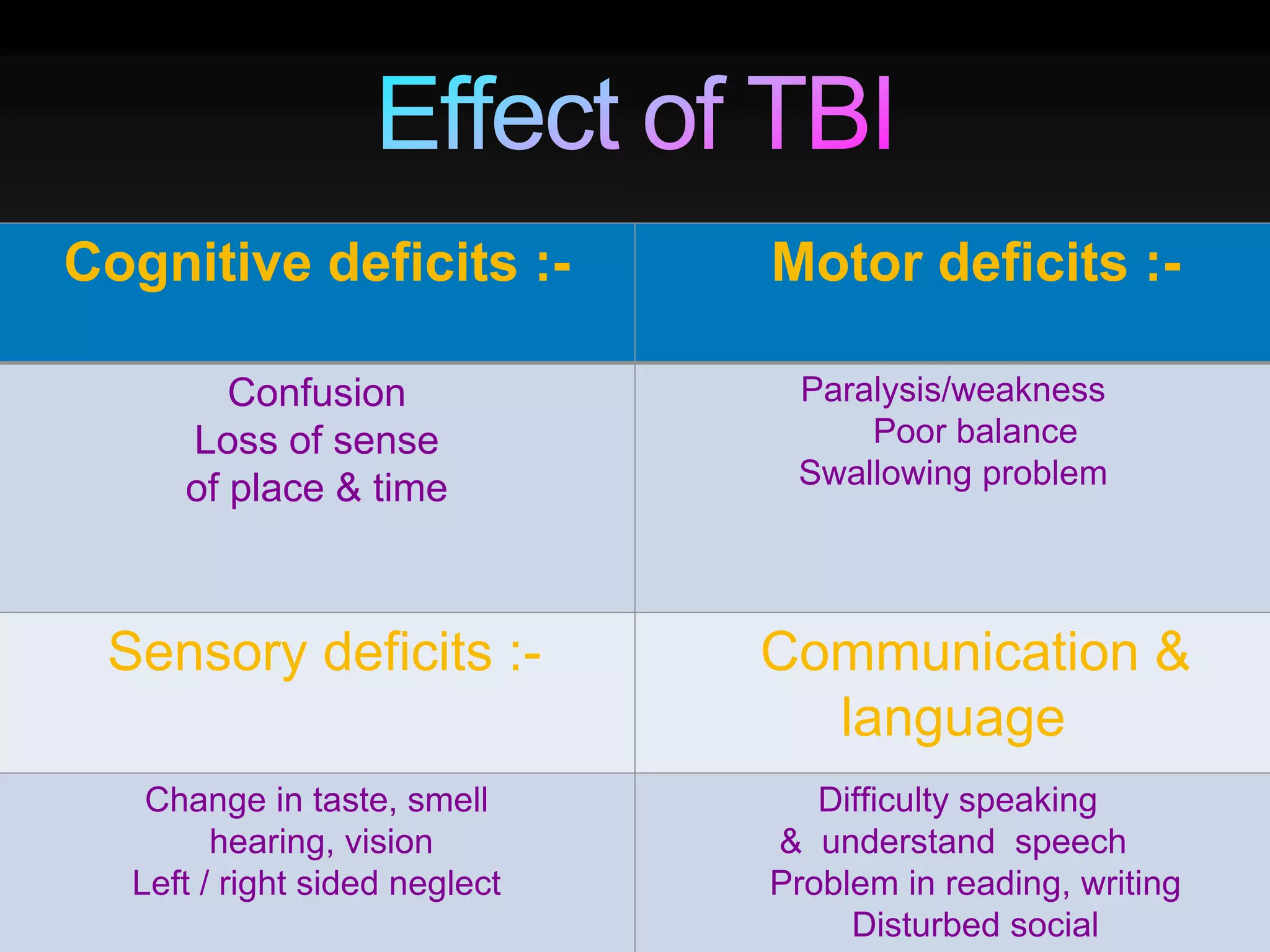
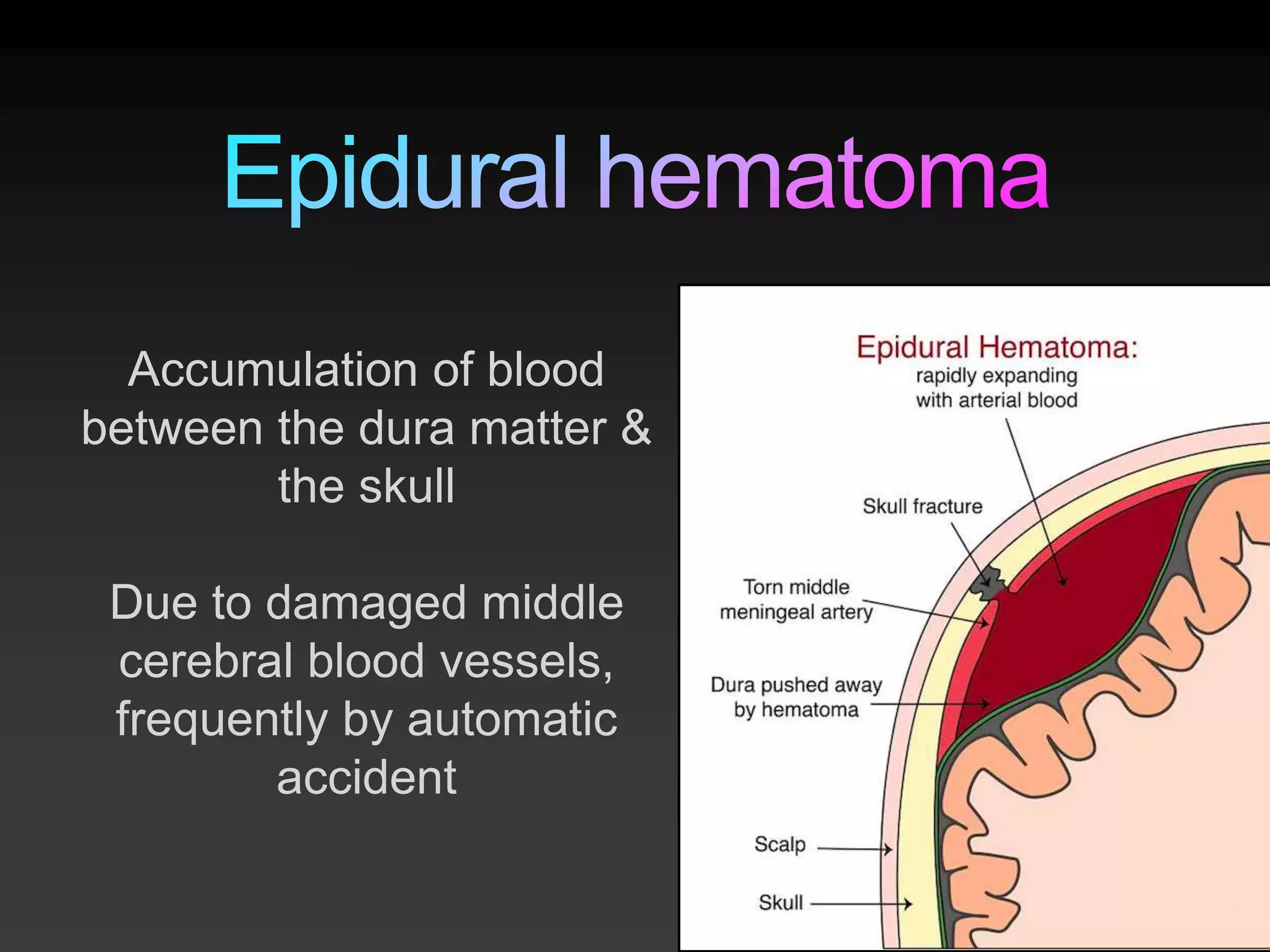
TBI is defined as a blow to the head that disrupts normal brain function. It can result from sudden violent impacts to the head or objects piercing the skull. 60% of TBIs are caused by road accidents and 15-20% involve alcohol. TBI can be penetrating or non-penetrating and cause hematomas, increased pressure in the brain, cognitive deficits, motor deficits and more. Initial assessment involves the Glasgow Coma Scale, medical history, and tests like X-rays and CT scans to evaluate functions like vision, hearing, swallowing and memory.