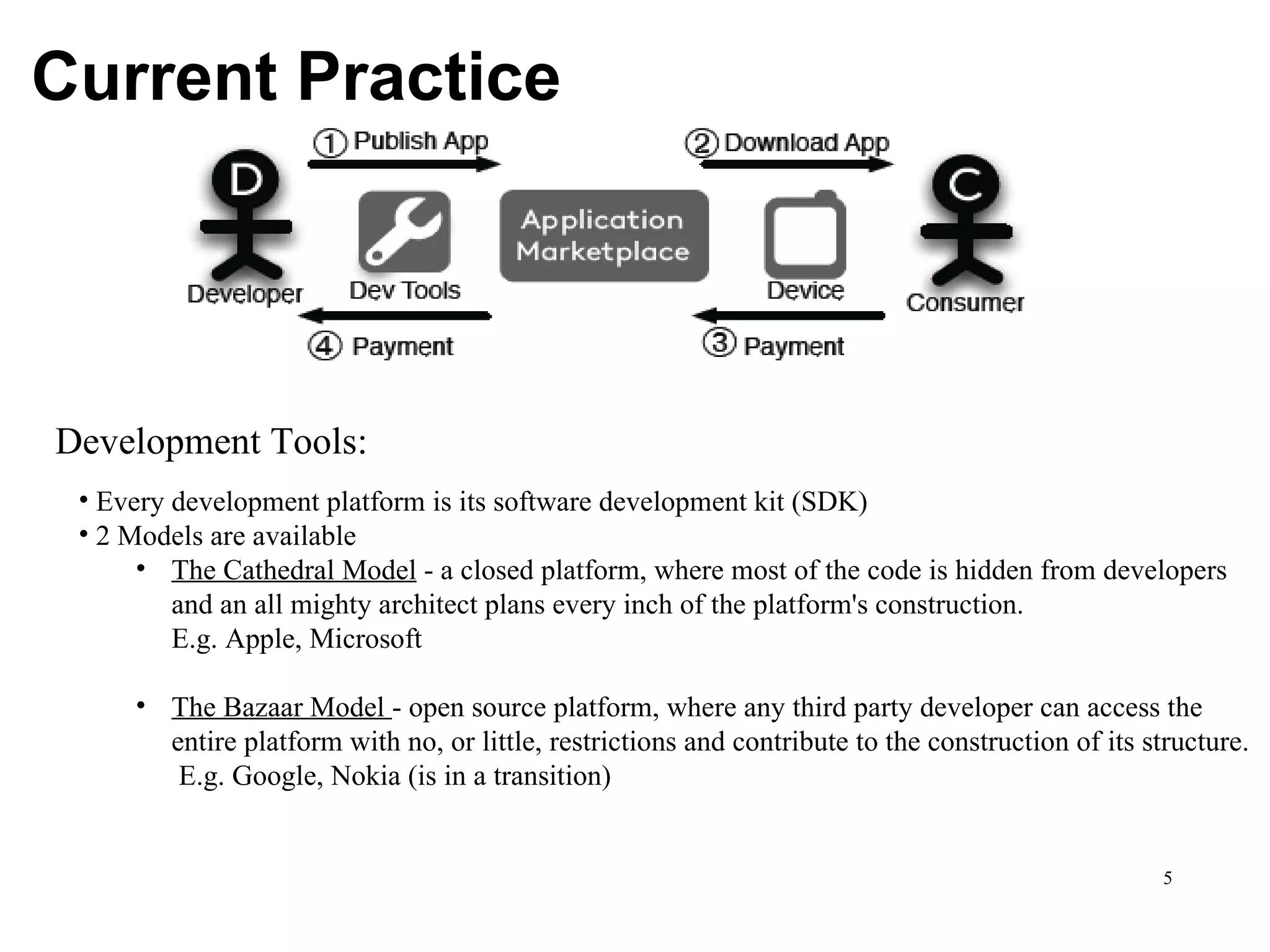
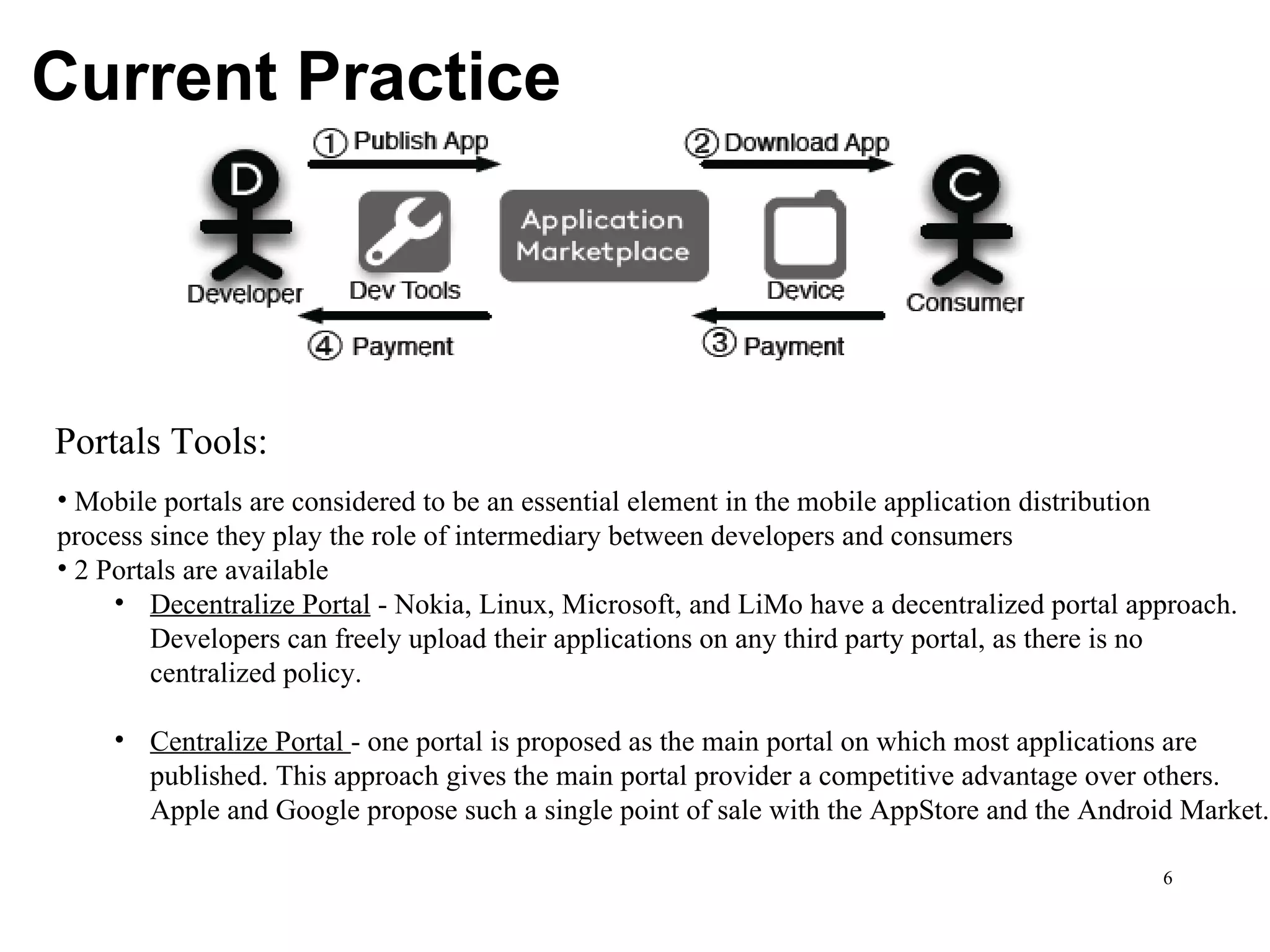
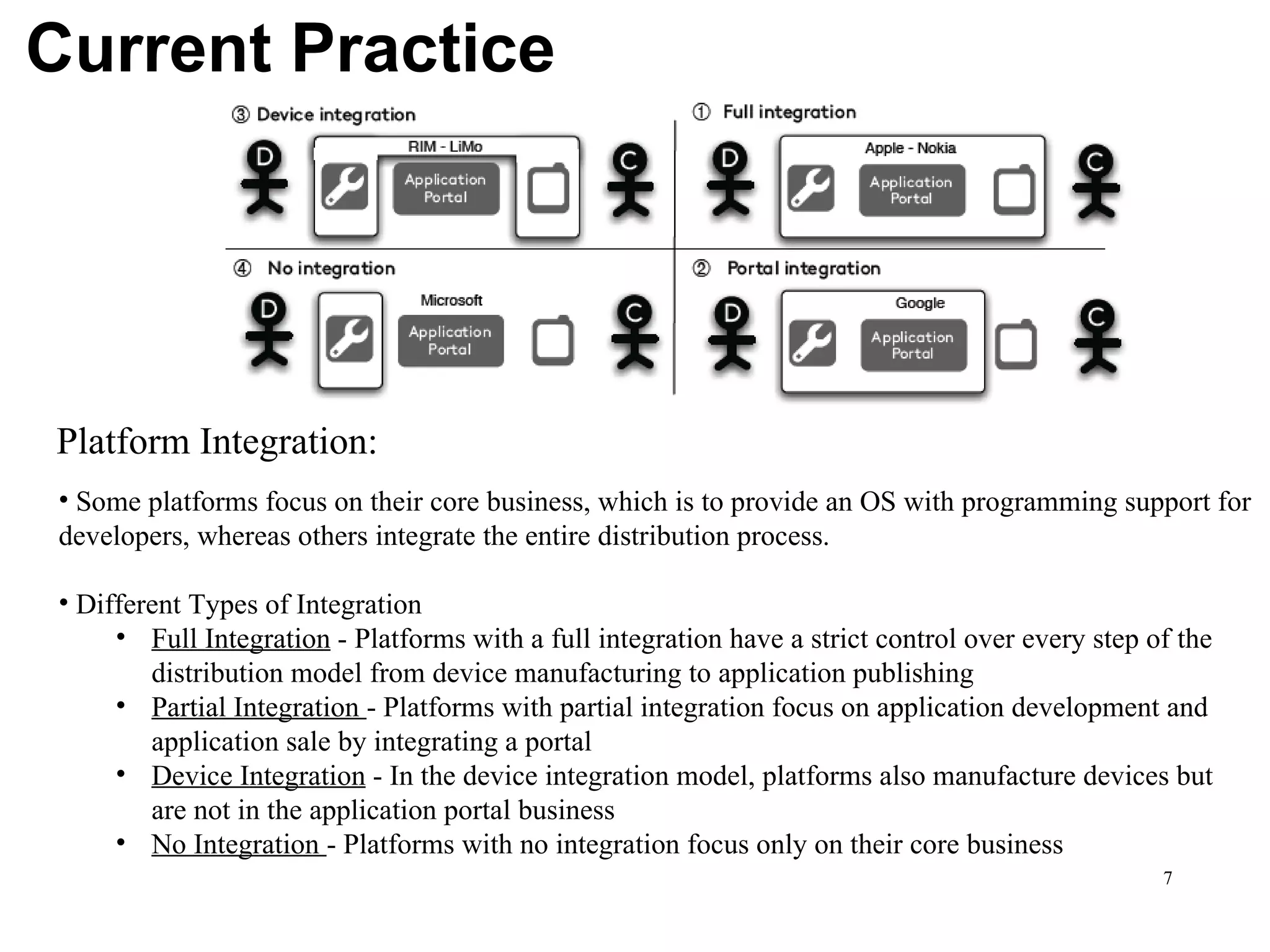
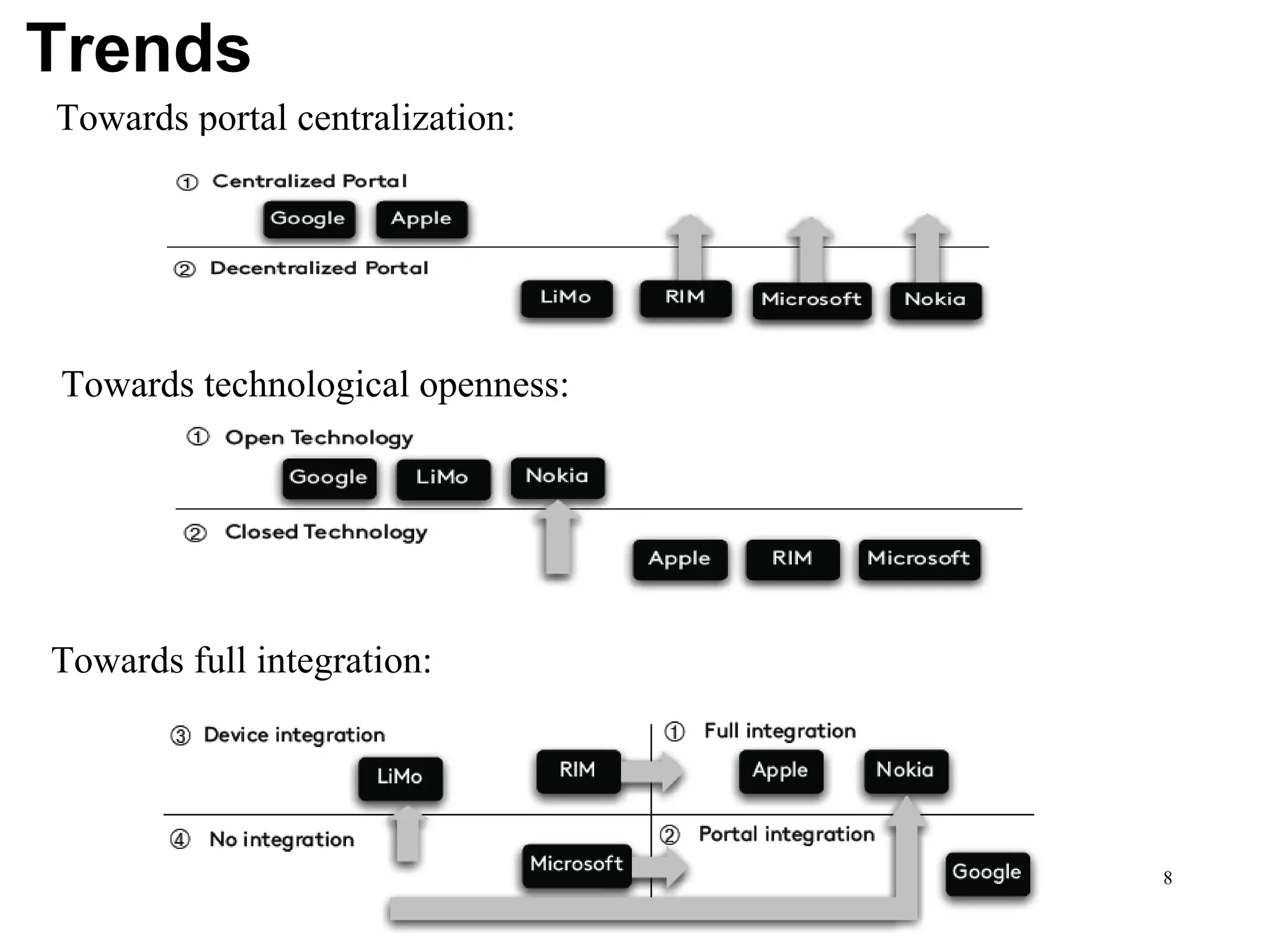
CuLogic, an offshore product development company, focuses on building innovative software products, particularly in mobile applications through its mobile innovation center, CueApps. The document discusses the evolution of mobile application development, highlighting trends like platform centralization, technological openness, and the changing roles of platform providers. It emphasizes the importance for developers to understand these trends and consider factors such as market size and career opportunities when choosing a development platform.