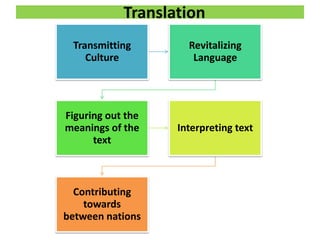
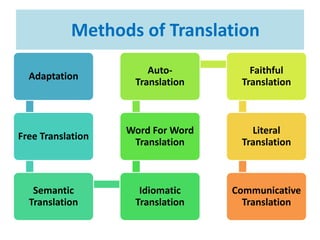
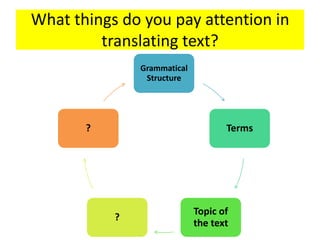
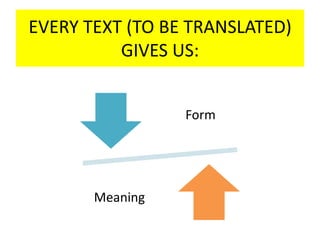
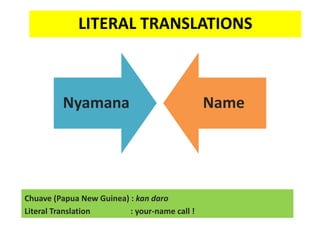
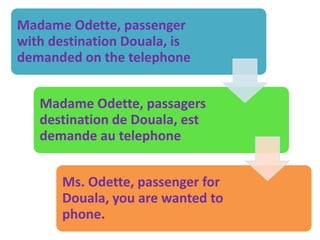
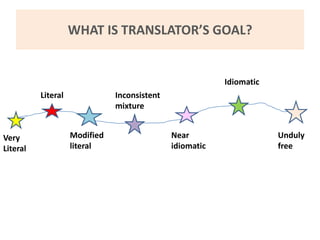
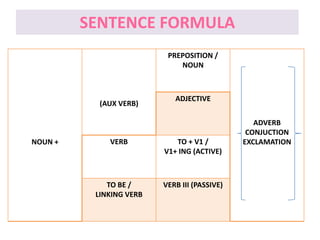
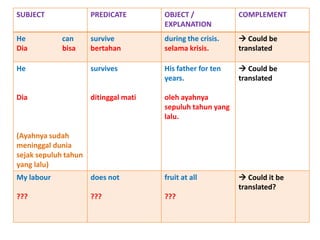
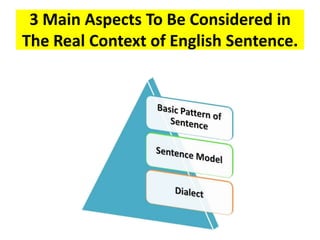
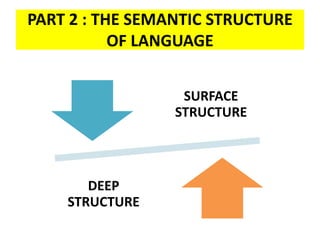
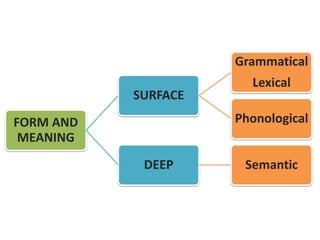
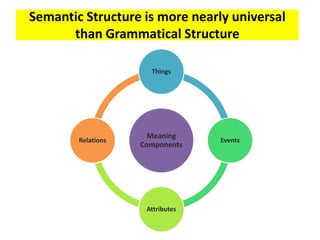
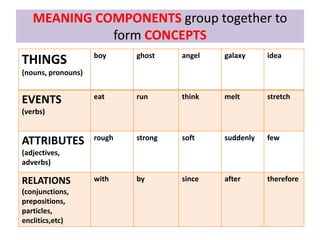
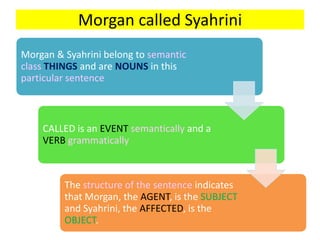
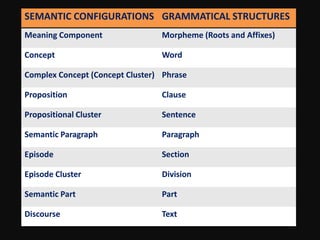
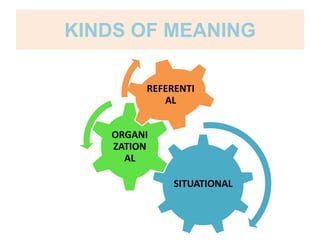
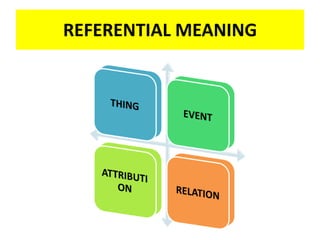
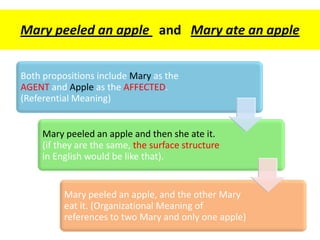
