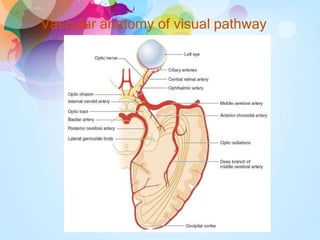
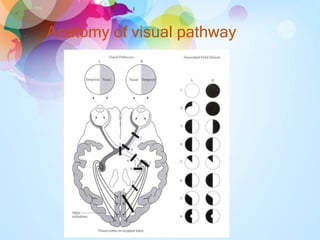
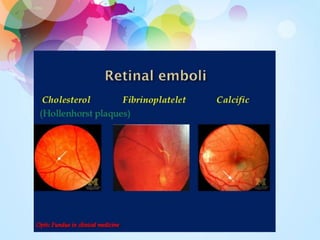
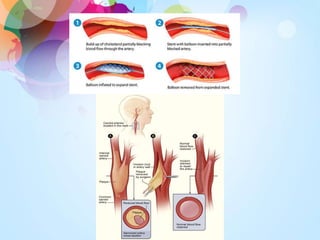
Transient visual loss (TVL) is a sudden loss of vision that can be either partial or complete and typically lasts less than 24 hours, primarily caused by retinal ischemia. It is essential to understand the different causes, including ocular pathology, vascular diseases, and optic nerve disorders, and to carefully evaluate patients to determine the underlying issues. Treatment varies based on the cause and may require a collaborative approach among ophthalmologists, internists, and neurologists.