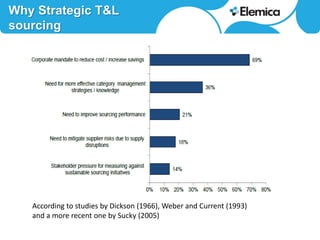
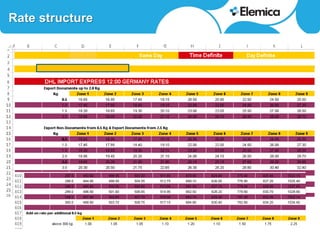
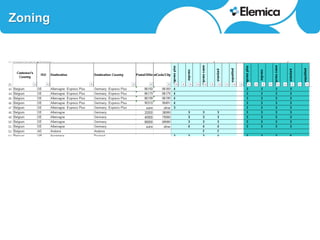
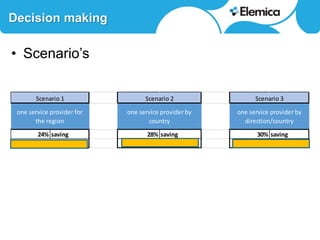
This document discusses optimizing transportation and logistics sourcing through strategic tendering. It recommends developing award scenarios upfront, knowing implementation costs, and focusing analyses on areas with the most potential gains. The best decisions balance current status with lowest cost while mitigating risks to quality, timeliness, and supply chain disruption. Historical data can provide insights into disturbances and reliability. Scenario modeling can quantify the financial impacts of objectives and constraints, like reducing carriers in a location. For small parcel shipping, the main players and their strong areas are identified. Rate structures have shifted from zones to more surcharges. Scenarios projecting 24-30% savings are presented based on consolidating carriers by region, country or direction. Reliability and