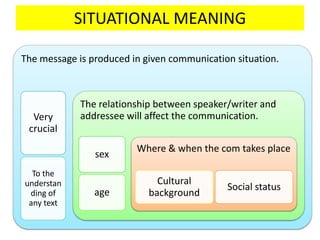
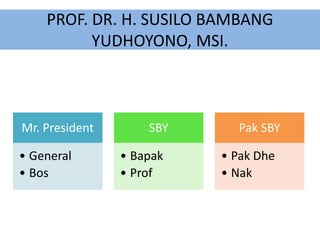
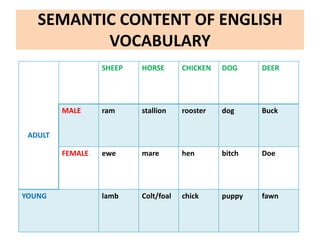
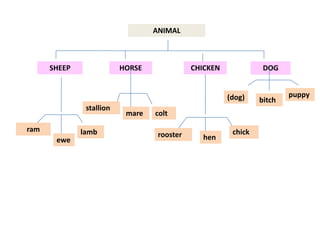
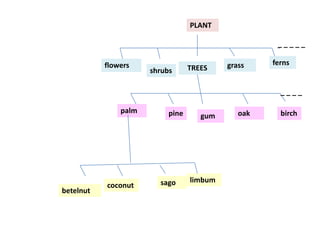
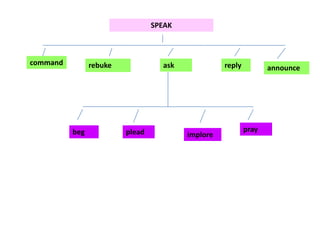
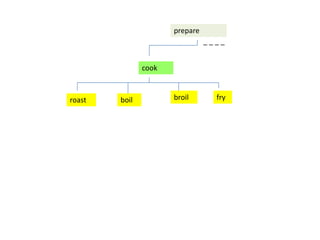
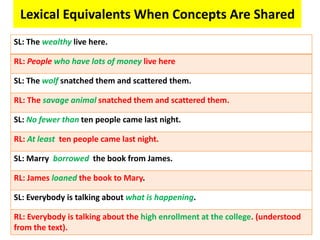
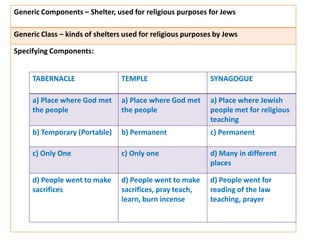
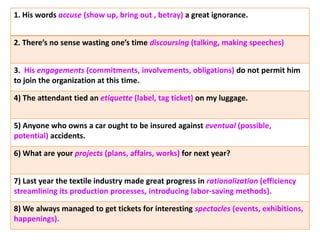
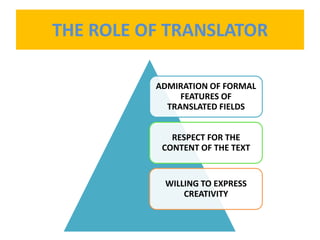
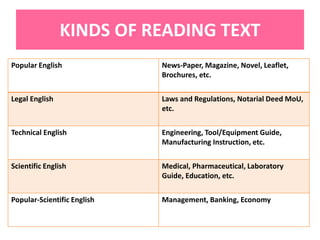
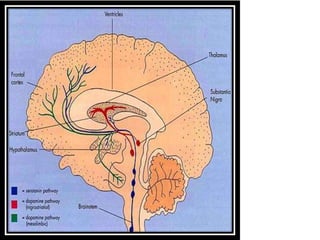
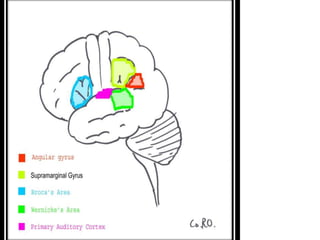
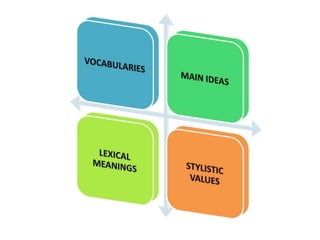
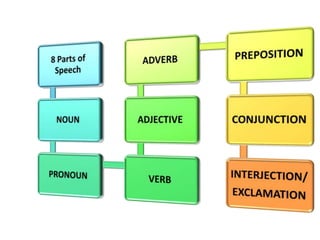
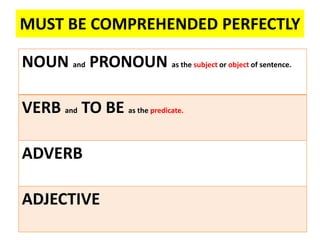
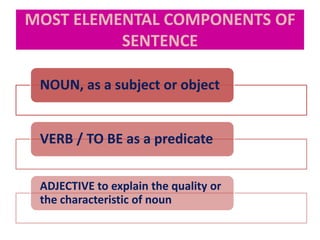
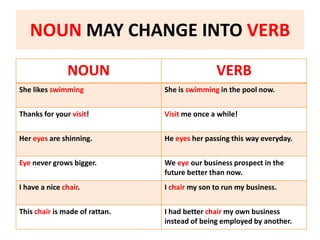
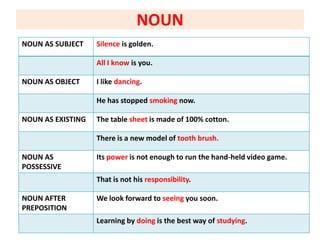
