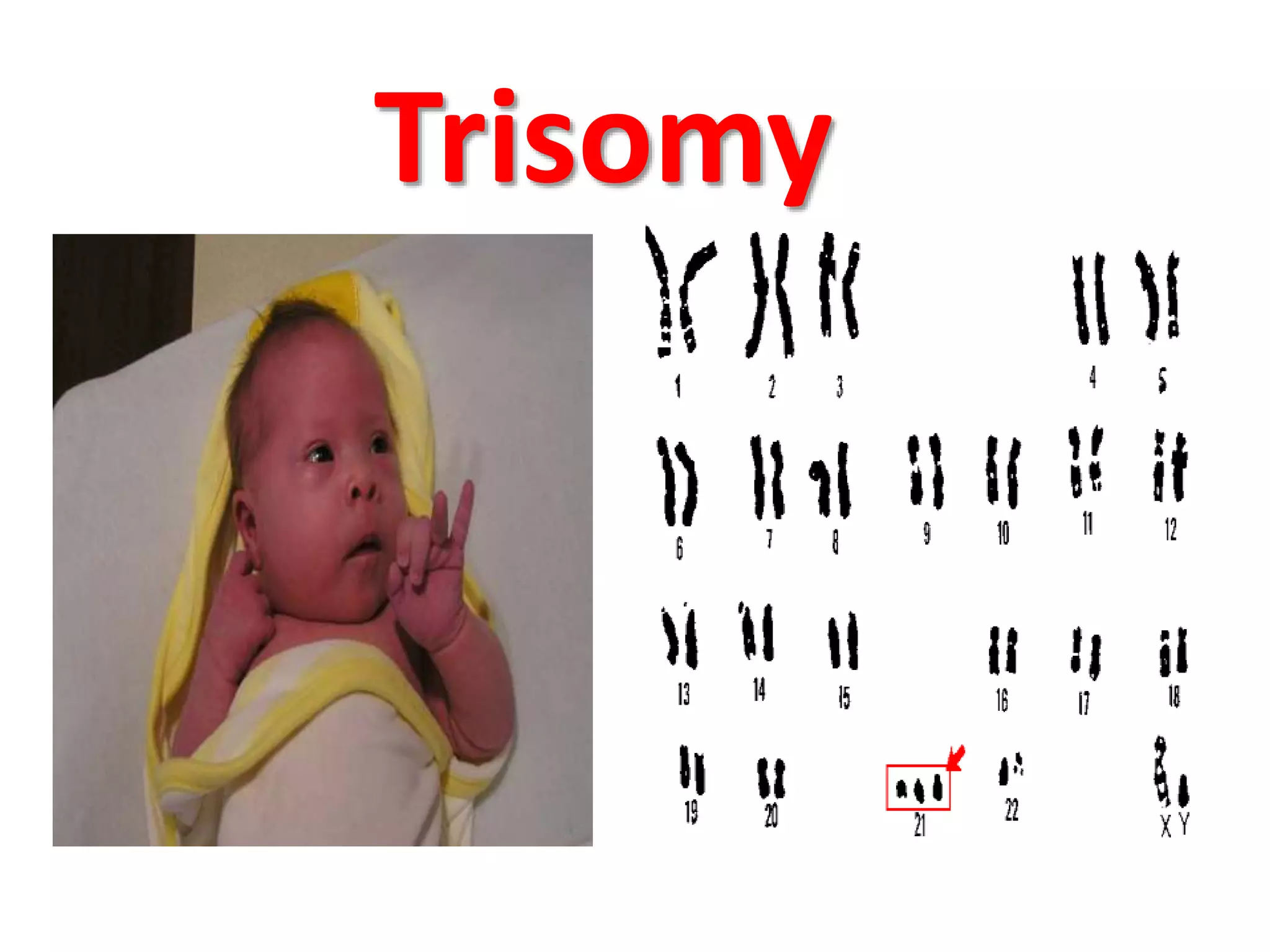
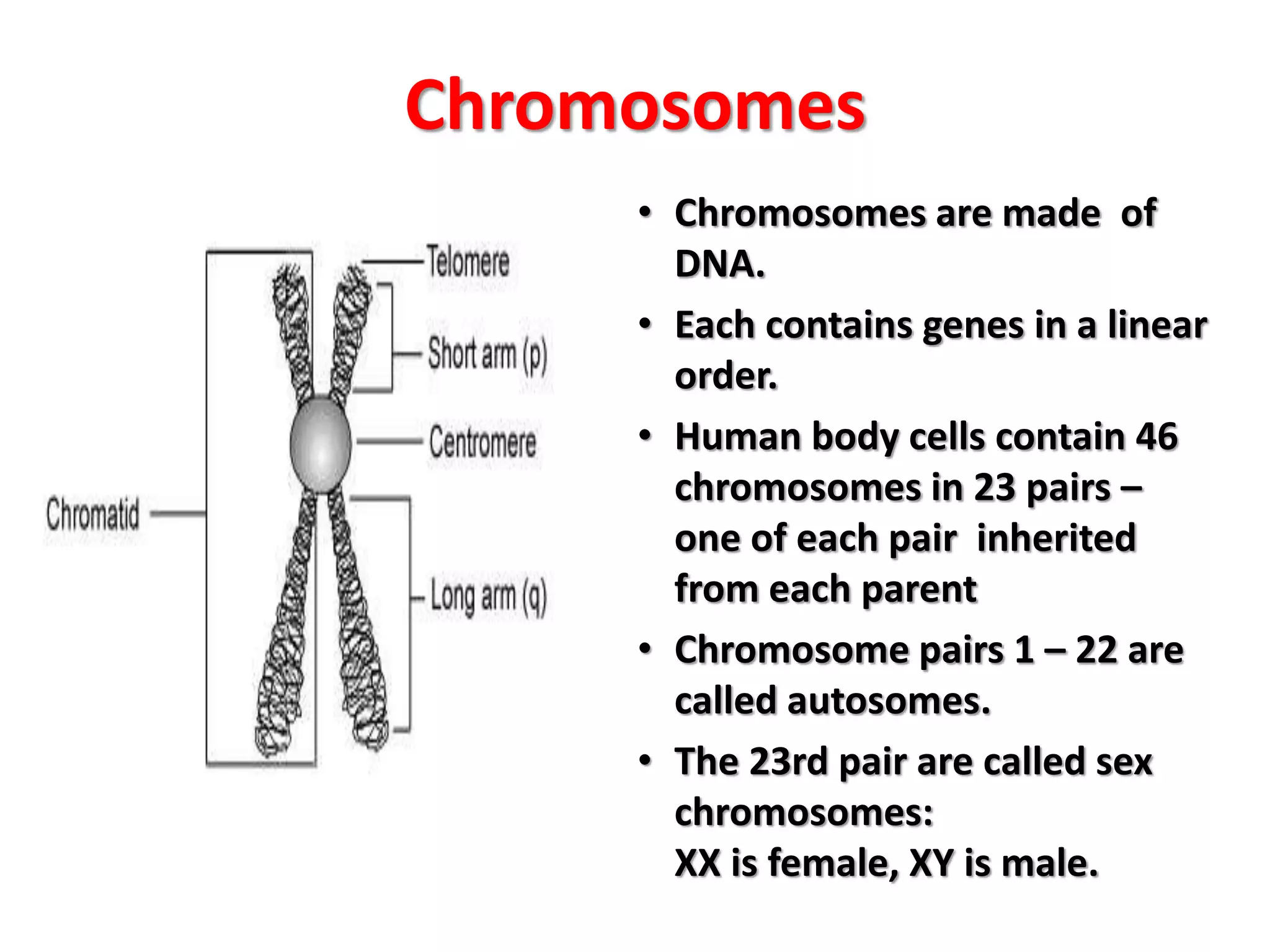
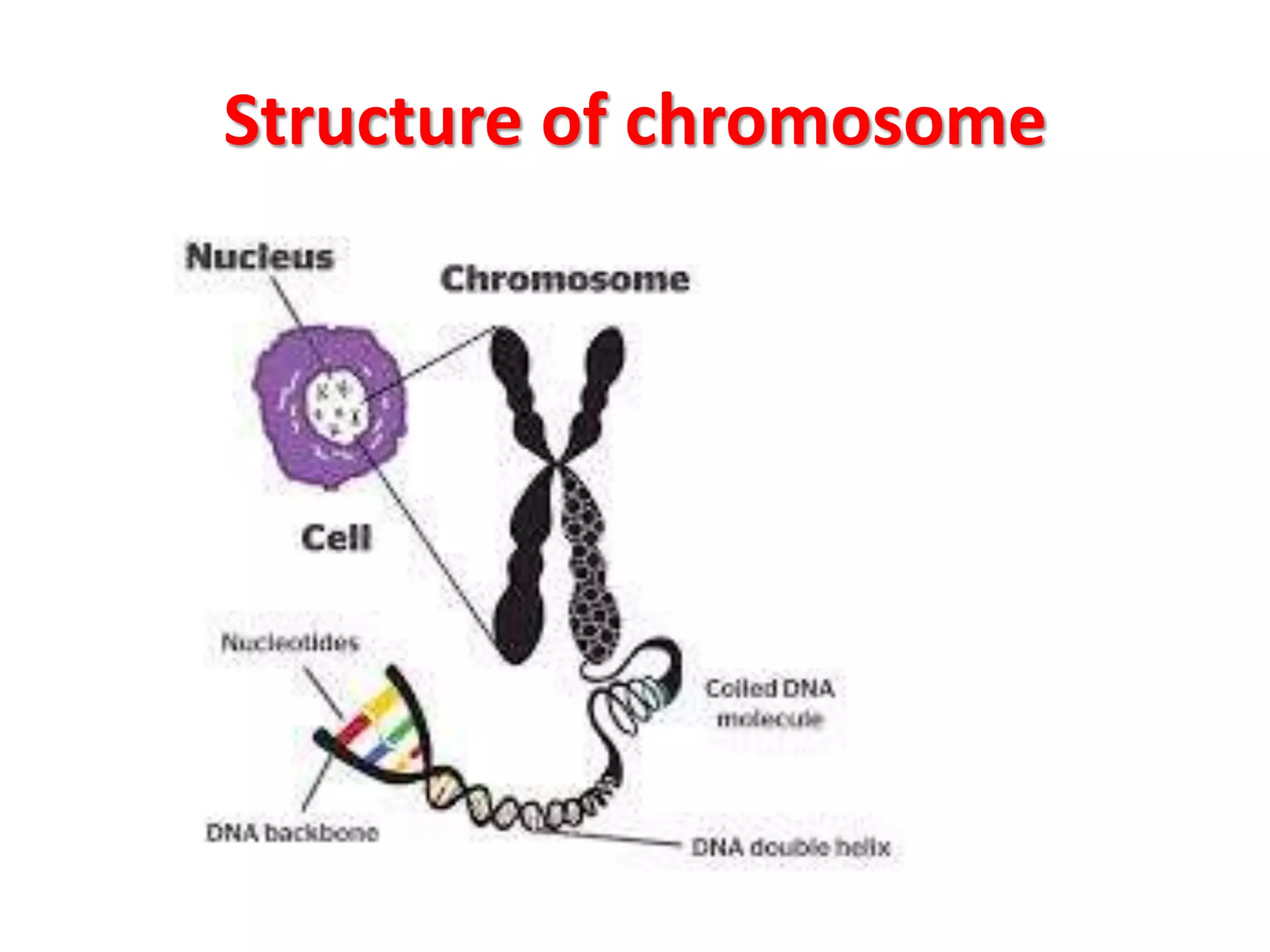
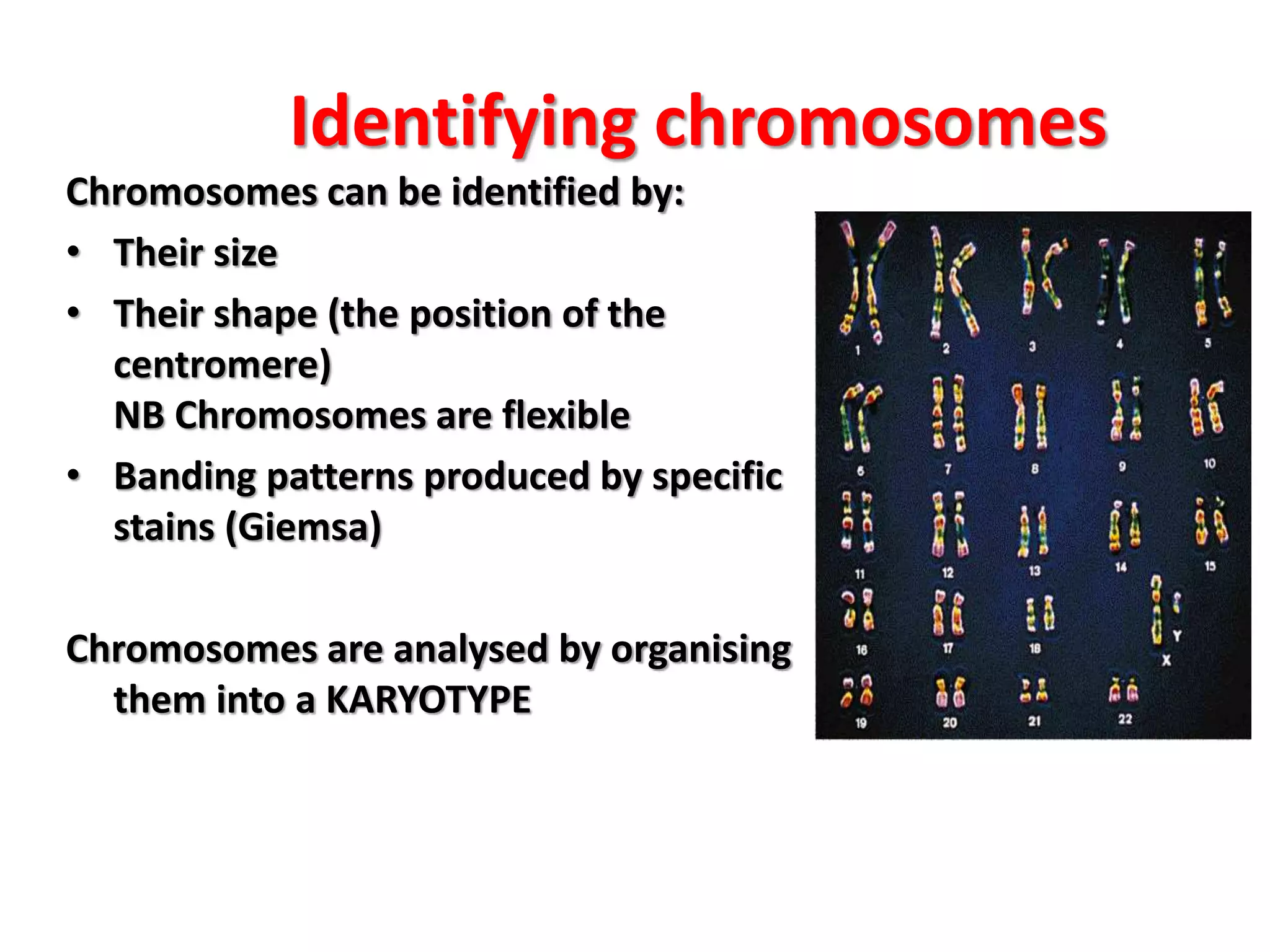
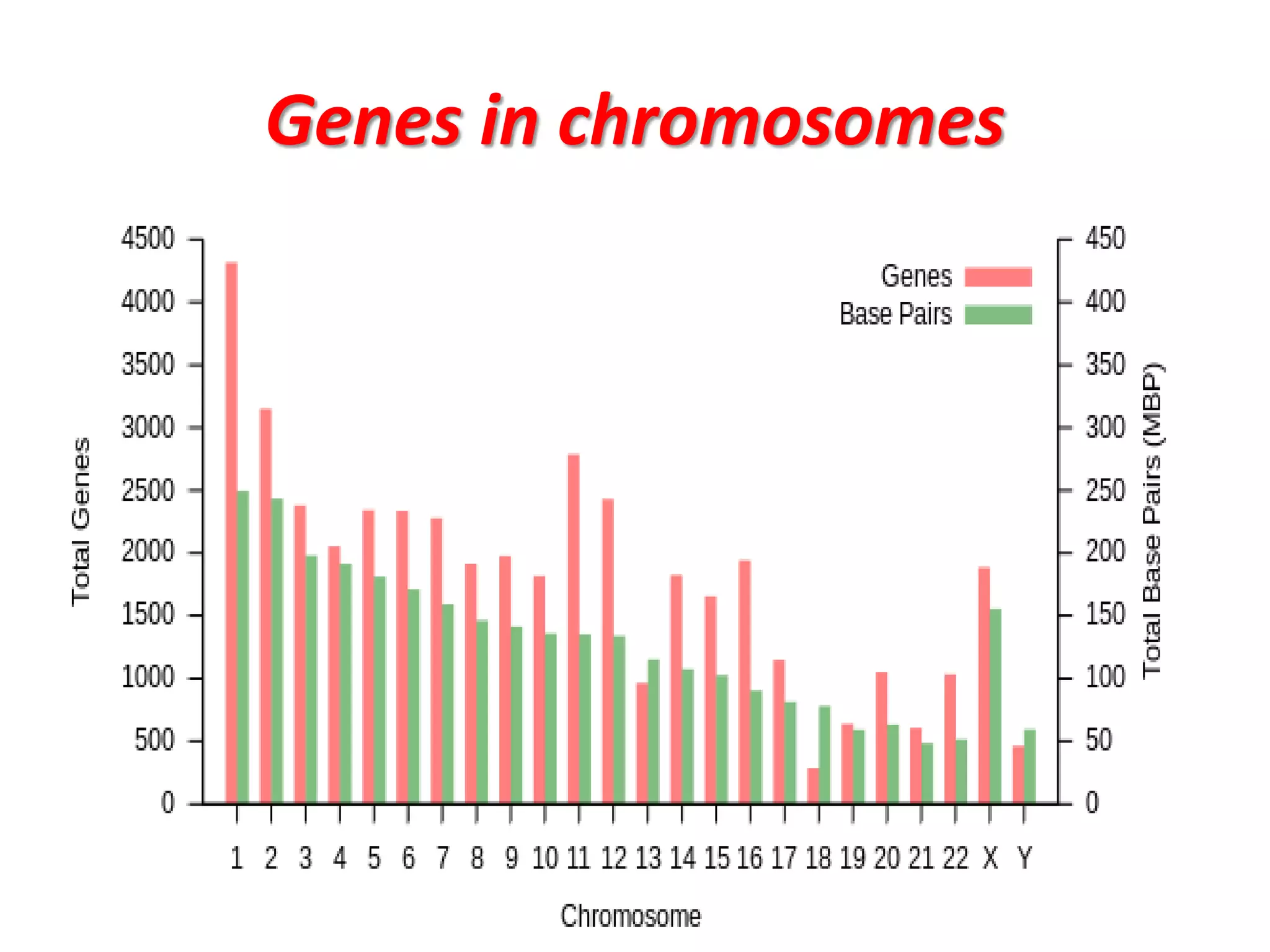
