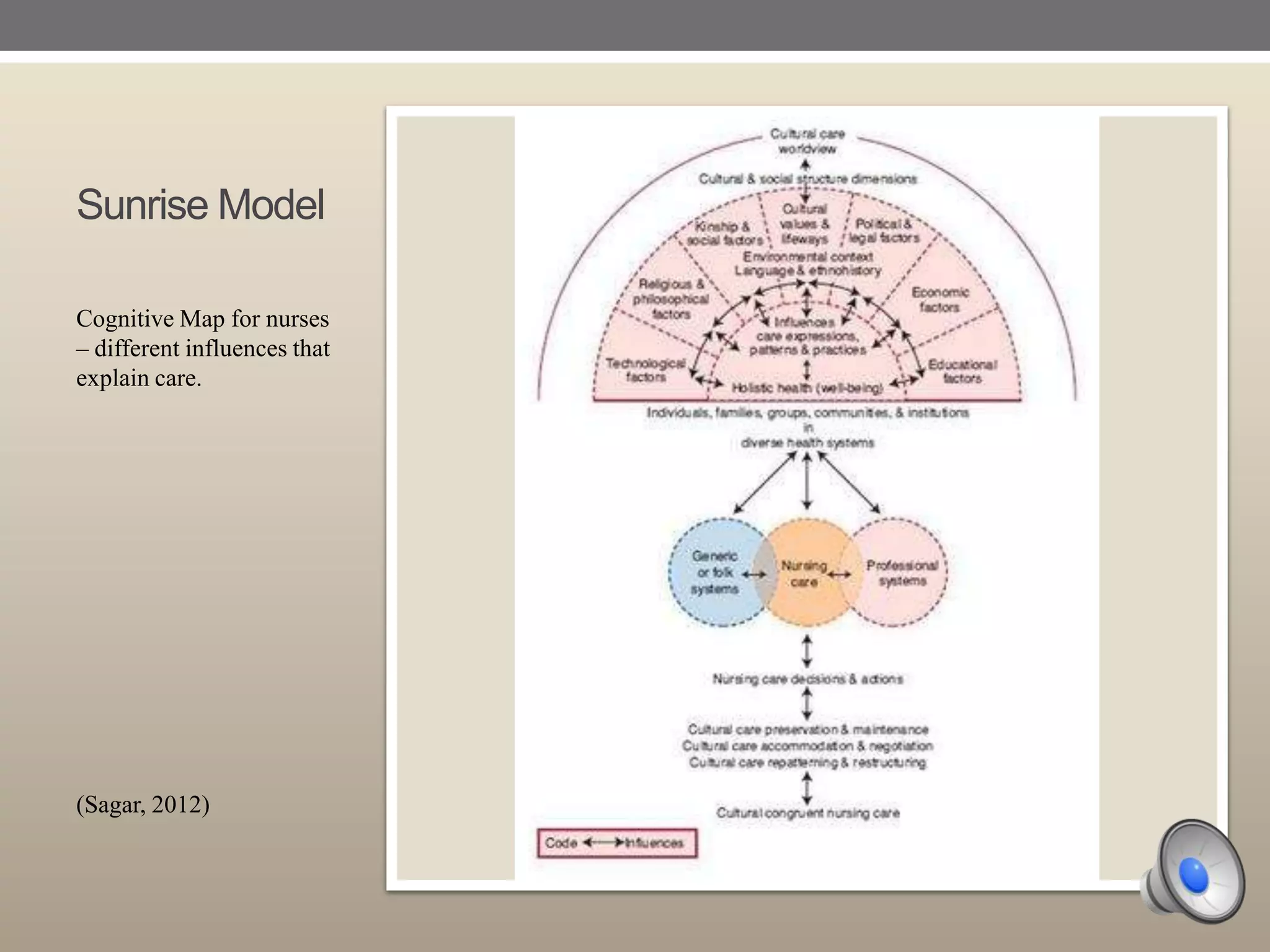
The document provides a biography and overview of Madeleine Leininger's Theory of Transcultural Nursing. Some key points:
- Leininger observed differences in patient behaviors from diverse cultures and questioned how culture impacts care. This led her to establish the theory of culture care.
- The theory is based on the assumptions that care is essential to health and culture influences all aspects of life, including views of health and illness.
- Leininger developed the Sunrise Model and three care modalities to guide culturally congruent nursing care: preservation, accommodation, and repatterning.
- The goal of the theory is for nurses to incorporate a patient's cultural beliefs, values and preferences