Aneuploidy
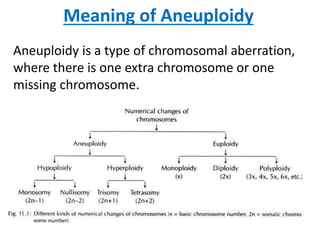
- 1. Meaning of Aneuploidy Aneuploidy is a type of chromosomal aberration, where there is one extra chromosome or one missing chromosome.
- 2. ANEUPLOIDY • Hypoploidy- When one or more chromosomes are less in number compared to the normal individual (2n) 1. Monosomy- When there is one chromosome less in the cells,(2n-1) e.g. Turner’s syndrome (XO) 2. Nullisomy- When there is loss of a pair of chromosomes, (2n-2). Often they do not survive. • Hyperploidy- When there is an addition of one or more chromosomes. 1. Trisomy- When there is one extra chromosome in the cells, e.g. Klinefelter’s syndrome (XXY), (Down’s syndrome-trisomy of the 21st chromosome.) 2. Tetrasomy- There is an addition of a pair of chromosomes, (2n+2). 3. Disomy- When there is one chromosome more in a monoploid organism, i.e. n+1.
- 4. Aneuploidy Causes If centromere gets deleted→ no attaching on spindle fibres. if small chromosome (ROBERTSONIAN TRANSLOCATION) gets deleted. Aneuploidy is caused due to non-disjunction of chromatids during cell division. • When chromatids fail to segregate during mitotic or meiotic cell division, it leads to one cell with an extra chromosome and another with one less chromosome. It causes aneuploidy. • Nondisjunction occurs during anaphase of cell division when sister chromatids separate.
- 7. BASIS EUPLOIDY ANEUPLOIDY DEFINITION state of having a chromosome number that is an exact multiple of a chromosome number. condition in which one or a few chromosomes are added or deleted from the normal chromosome number. TYPE OF VARIATION a large variation in which the amount of genetic material increases by means of chromosome sets. small variation in which the amount of genetic material varies by means of the number of chromosomes. VARIATIONS Diploid (2n), triploid (3n), and tetraploid (4n) are the variations in euploidy. Nullisomy, monosomy, trisomy, and tetrasomy are the variations in aneuploidy. OCCURENCE occurs in plants and rarely in animals. occurs in both animals and plants. CAUSES Complete nondisjunction and interspecies crosses lead to euploidy. Meiotic nondisjunction, mitotic nondisjunction, and chromosome loss lead to aneuploidy. ROLE Euploidy may lead to the formation of new species. Aneuploidy leads to the imbalance in the number of gene products.
- 8. Forms of Aneuploidy 1. Monosomy - Monosomy is the phenomenon where an individual lacks one or a few non-homologous chromosome(s) of a diploid complement. Types of Monosomy: • Single monosomies (2n – 1) • Double monosomies (2n – 1 – 1) • triple monosomies (2n – 1 – 1 – 1) [ No.of possible monosomies = haploid chromosome no.]
- 9. Origin of Monosomy: The origin of the monosomies may be from the production of n – 1 types of gametes due to rare nondisjunction of a bivalent. Meiotie Behaviour: Monosomies show irregular meiosis (univalents in addition to bivalents). Moreover, in progeny of a monosomic, a mixture of disomic (2n), monosomies (2n – 1) and nuilisomics (2n – 2) is obtained.
- 10. HUMAN MONOSOMIES TURNER SYNDROME • Turner syndrome or Ullrich-Turner syndrome encompasses several conditions, of which monosomy X is the most common. • It occurs in about 1 out of every 2500 female births. • Instead of the normal XX sex chromosomes for a female, (or XY for a normal male) only one X chromosome is present and fully functional. • A normal female karyotype is labeled 46,XX; individuals with Turner syndrome are 45,X. • In Turner syndrome, female sexual characteristics are present but generally under-developed. Symptoms • Short stature • Lymphedema (swelling) of the hands and feet • Broad chest • Low hairline • Low-set ears • Reproductive sterility
- 12. CRI DU CHAT SYNDROME • Example of PARTIAL MONOSOMY. • Cri-du-Chat syndrome (French for Cry or call of the cat referring to the specific cry of the child) • Also called deletion 5p syndrome, 5p minus or Lejeune’s syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder due to a missing portion of chromosome 5. • It was first described by Jérôme Lejeune in 1963. • The condition affects an estimated 1 in 20,000 to 50,000 live births. • more common in females by a 3:1 ratio. SYMPTOMS • The syndrome gets its name from the characteristic cry of infants born with the disorder. • The infant sounds just like a meowing kitten, due to problems with the larynx and nervous system.
