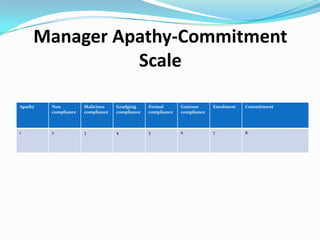
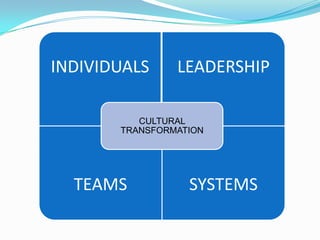
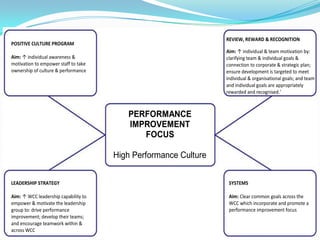
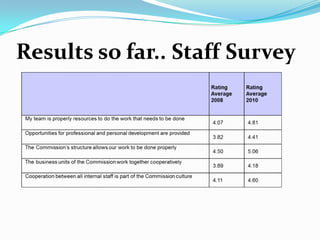
This document summarizes Lorraine Salloum's presentation on the cultural transformation efforts at the NSW Workers Compensation Commission. The Commission implemented a bottom-up cultural transformation strategy involving staff surveys, defining a cultural agenda, and establishing change champion groups. Key initiatives included a positive culture program, leadership development, and integrating cultural goals into performance management. Initial results showed improvements in staff understanding of values and opportunities. Lessons learned included the time required for bottom-up change and balancing top-down and bottom-up approaches.