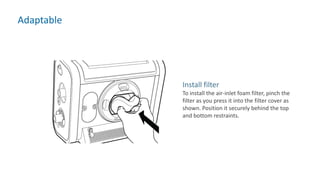
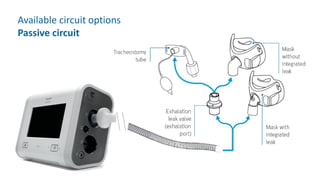
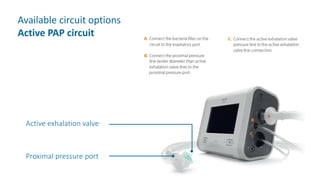
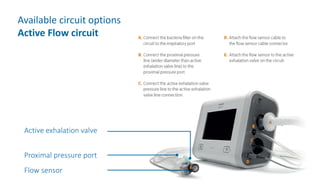
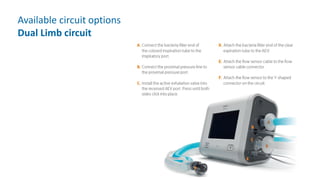
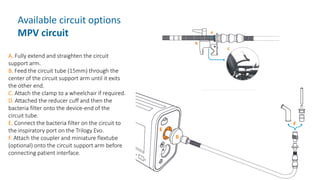
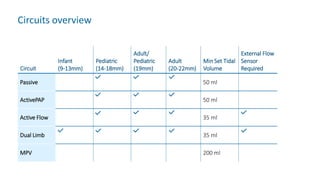
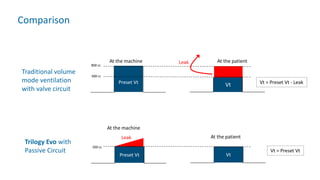
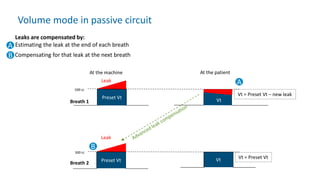
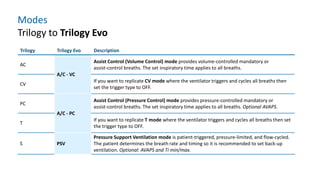
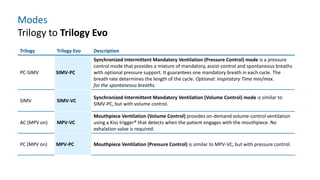
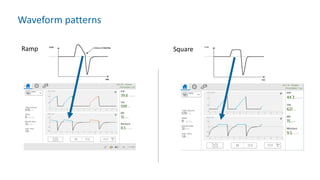
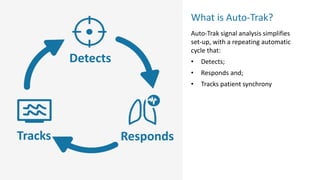
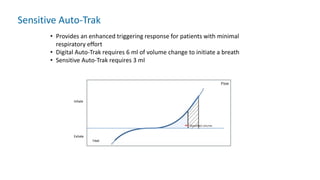
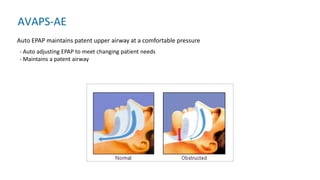
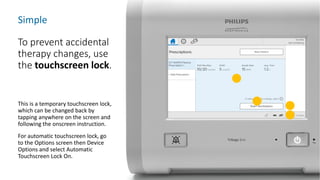
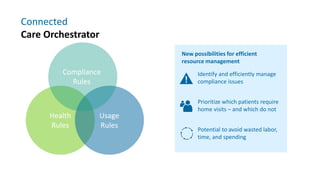
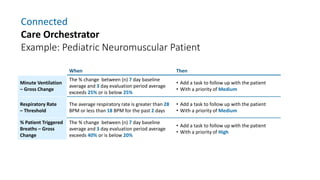
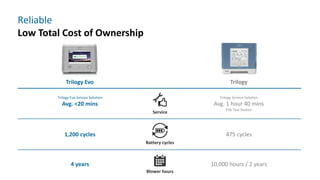
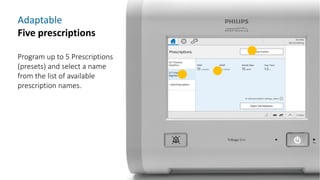
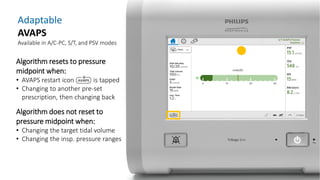
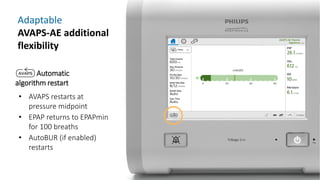
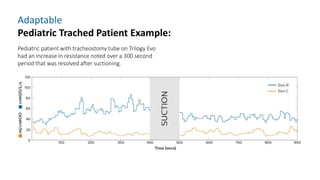
The document provides information about a home ventilation workshop that will cover various topics related to the Trilogy Evo ventilator, including circuit options, ventilation modes, alarms, features, and troubleshooting. Specifically, it will review the mouthpiece ventilation mode, AVAPS-AE mode, and dynamic parameters. The Trilogy Evo is a portable ventilator suitable for both institutional and home use that can provide invasive and non-invasive positive pressure ventilation for patients ranging from infants to adults. It has rechargeable batteries, a large touchscreen, and can integrate with accessories to monitor patients' oxygen, carbon dioxide, respiratory rate, and pulse rate.