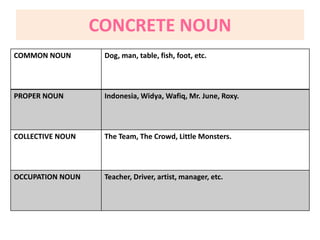
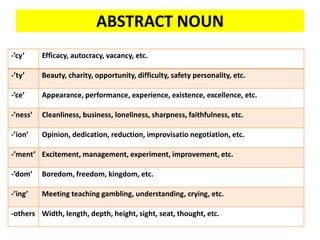
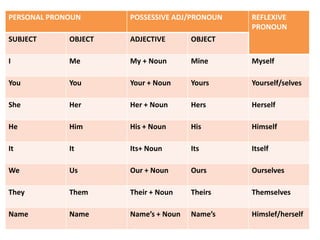
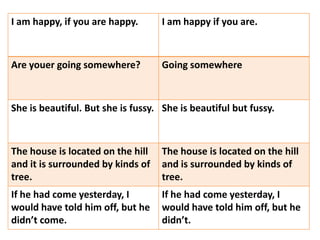
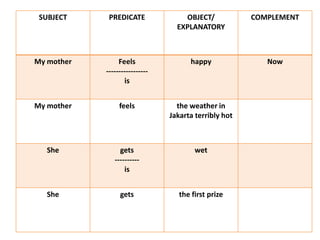
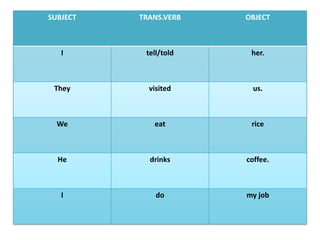
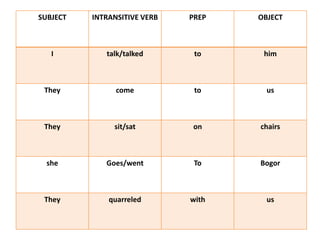
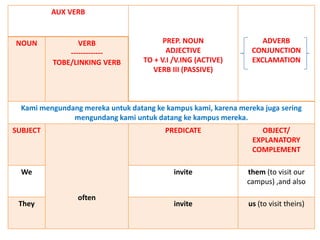
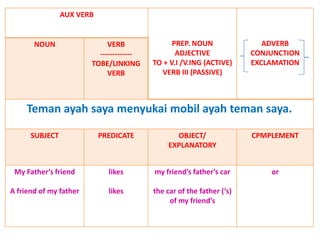
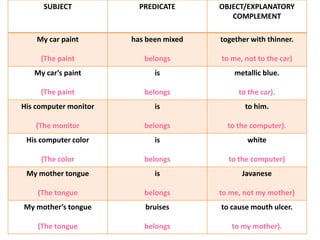
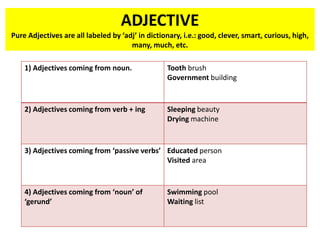
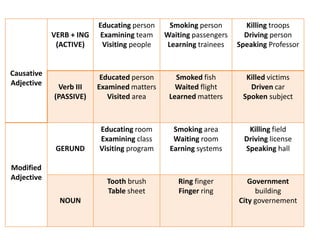
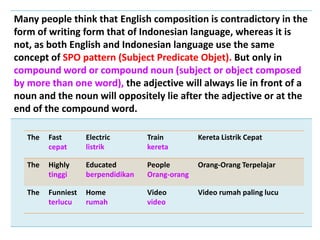
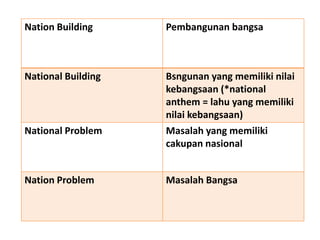
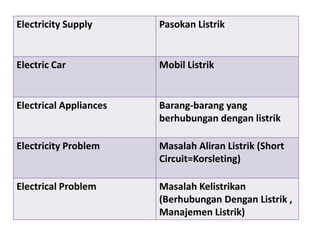
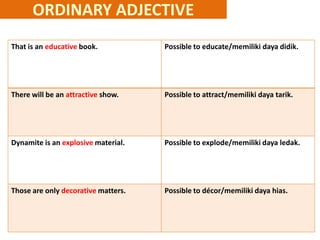
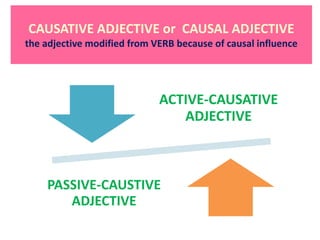
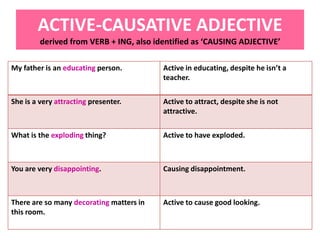
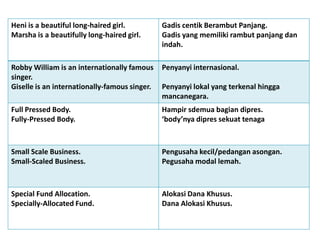
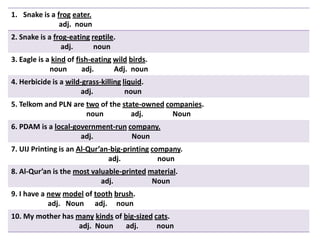
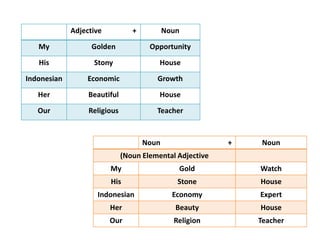
This document discusses translation and the translator's role. It begins by explaining that translation involves transmitting culture, revitalizing language, and interpreting texts between nations. There are various methods of translation including adaptation, free translation, semantic translation, and more. When translating a text, the translator must pay attention to grammatical structure, terms, and the topic. Every text provides form and meaning that influence translation approaches. The translator's goal should be to communicate the same message in the target language using natural grammar and lexicon. Understanding both the referential and situational meaning of a text is important for accurate translation.