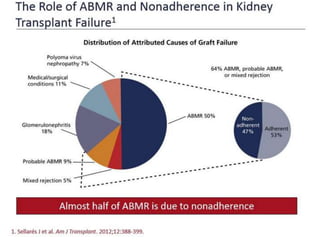
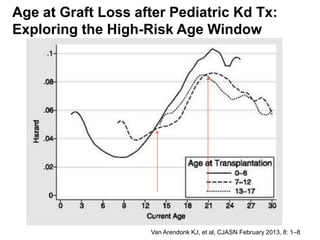
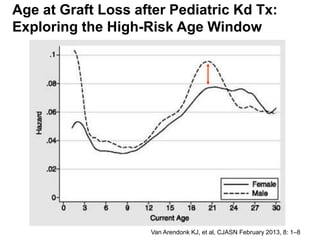
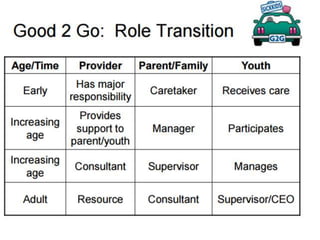
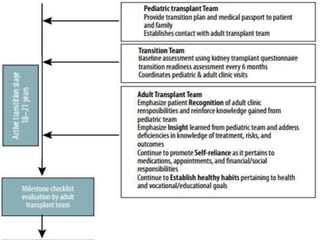
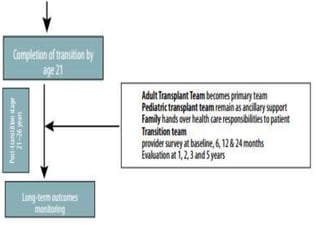
This document discusses the transition of pediatric renal transplant recipients to adult care. It notes that while pediatric patients are different and pediatric hospitals are not meant for adults, patients must eventually transition to adult services. However, an unplanned transition can be problematic. The document recommends a phased transition process beginning in the teen years that addresses medical, psychosocial and educational needs through a dedicated transition clinic involving both pediatric and adult teams to ensure continuous care and support during the vulnerable transition period.