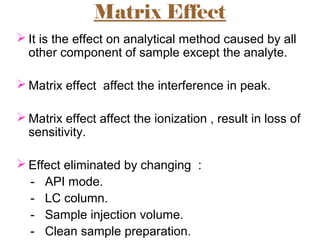
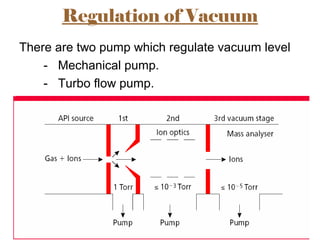
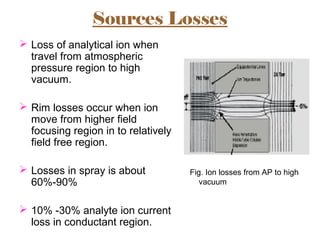
The document provides an overview of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS), highlighting its advantages, applications, and troubleshooting strategies for various problems such as carry over, matrix effects, and instrumental issues. It emphasizes the importance of proper sample preparation, injection solvent selection, and maintaining instrumental integrity to enhance the efficiency and reproducibility of the technique. The conclusion reiterates that LC-MS is a powerful analytical tool that can be improved through systematic troubleshooting.