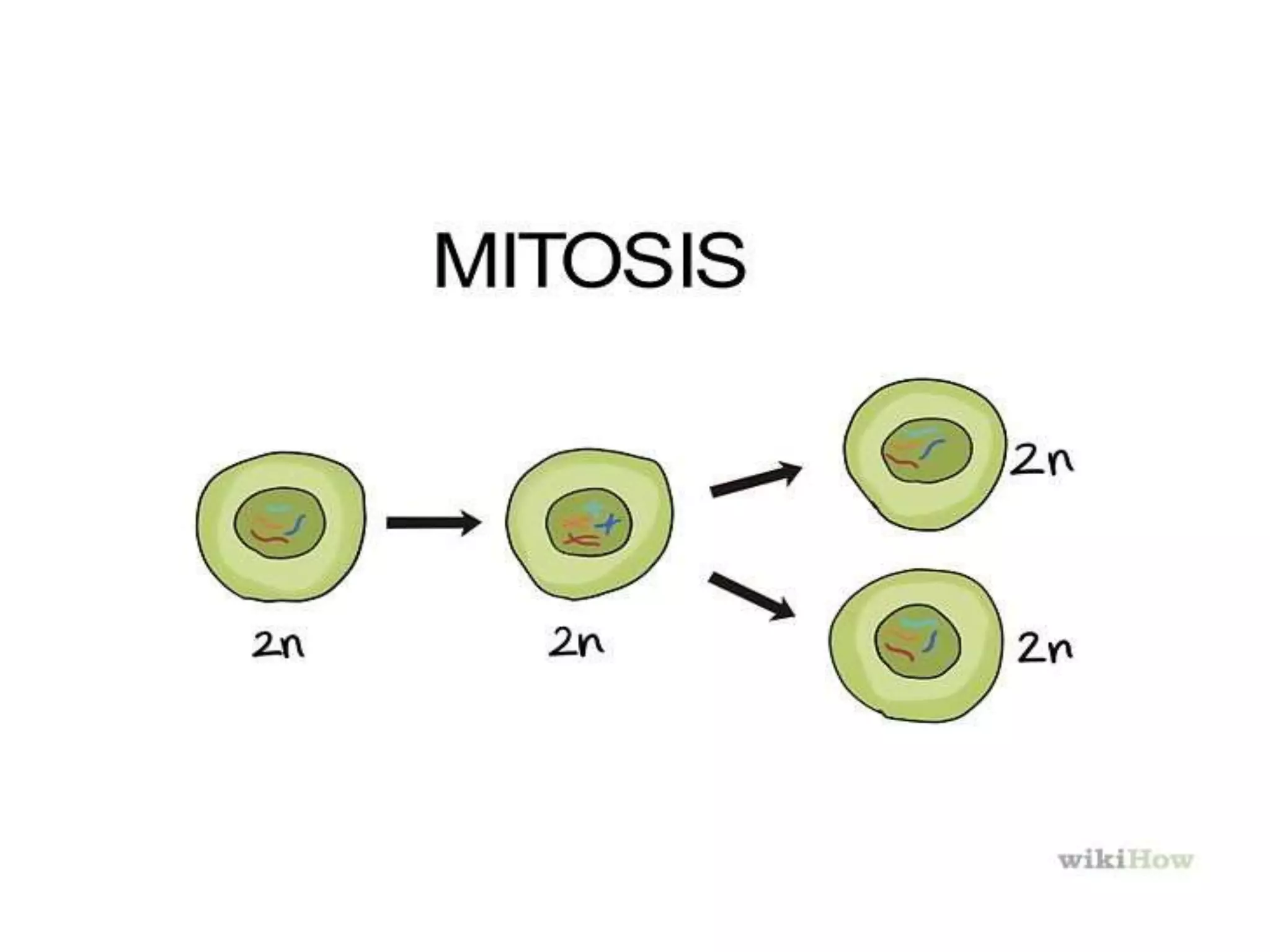
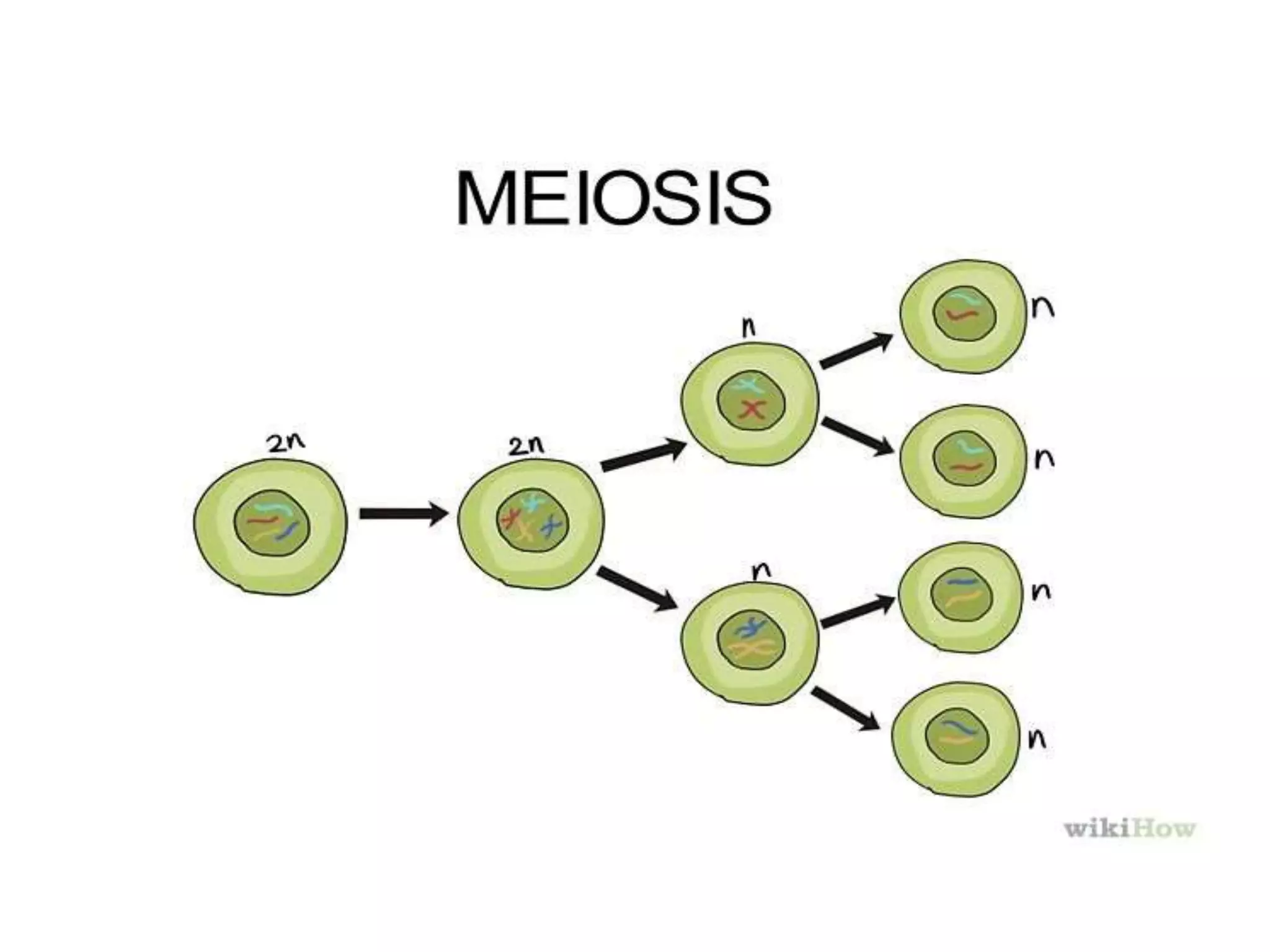
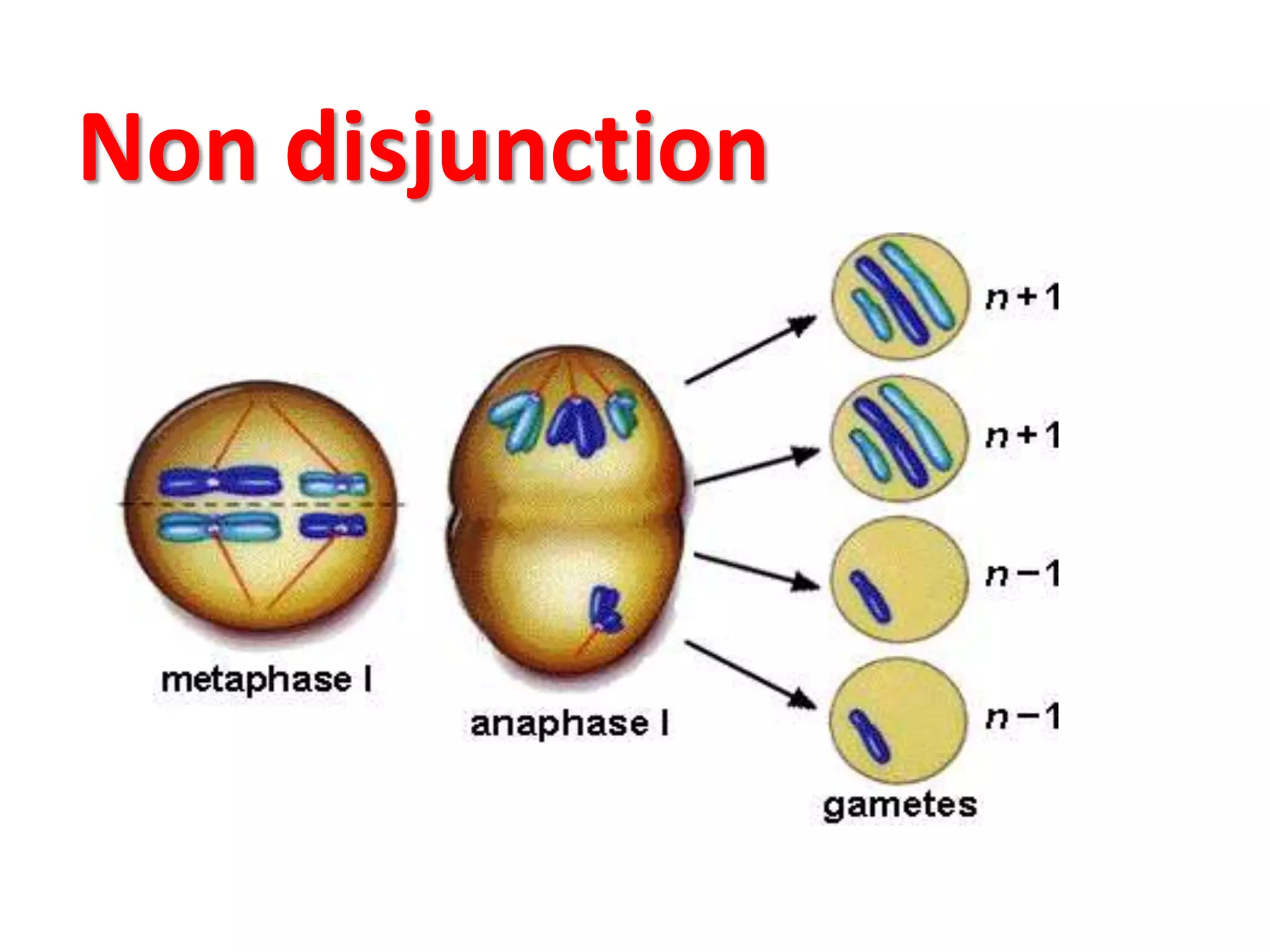
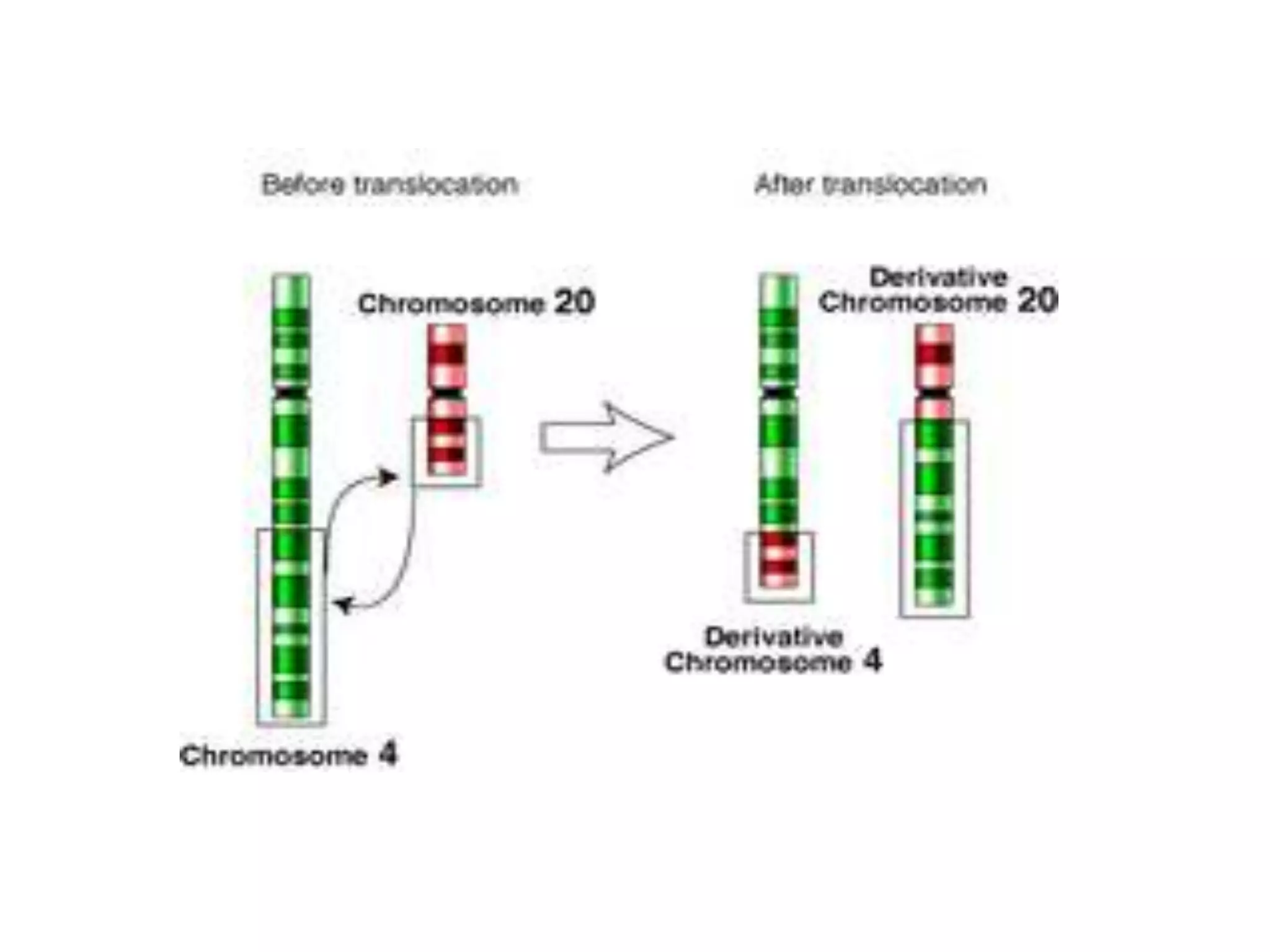
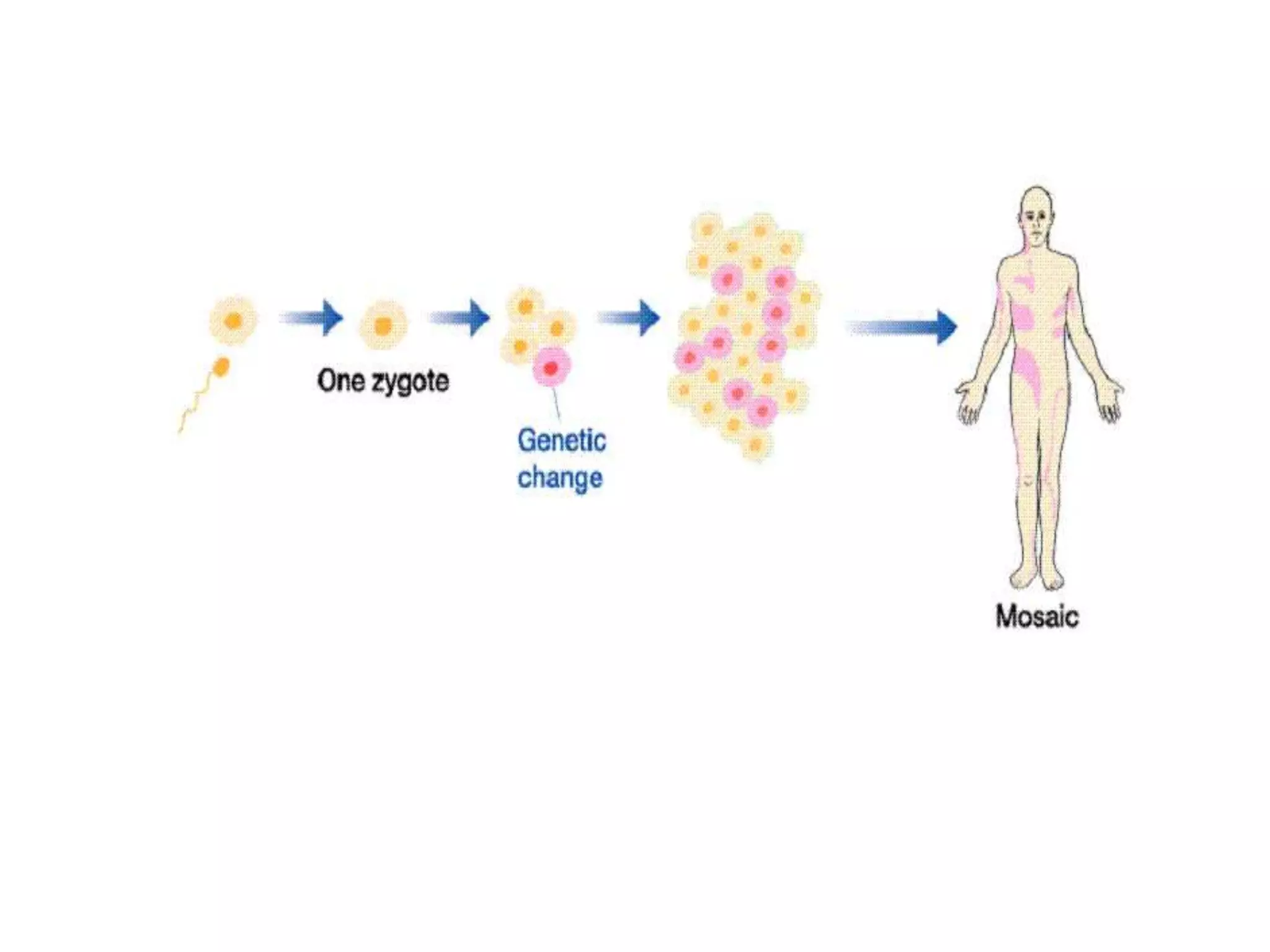
