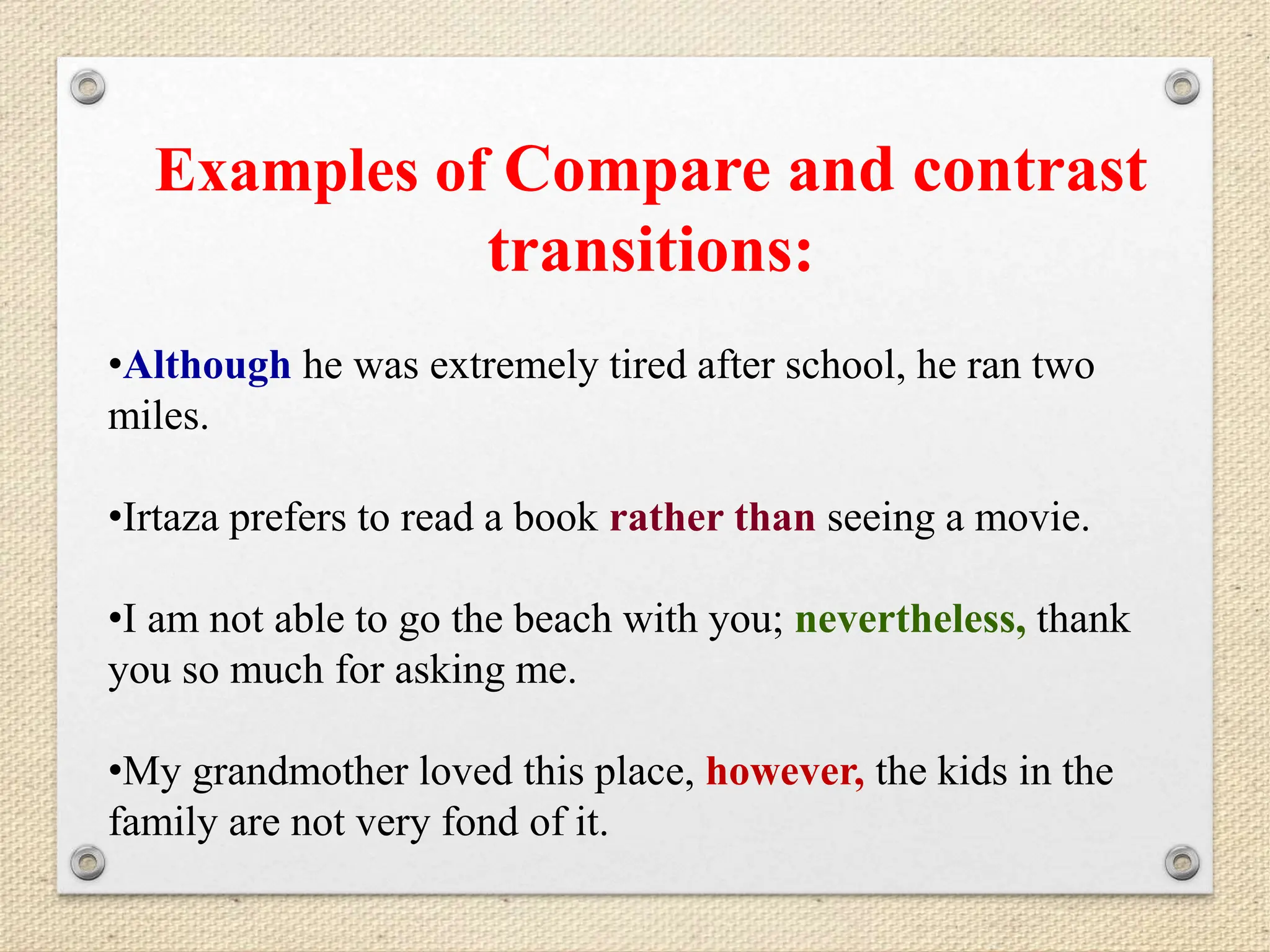
Transition words and phrases help provide coherence and flow in writing. They signal connections between ideas for the reader and move smoothly between subjects. Different types of transitions include those showing time and location, continuing ideas, comparing and contrasting, and adding or concluding information. Using a variety of transitions helps writing sound natural instead of choppy.