- 13. 2. Nullisomy: • The plants in which a chromosome pair is missing, are called nullisomics. • Chromosome formula would be (2n – 2) and not (2n – 1 – 1), i.e.double monosomic. • No.of possible nullisomics = haploid chromosome no. Origin of Nullisomy: The origin of nullisomics is generally by the selfing of the monosomies. Use of Nullisomy: • used in locating different genes. •In wheat, nullisomics have been obtained with 40 chromosomes instead of 42 chromosomes.
- 14. 3. TRISOMY: ~ Trisomies are those organisms,which have an extra chromosome (2n -t- 1). ~ The number of possible trisomies in an organism is equal to the haploid chromosome number. •Types of Trisomy: Primary Trisomies- where extra chromosome is identical to two homologues • Secondary Trisomies- where the extra chromosome is an iso-chromosome with two genetically identical arms • Tertiary Trisomies- are the products of translocation. • Double Trisomies (2n + 1 + 1) are also available in nature.
- 15. Origin of Trisomy: from the production of n + 1 types of gametes due to rare non-disjunction of a bivalent in a diploid also be produced by triploids through irregular meiosis. Meiotic Behaviour: Trisomies show irregular’ meiosis . Since the trisomies have an extra chromosome which is homologous to one of the chromosomes of the complement, they form a trivalent. Blakeslee and Belling obtained trisomic individuals in Datura stramonium having 25 instead of 24 chromosomes. Gradually, all the 12 kinds of trisomies,were obtained; each one of the 12 qualitatively different chromosomes in the genome appeared as an extra chromosome. Use: The trisomies are of significance in locating genes on specific chromosomes. The trisomies have somewhat poorer vigour and less fertility than the normal diploid form.
- 16. TRISOMY 21 : DOWN SYNDROME • In trisomy 21, the presence of an extra set of genes leads to over expression of the involved genes, leading to increased production of certain products. • There is a wide range of mental retardation and developmental delay noted among children with Down syndrome. • Some babies are born with heart defects.
- 18. EDWARD’S SYNDROME • Trisomy 18 is the second most common trisomy and occurs when a baby has three of the 18th chromosome. • This results in 47 chromosomes instead of the normal 46 in the affected cells. occurs in about 1:3000 live births.
- 19. PATAU SYNDROME •The syndrome or trisomy 13 is the least common trisomic condition observed.It is a full trisomic condition. • In this disorder three copies of chromosome 13 are present thereby bringing about a diseased condition. • The occurrence of the disorder is 1 in 5000 live births. SYMPTOMS- • facial defect • Polydactyly • Characteristic facial features • Retarded growth • Poorly developed sexual characters
- 20. CHROMOSOME NO. MONOSOMY TRISOMY 4 Wolf-hirschhorn Syndrome - 5 Cri Du Chat 5p Deletion Syndrome - 7 Williams Syndrome - 8 - Warkany Syndrome 11 Jacobsen Syndrome 13 - Patau Syndrome 15 Angelman Syndrome Prader-willi Syndrome - 17 Miller-dieker Syndrome Smith-magenis Syndrome - 18 18q Deletion Syndrome Edward’s Syndrome 21 - Down Syndrome 22 Digeorge Syndrome Cat Eye Syndrome
- 21. Tetrasomy: → Tetrasomics have a particular chromosome represented in four doses (2n+2). → possible tetrasomics is equal to the haploid chromosome number of an organism. →All 21 possible tetrasomics are available in wheat. Origin of Tetrasomy: Tetrasomics may be originated by selfing of trisomies. Meiotic Behaviour: During meiosis, the four homologues of the tetrasomic set tend to form a quadrivalent.
- 22. KLINEFELTER’S SYNDROME • Klinefelter's syndrome, 47, XXY or XXY syndrome is a condition in which Affected individuals have at least two X chromosomes and at least one Y chromosome.
- 23. Importance Of Aneuploidy In Plants (a) Detecting linkage group: Particularly nullisomics, monosomies and trisomies used to determine linkage groups in tobacco, wheat, etc. (b) Chromosome substitution in plant breeding: The substitution of whole chromosome or part of the chromosome using aneuploids has been done. These substitutions resulted in significant modification of yield, resistance, lodging, etc. (c) Speciation: In Crepis, aneuploid variations form a series X = 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 among species. A very extensive aneuploid series has been observed in Carex (n = 6 to 56). (d) Aneuploidy useful in studying the effects of loss or gain of an entire chromosome of an individual. (e) They are useful in identifying the chromosome involves in translocation.
- 24. DEMERITS OF ANEUPLOIDY Aneuploidy causes sterility in crosses. Effected organism can’t be further used as parent in hybridisatioon programmes. In diploid species, nullisomics and monosomics are inviable. Maintenance, production, identification of aneuploidy is time consuming, requires considerable skills.