Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

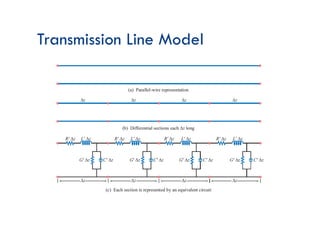
![Transmission-Line Equations
Kirchhoff Voltage Law:
Vin-Vout – VRʼ – VLʼ=0
Kirchhoff Current Law:
Iin – Iout – Icʼ – IGʼ=0
Note:
VL=L . di/dt
Ic=C . dv/dt
Remember:
2
2
|
|
;
tan
1
|
|
|
)
(
|
)
(
]
Im[
)
sin(
]
Re[
)
cos(
)
sin(
)
cos(
B
A
C
A
B
jB
A
C
e
e
z
E
z
E
Ae
A
Ae
A
Aj
A
Ae
j
j
j
j
j
z
+
=
=
→
+
=
=
=
=
=
+
=
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transmissionlinespartii-240703041326-47a27a2a/85/TransmissionLines-electrical-engineering-a-transmission-line-4-320.jpg)
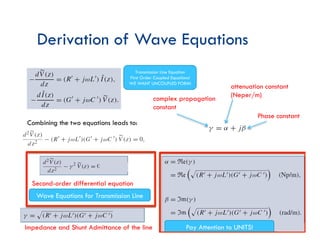
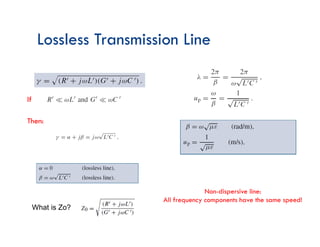
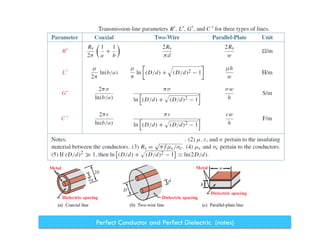
The document discusses transmission lines, focusing on the equations governing their behavior, including Kirchhoff's laws and the use of phasors for AC signals. It covers the derivation of wave equations, highlighting the attenuation and phase constants and the transition to uncoupled forms. Additionally, it mentions the characteristics of lossless and non-dispersive transmission lines.



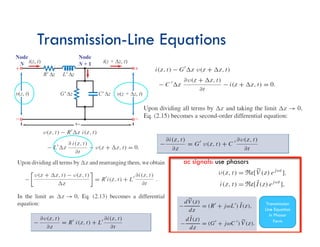
![Transmission-Line Equations
Kirchhoff Voltage Law:
Vin-Vout – VRʼ – VLʼ=0
Kirchhoff Current Law:
Iin – Iout – Icʼ – IGʼ=0
Note:
VL=L . di/dt
Ic=C . dv/dt
Remember:
2
2
|
|
;
tan
1
|
|
|
)
(
|
)
(
]
Im[
)
sin(
]
Re[
)
cos(
)
sin(
)
cos(
B
A
C
A
B
jB
A
C
e
e
z
E
z
E
Ae
A
Ae
A
Aj
A
Ae
j
j
j
j
j
z
+
=
=
→
+
=
=
=
=
=
+
=
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transmissionlinespartii-240703041326-47a27a2a/85/TransmissionLines-electrical-engineering-a-transmission-line-4-320.jpg)