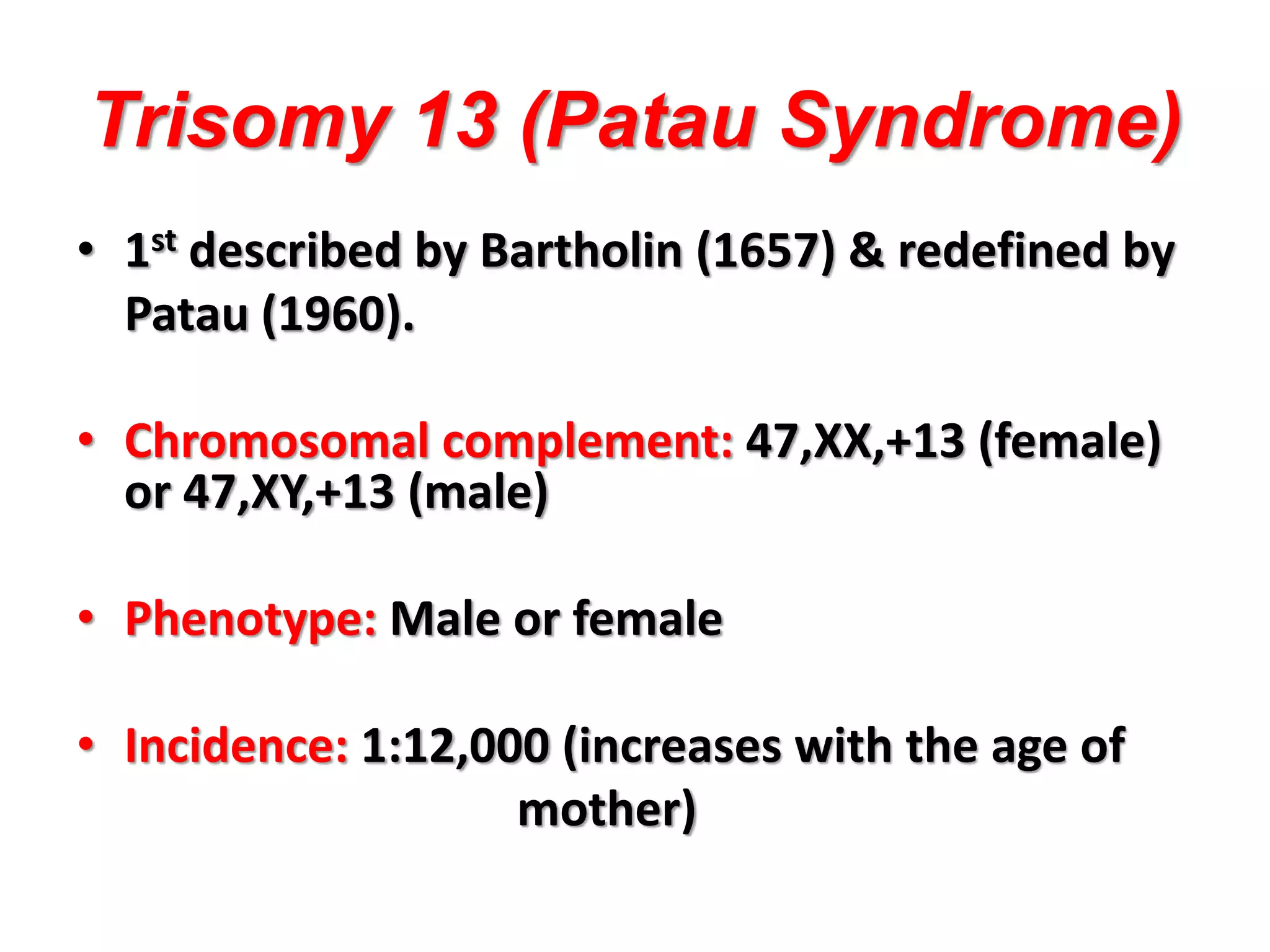
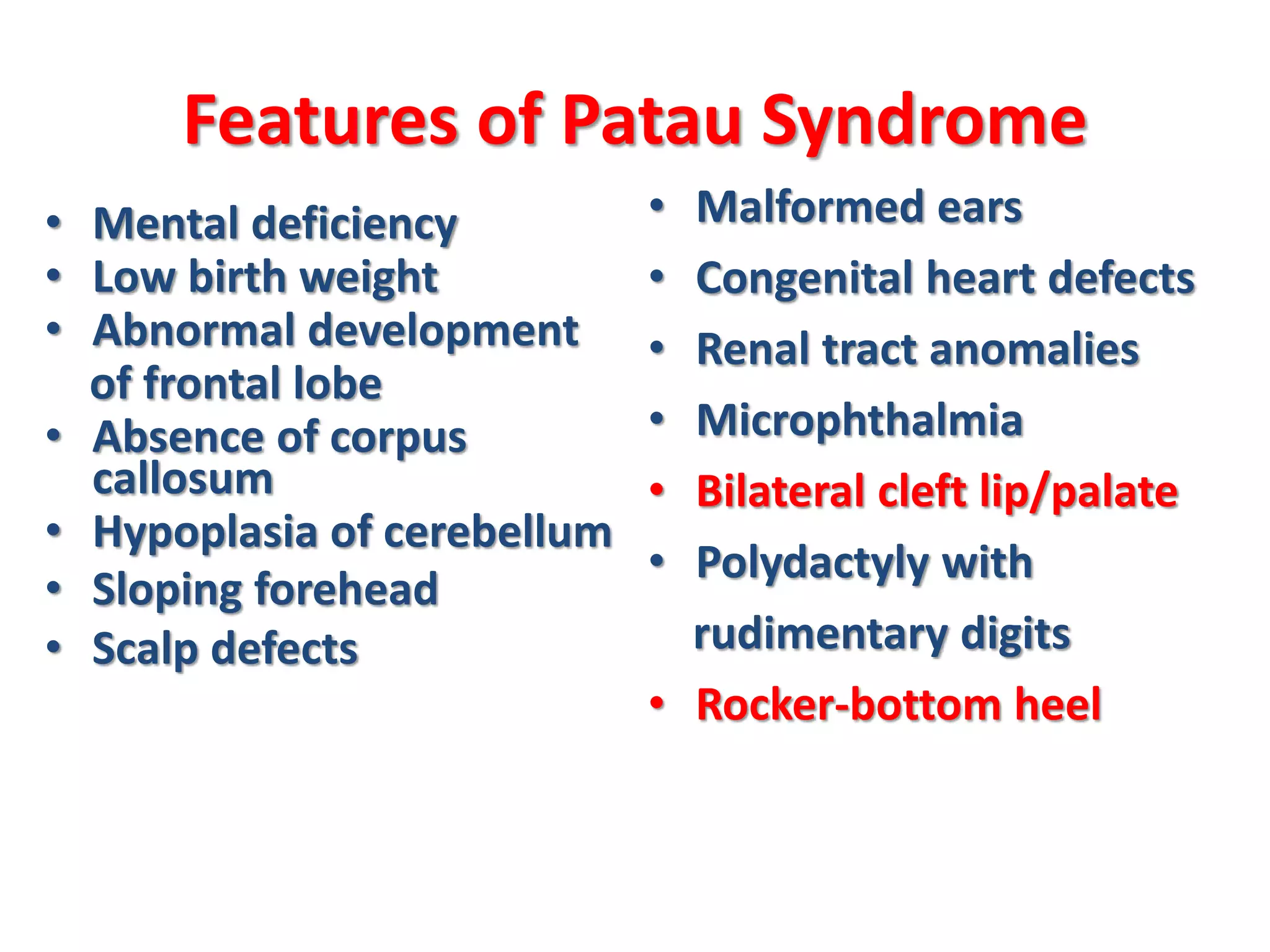
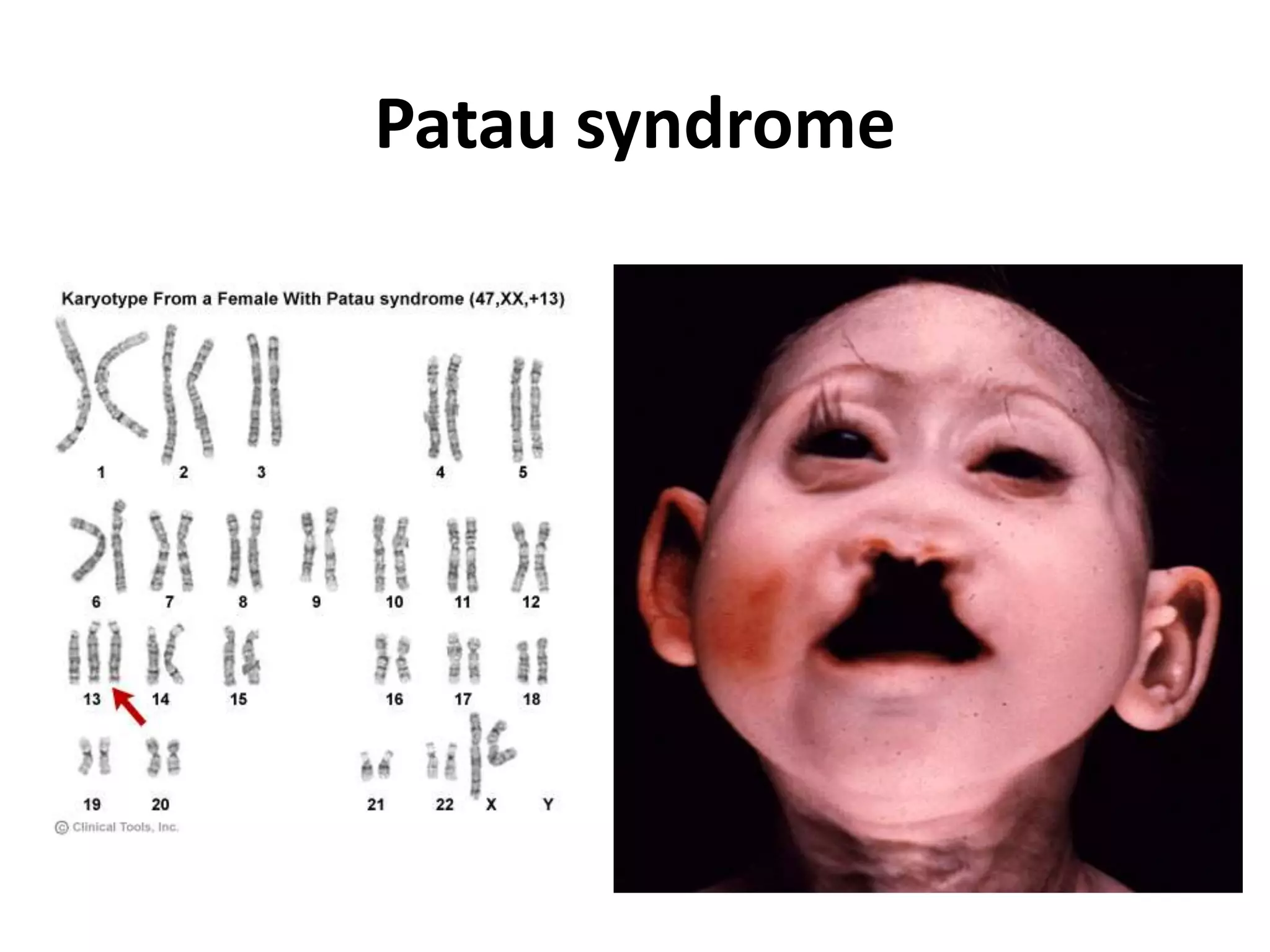
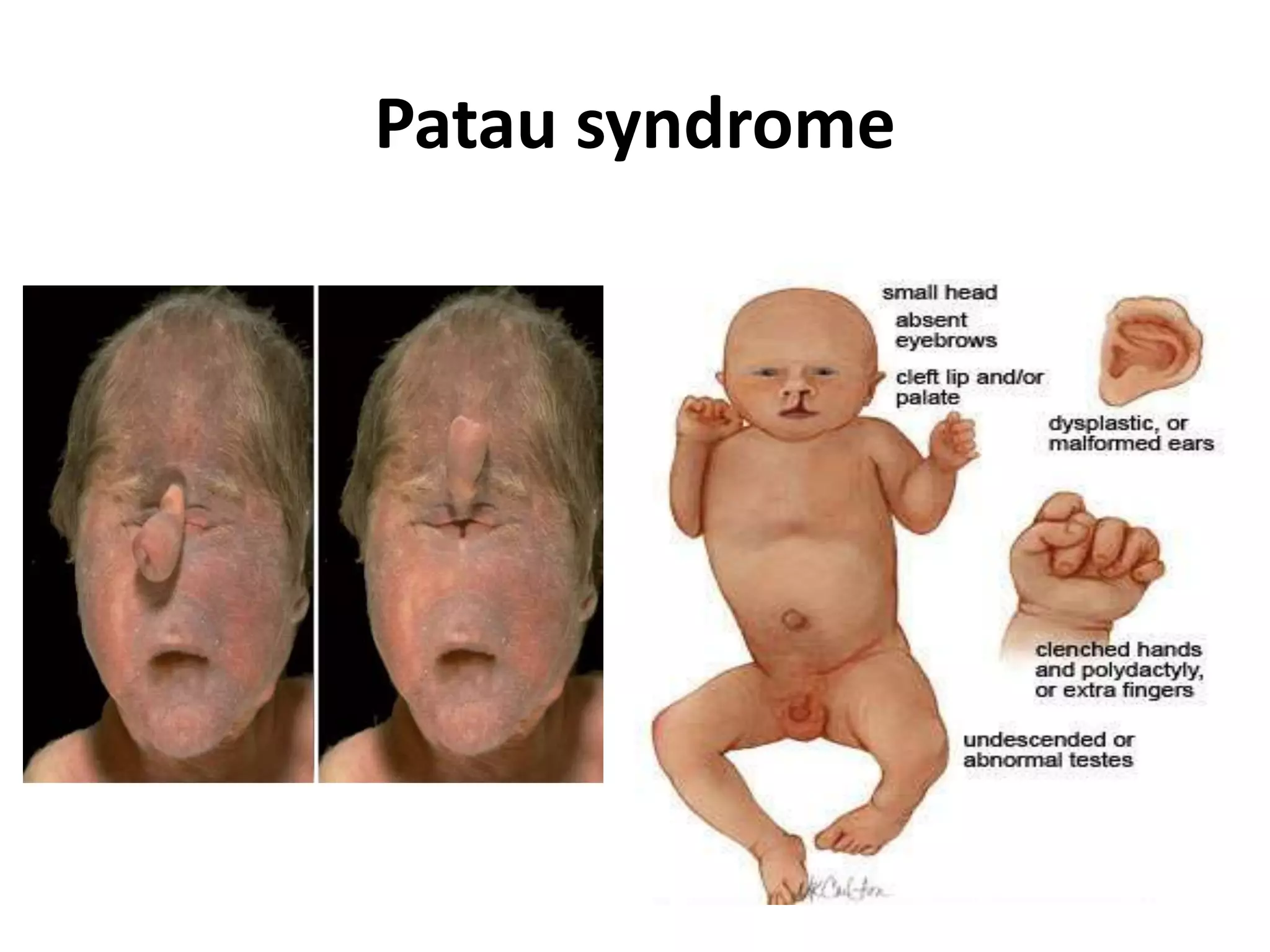
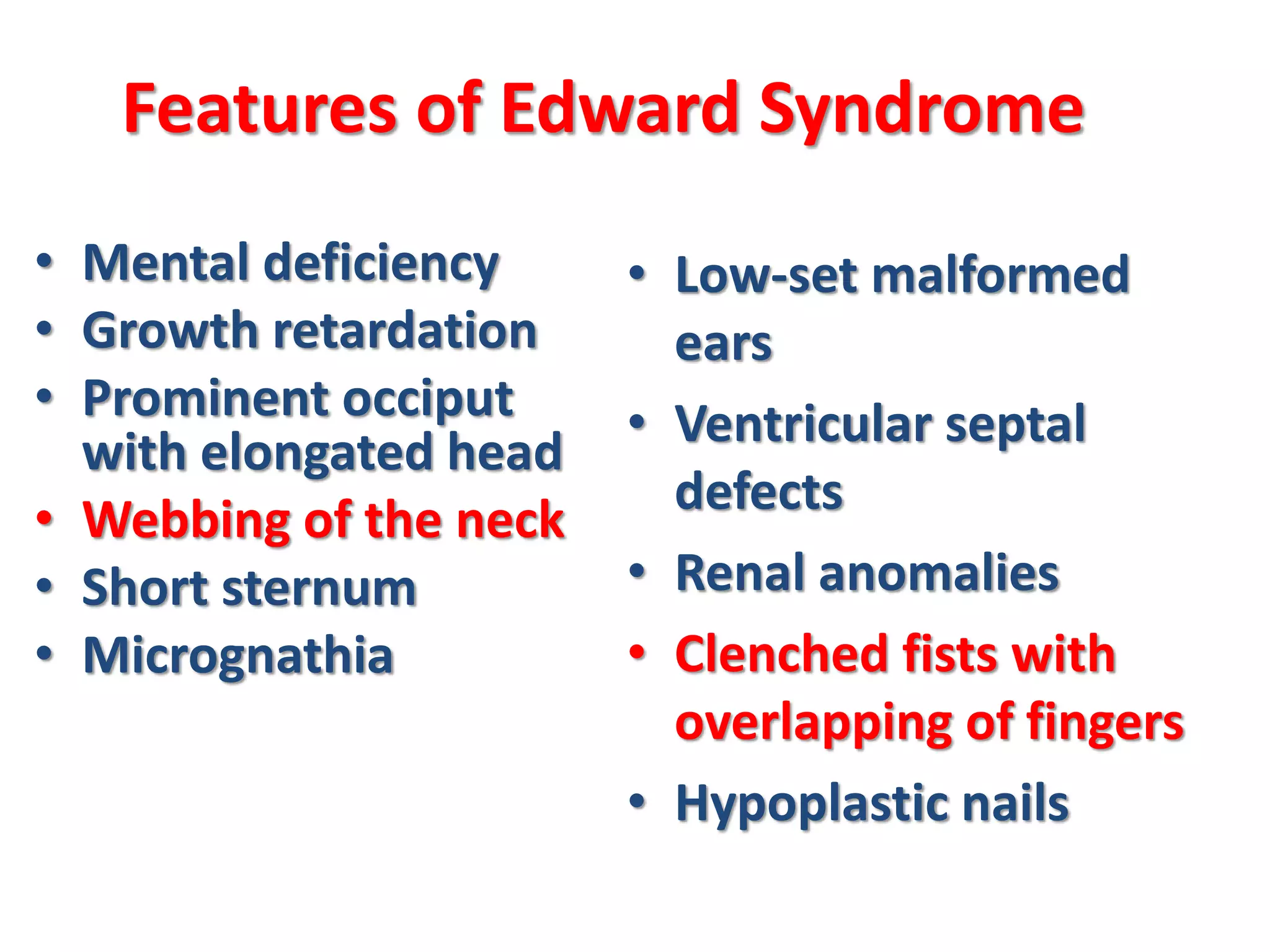
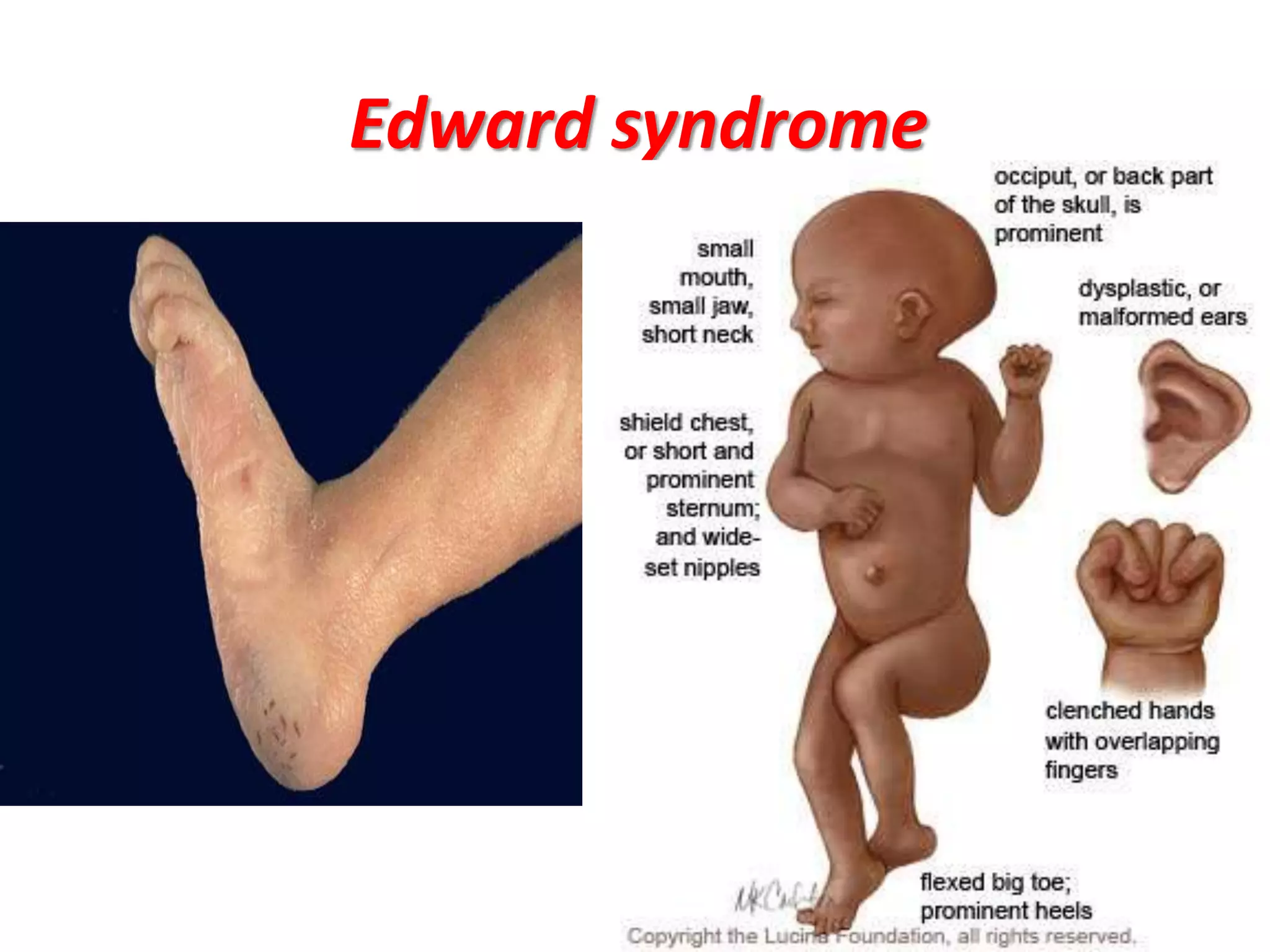
