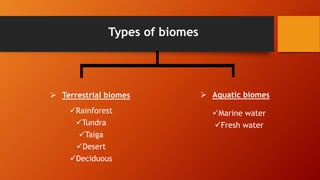
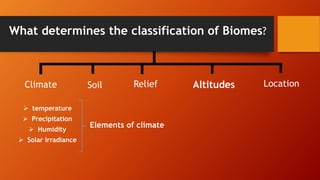
The document provides a comprehensive overview of tropical rainforest biomes, detailing their characteristics, classification, and significance. It covers abiotic factors such as climate and soil, as well as plant and animal adaptations, while also addressing the major threats posed by human activities and natural disasters. Tropical rainforests, which make up about 7% of Earth's surface, are primarily found near the equator and are home to an incredibly diverse range of species.