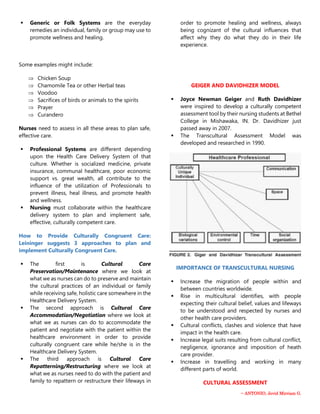
This document provides information on transcultural nursing concepts and models. It discusses Madeleine Leininger's theory of transcultural nursing, which introduced the concepts of cultural care preservation, accommodation, and repatterning. It also describes Joyce Geiger and Ruth Davidhizer's transcultural assessment model, which identifies six cultural phenomena to assess: communication, space, social organization, time, environmental control, and biological variations. Finally, it examines cultural values and care meanings and actions for several cultures including Anglo-American, Mexican American, Haitian American, African American, and North American Indian cultures.