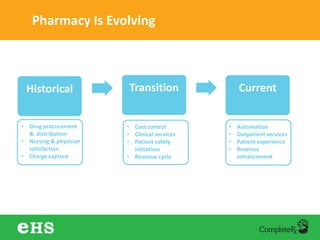
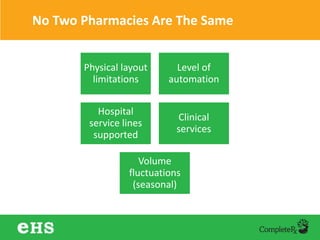
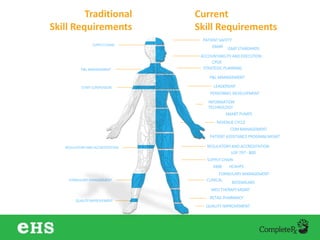
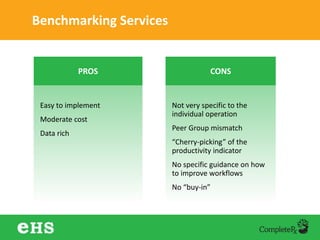
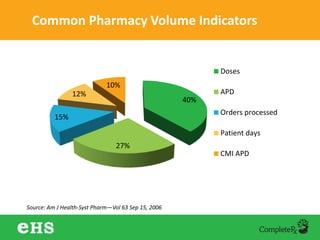
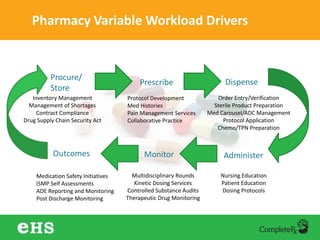
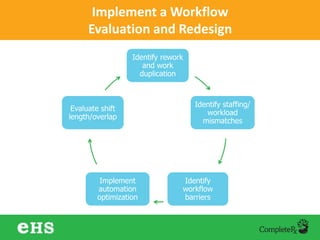
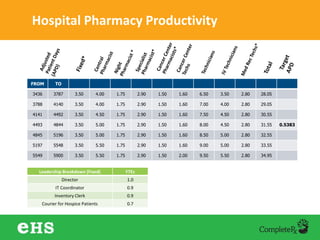
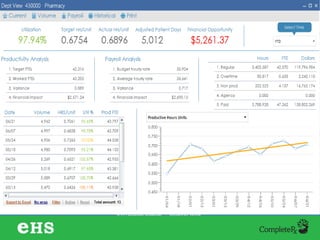
The document discusses strategies to enhance hospital pharmacy performance through effective resource management and productivity optimization. It covers various metrics, tools, and techniques that assist in reducing drug expenses, improving patient safety, and increasing the overall efficiency of pharmacy services. Key components include gap analysis, workflow redesign, and employee engagement tailored to the unique needs of each pharmacy.