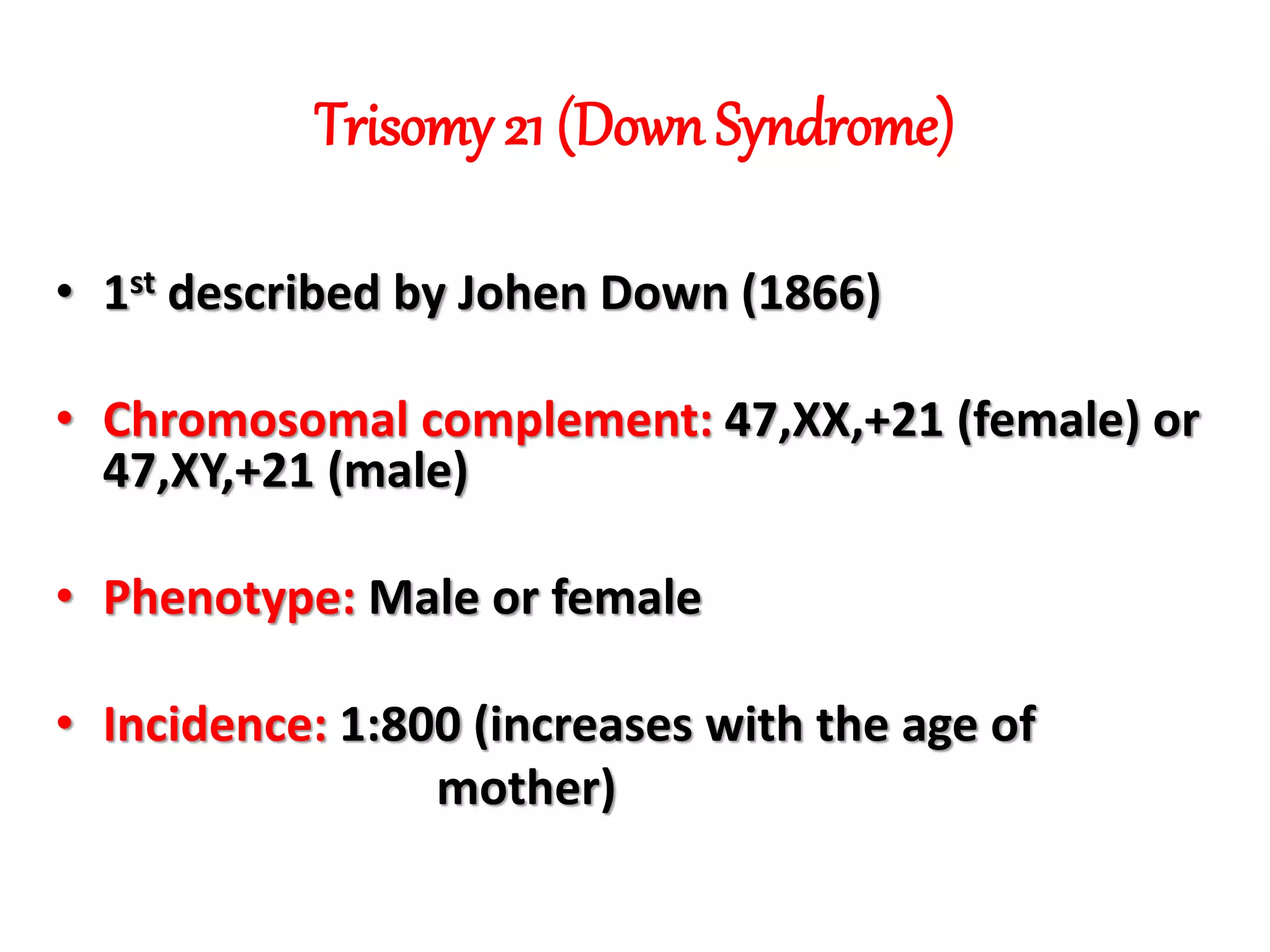
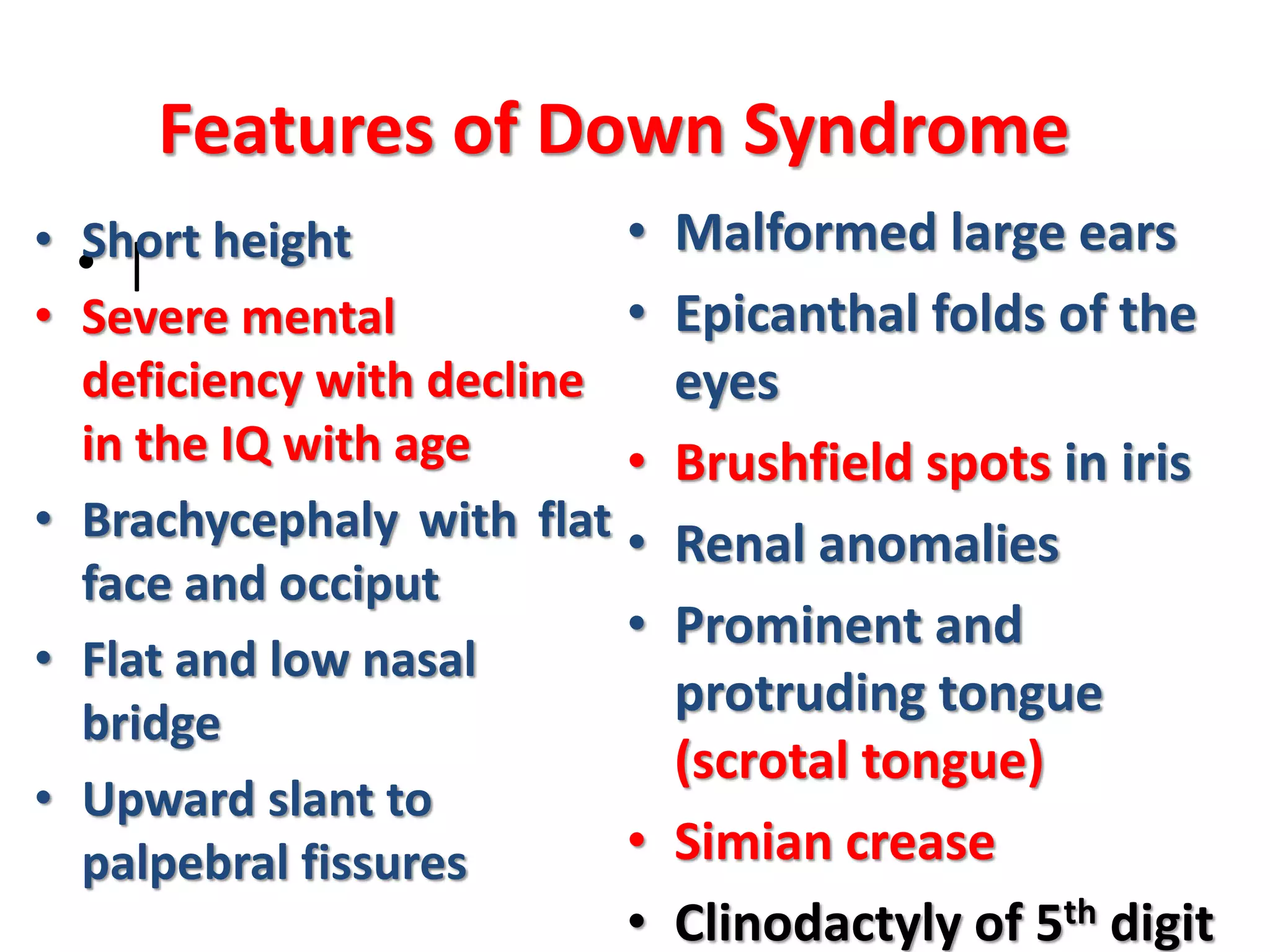
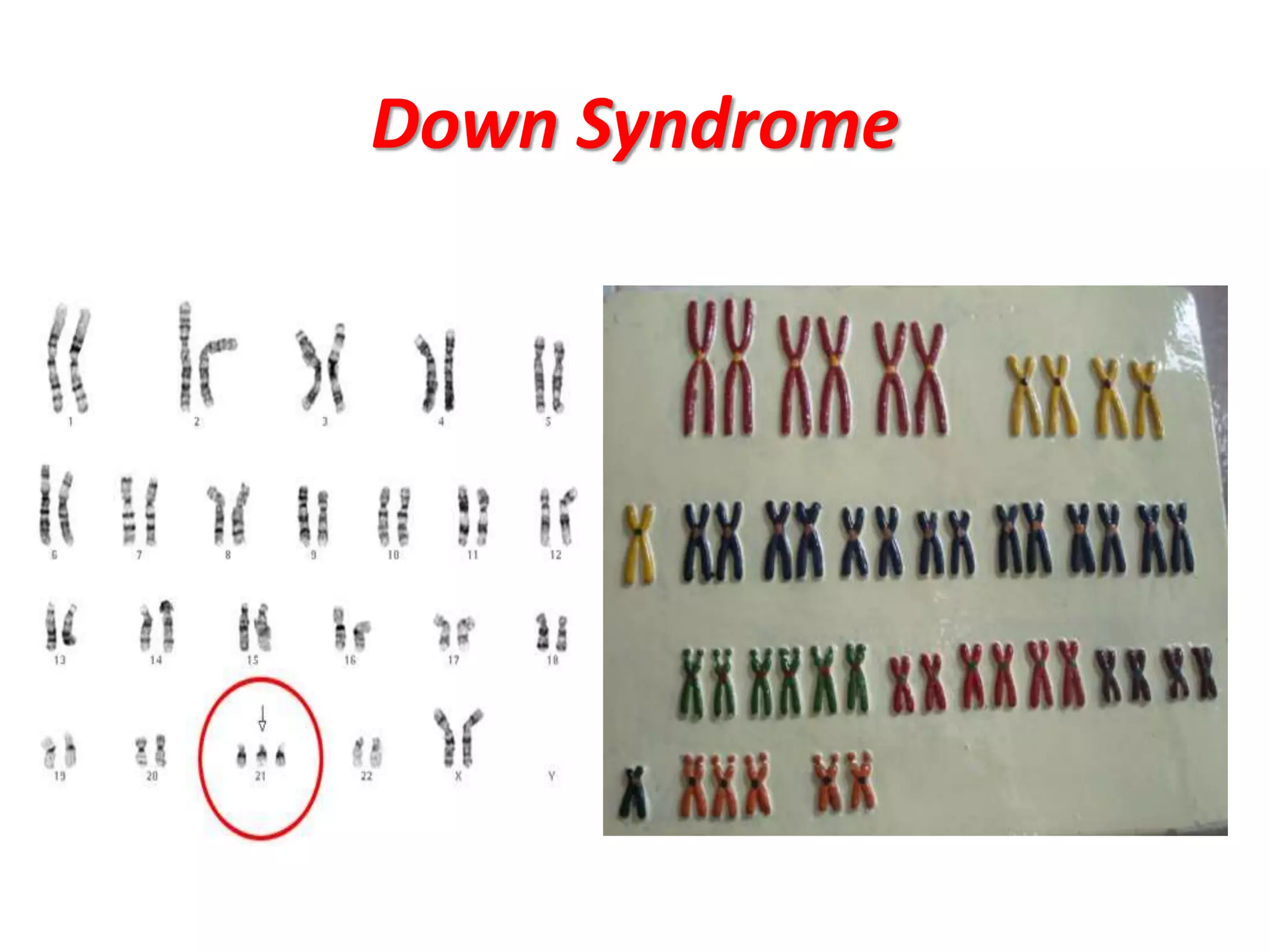
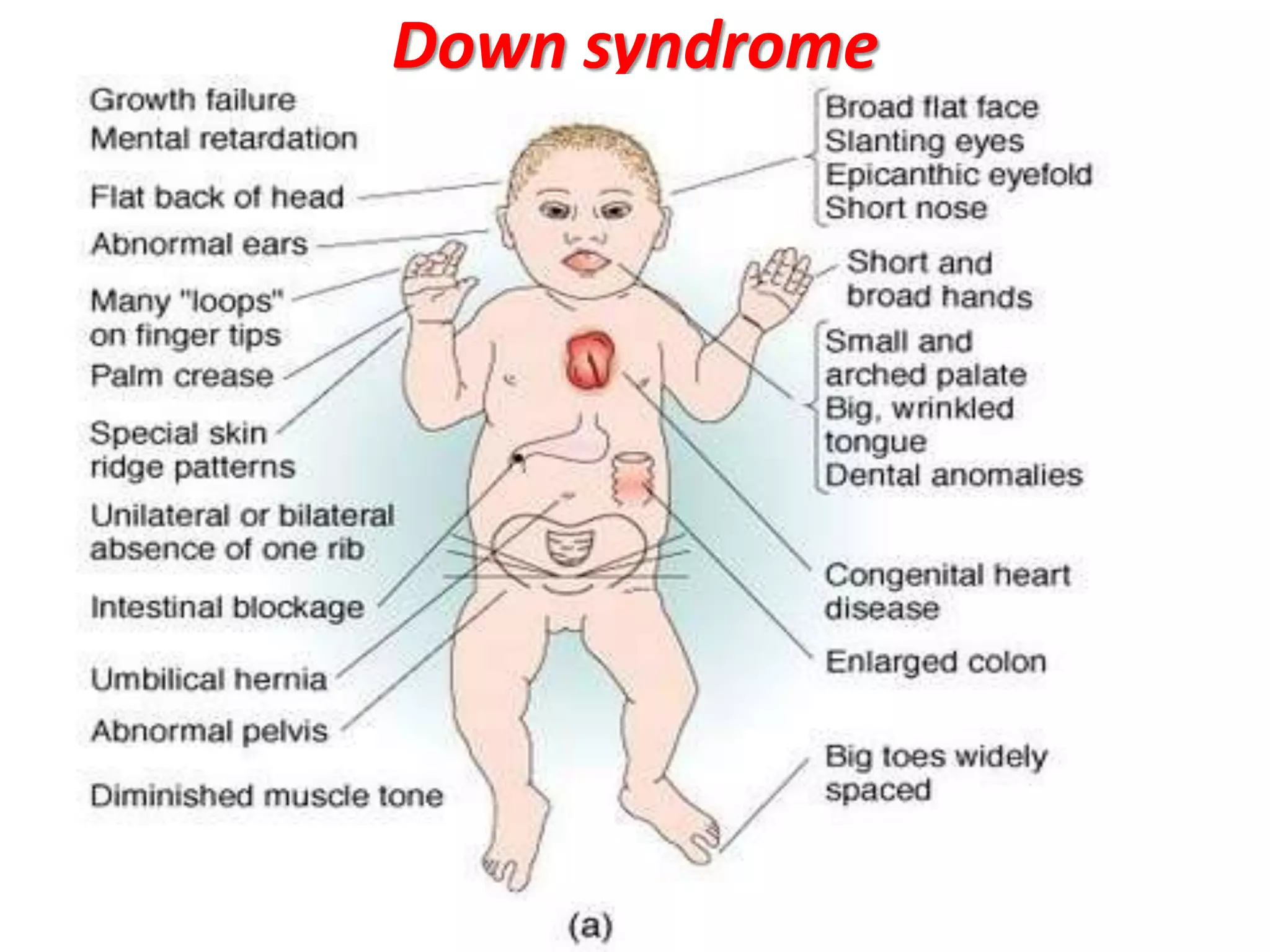
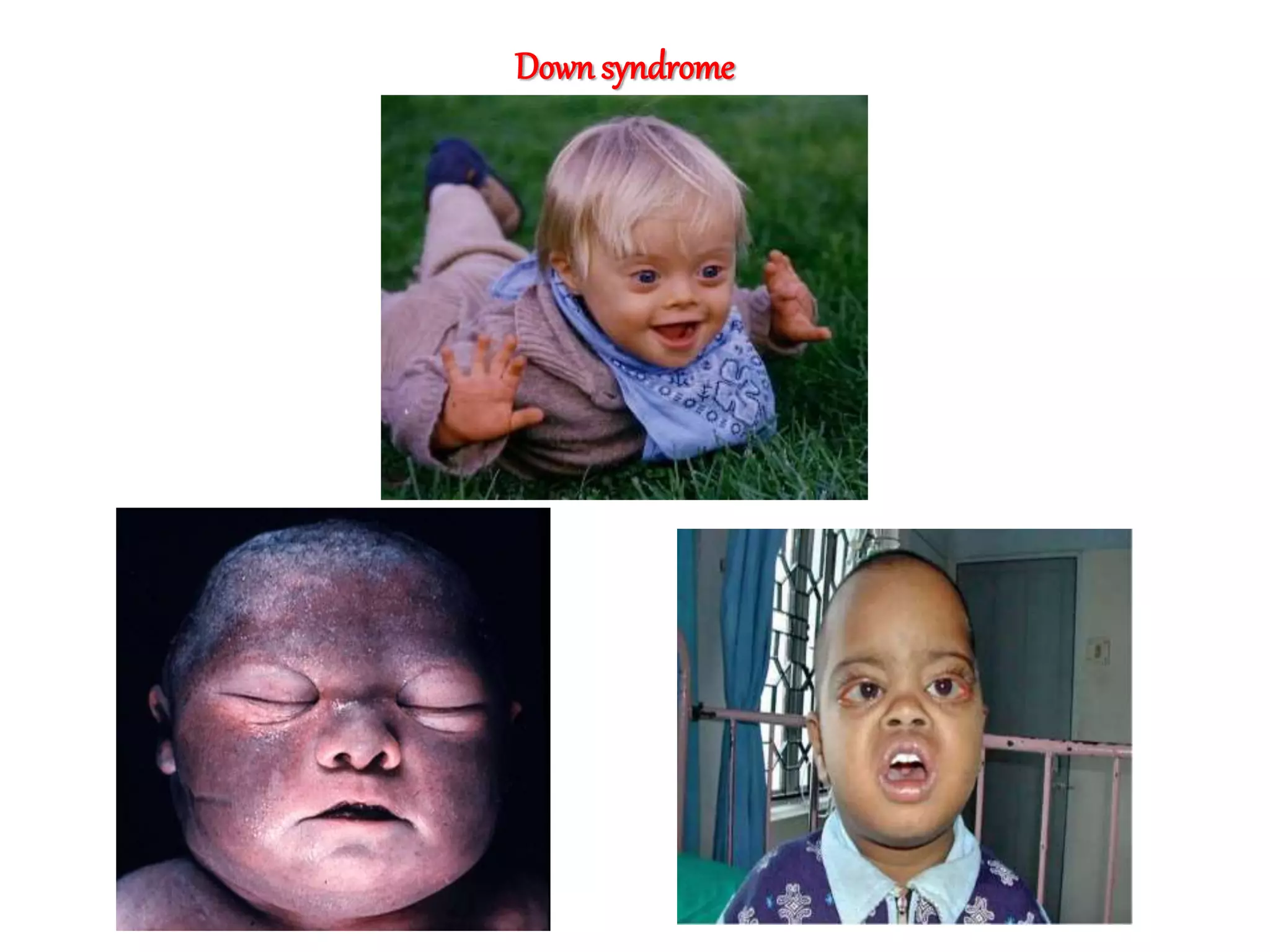
