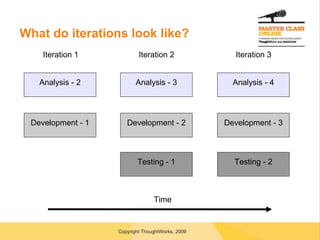
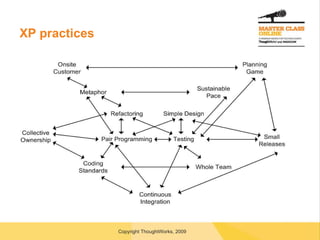
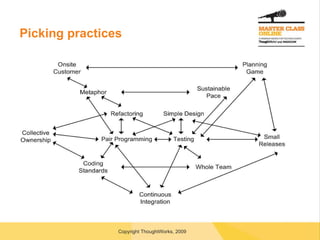
The document discusses transitioning to agile software development, highlighting key concepts such as incremental and iterative processes, collaboration, and the importance of defined roles within agile teams. It stresses the need for executive commitment, careful planning, and the potential cultural impacts when adopting agile practices. Various roles in agile teams, along with practices for managers, developers, and testers, are outlined, emphasizing the necessity for team involvement and continuous integration.

![Transitioning to Agile Vivek Prahlad, ThoughtWorks [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transitiontoagile-091127020851-phpapp02/85/Transitioning-To-Agile-2-320.jpg)






































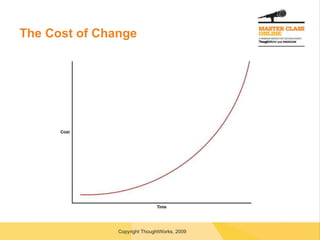
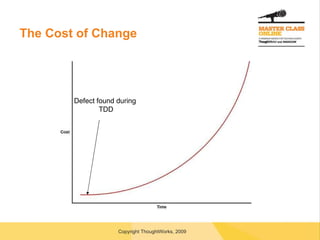
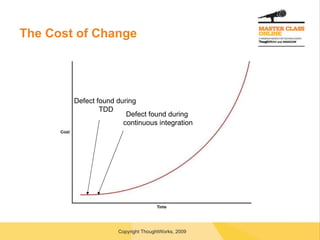
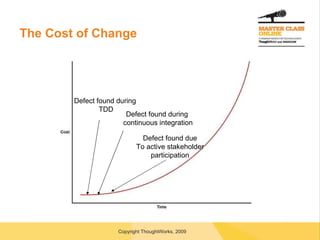







![Questions? [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transitiontoagile-091127020851-phpapp02/85/Transitioning-To-Agile-56-320.jpg)
![All responses to questions will be posted at http://thoughtworker.com/masterclass To know more about our events and up coming webinars please visit www.thoughtworker.com/events To get in touch with us, please email us at [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transitiontoagile-091127020851-phpapp02/85/Transitioning-To-Agile-57-320.jpg)