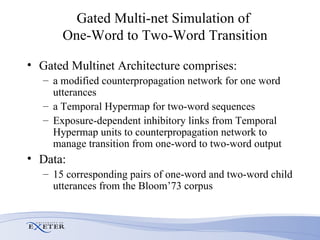
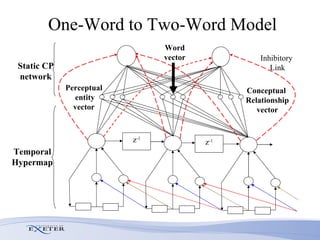
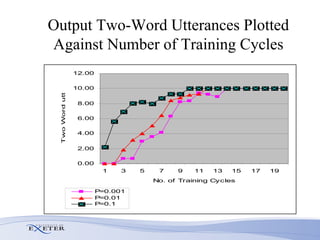
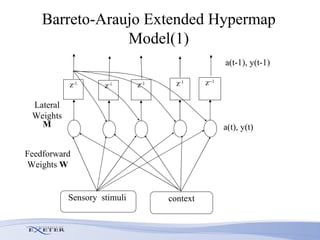
The document summarizes research on modeling multiple sequence processing using an unsupervised neural network approach based on the Hypermap Model. Key points:
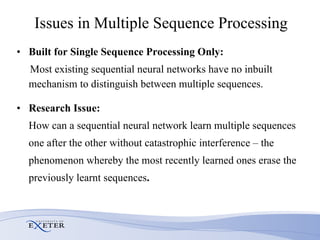
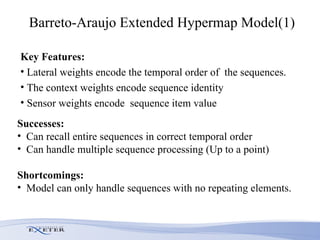
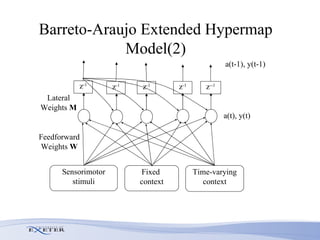
- The researcher extends previous models to handle complex sequences with repeating subsequences and multiple sequences occurring together without interference.
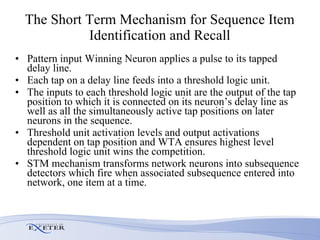
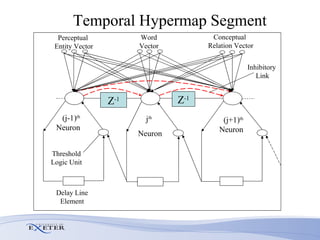
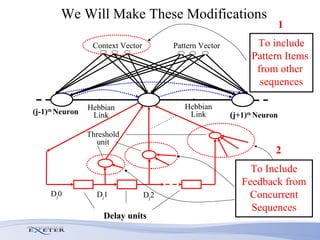
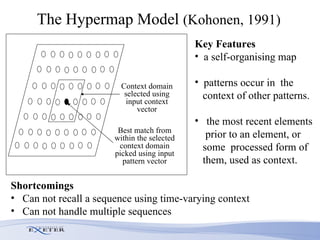
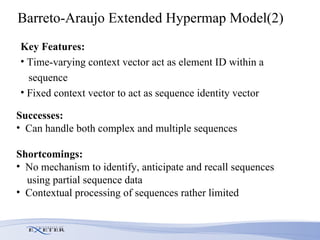
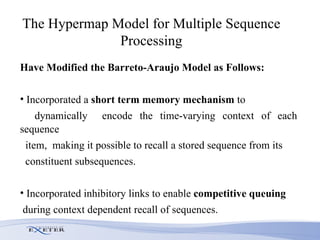
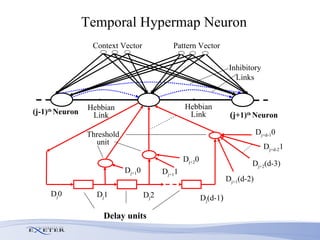
- Modifications include incorporating short-term memory to dynamically encode time-varying sequence context and inhibitory links to enable competitive queuing during recall.
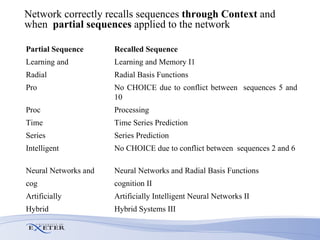
- Experimental evaluation shows the network can correctly recall sequences using partial context and when sequences overlap.
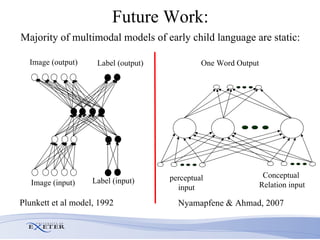
- Future work aims to model the transition from single-word to two-word child speech and incorporate temporal processing of multimodal inputs like gestures.


![The Competitive Queuing Scheme for Context- Based Recall Context vector applied to the network and Winner Take All mechanism activates all the target sequence neurons Inhibitory links ensure that only the first neuron is free to fire. Next sequence neuron fires on deactivation of first neuron Neuron activation and deactivation continues until entire sequence is retrieved Scheme first proposed by Estes [17], and used by Rumelhart and Norman [18] in their model of how skilled typists generate transposition errors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/trinitypresentation07-100415122140-phpapp01/85/Temporal-Hypermap-Theory-and-Application-15-320.jpg)