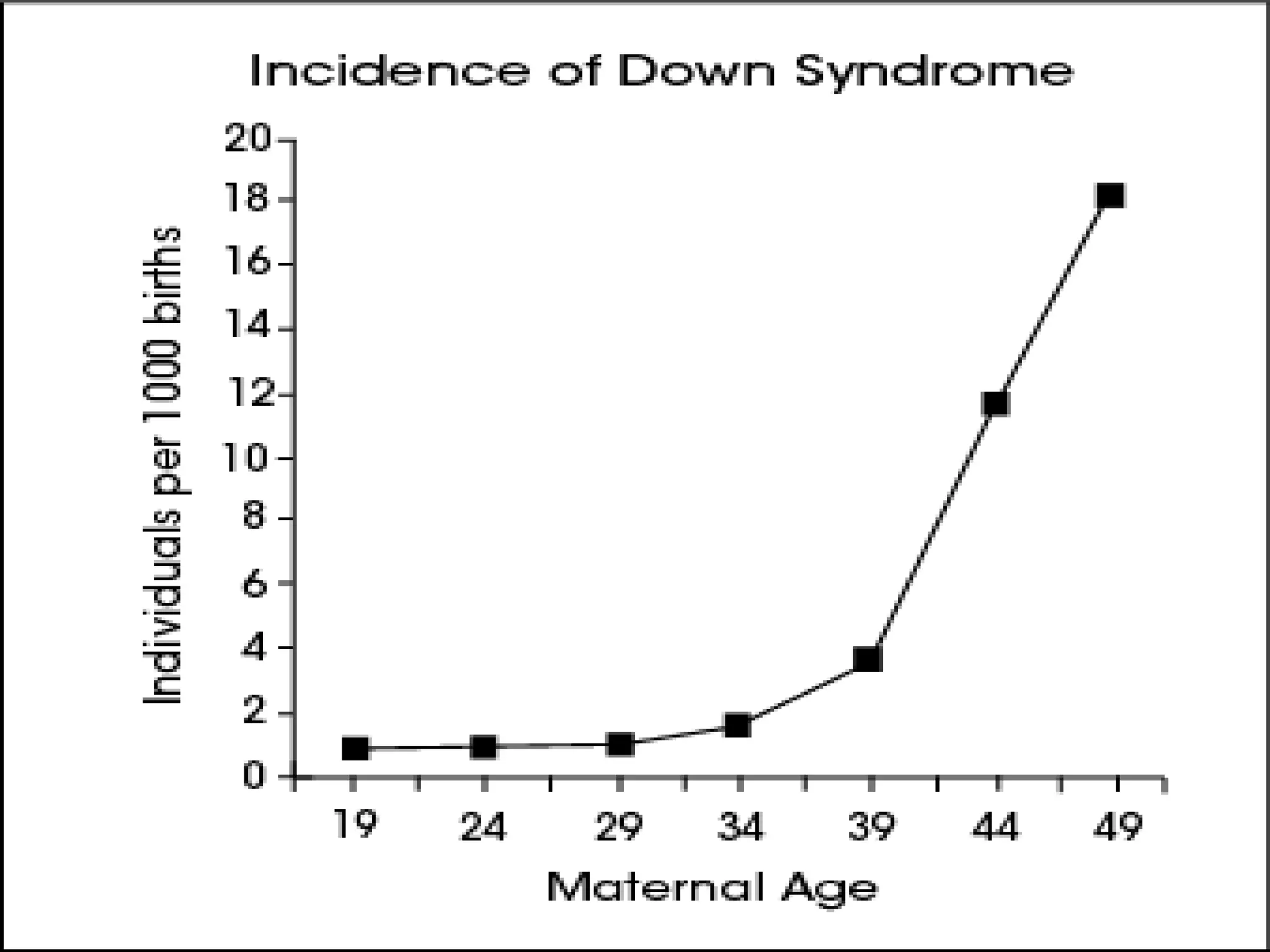
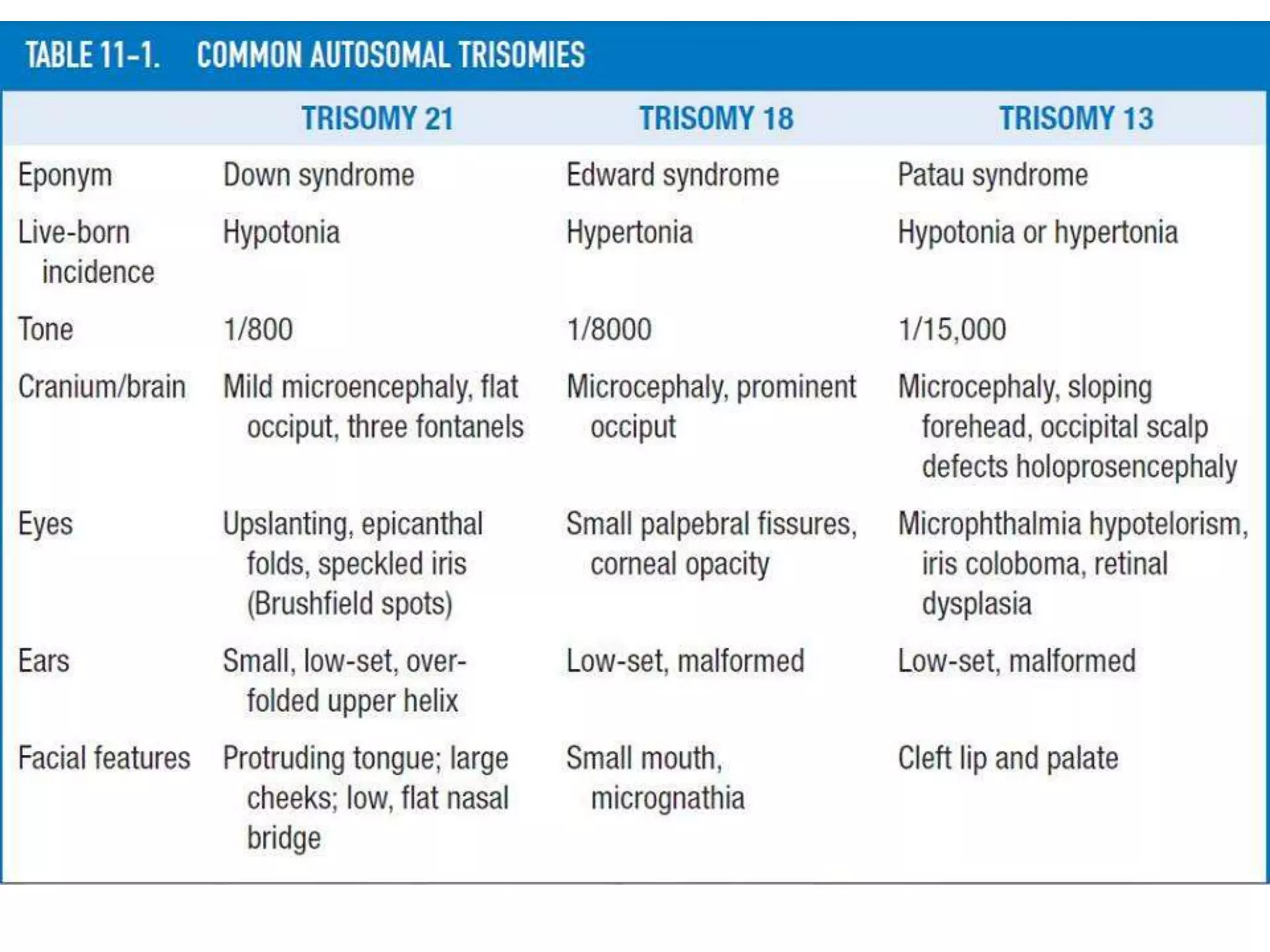
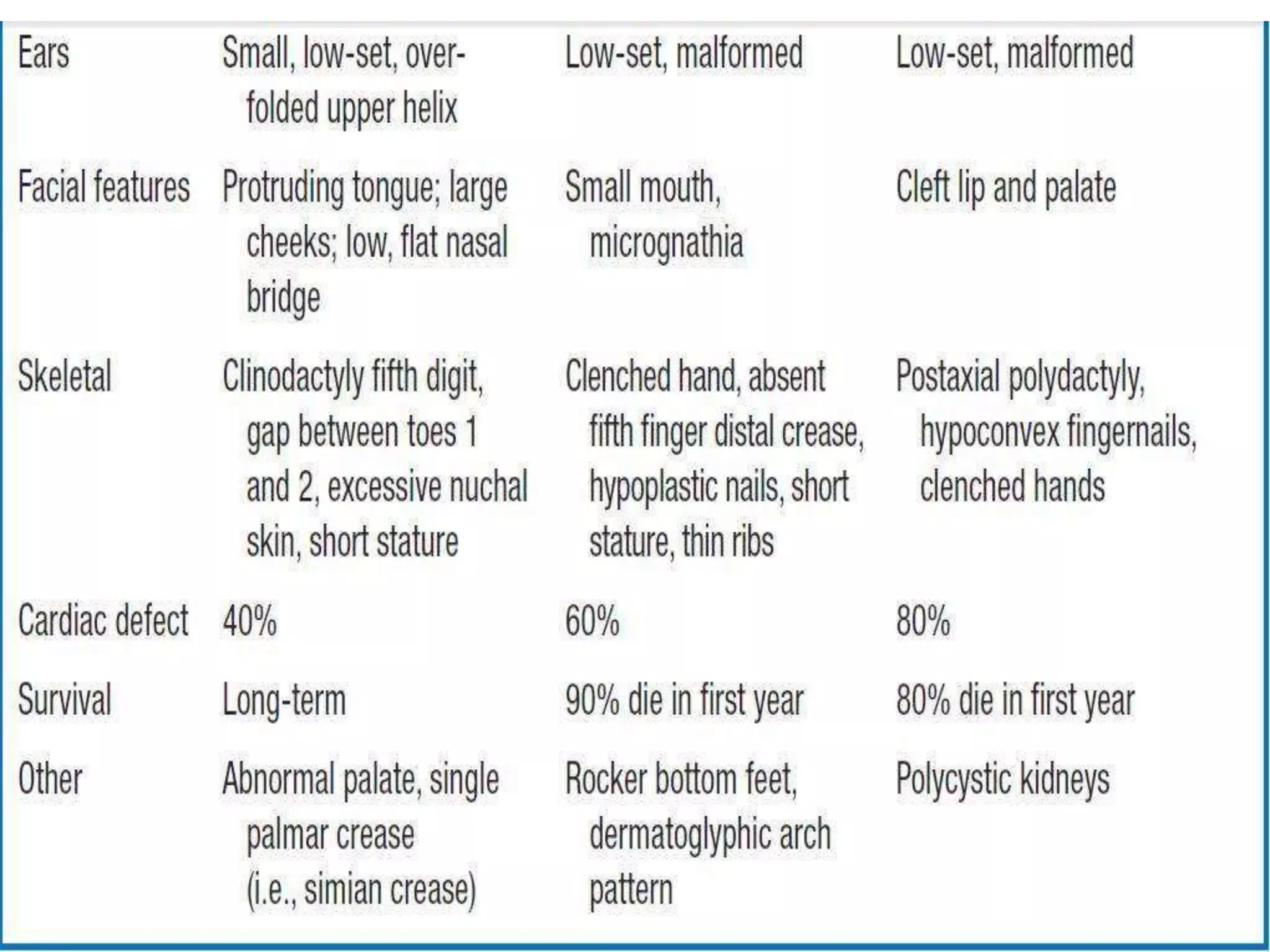
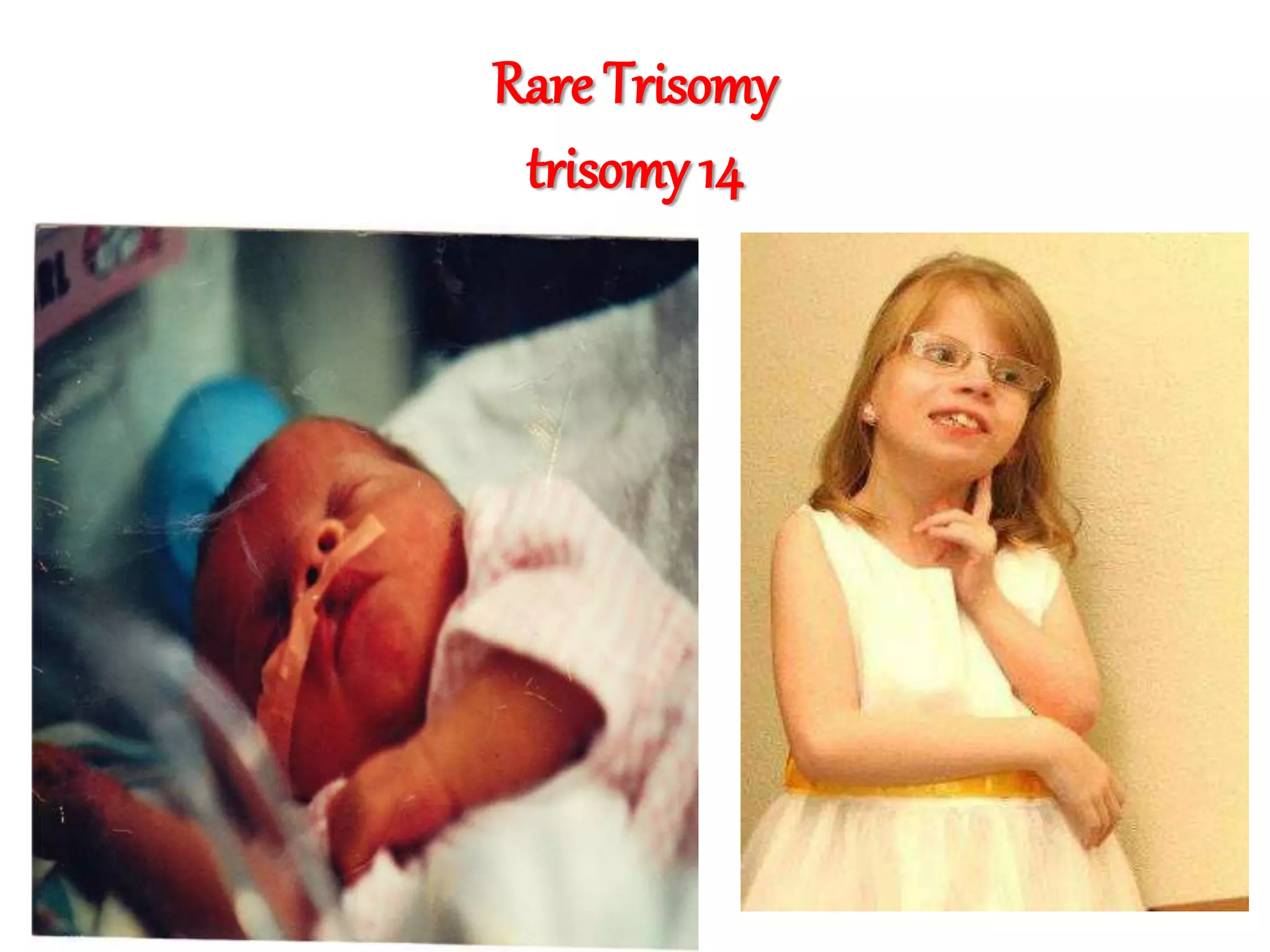
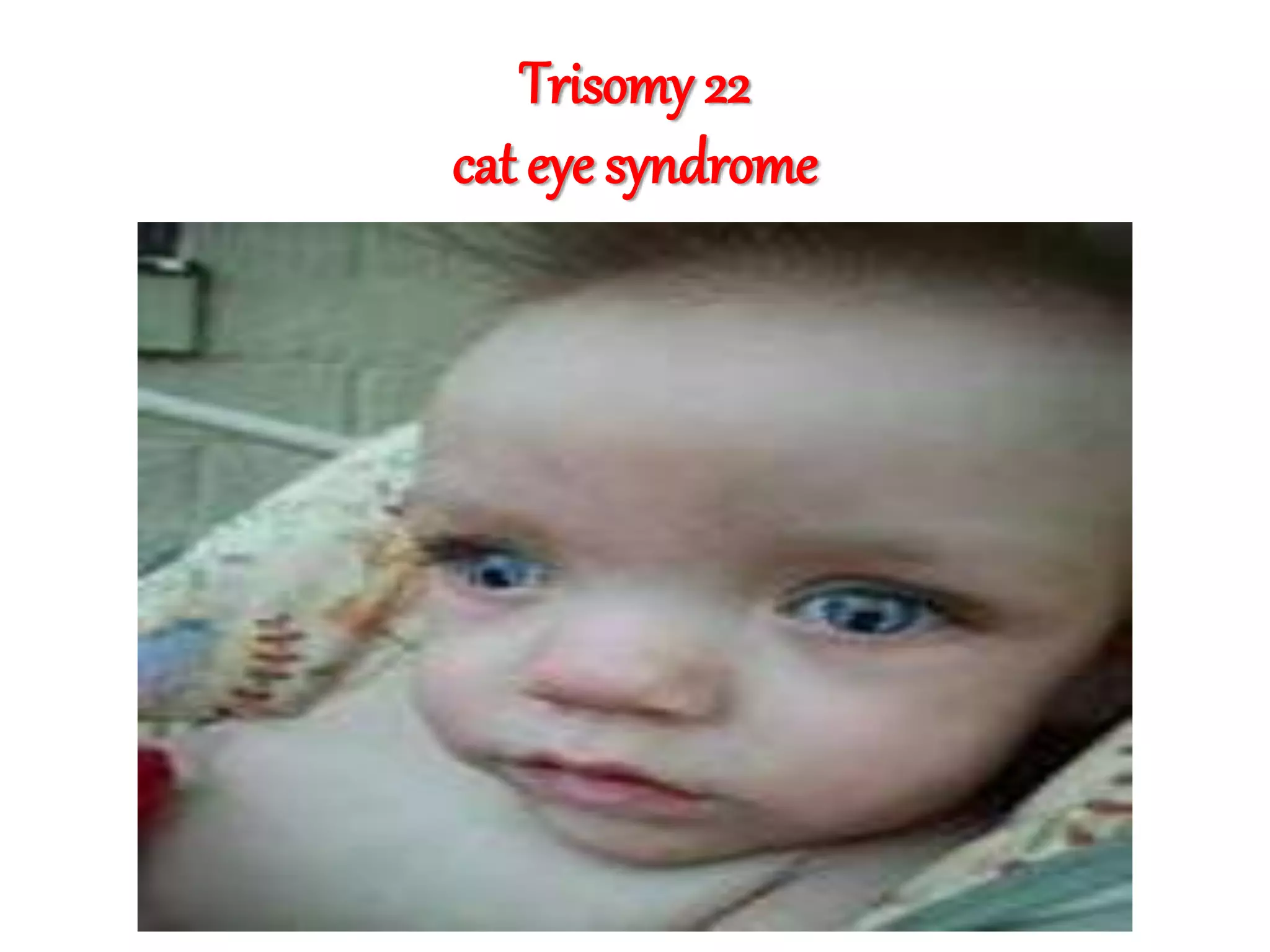
This document discusses trisomy, which is a type of aneuploidy where there are three instances of a particular chromosome instead of the normal two. It describes how trisomy occurs due to errors in meiosis where chromosomes fail to separate properly. The most common types of trisomy in humans are trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome), and trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome). Trisomy can cause birth defects, intellectual disabilities, and shortened life expectancy depending on which chromosome is involved. Rare cases of other trisomies like 8, 9, 14, 16, and 22 are also discussed.