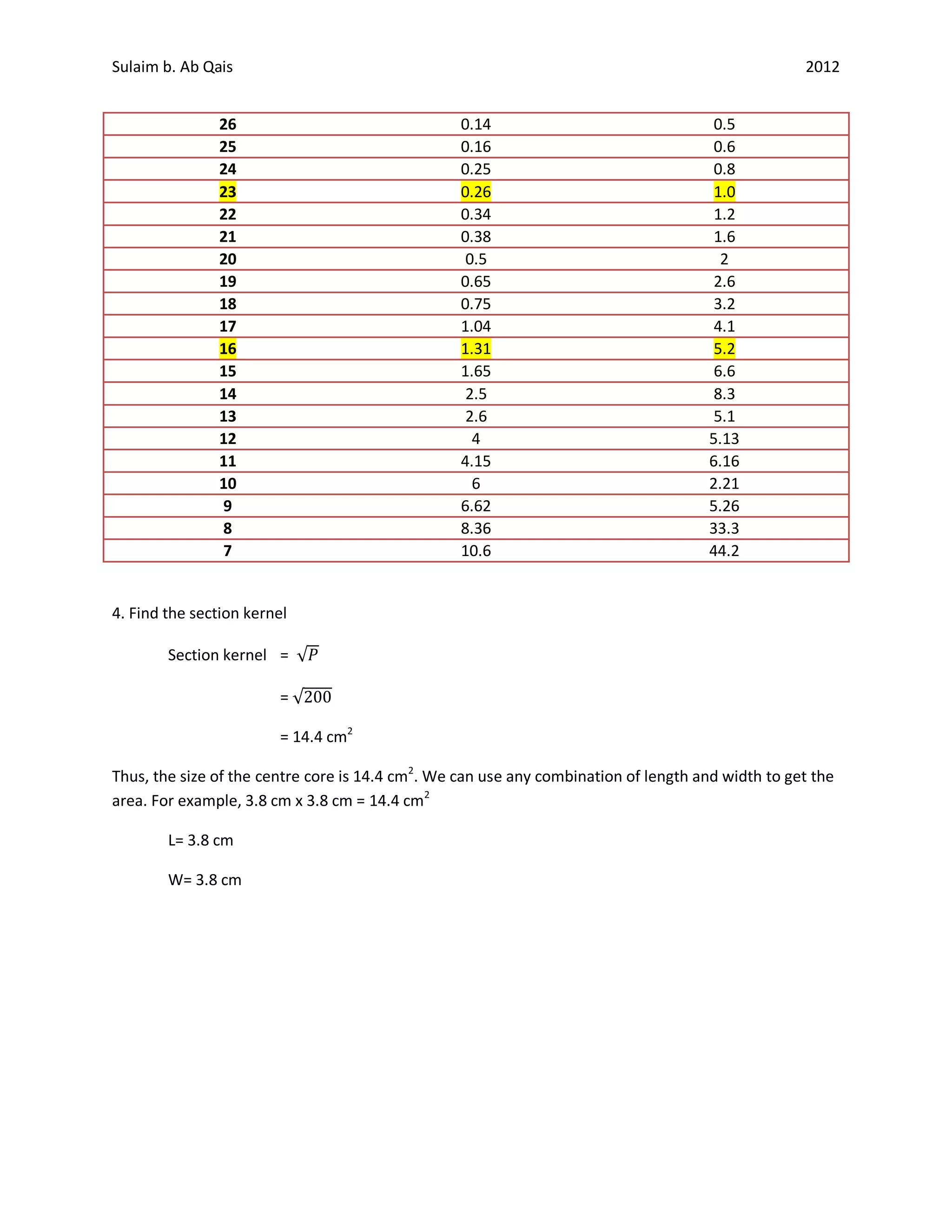
This document provides a guide for designing a simple transformer with step-by-step calculations. It outlines determining the load power and primary/secondary currents based on the voltage. Wire gauges are selected based on current capacities. The core size is calculated based on the power. Finally, the number of turns for the primary and secondary windings are calculated based on the core size and voltages. Key materials include copper wire, silicon-iron sheets, and insulation to prevent short circuits between windings.