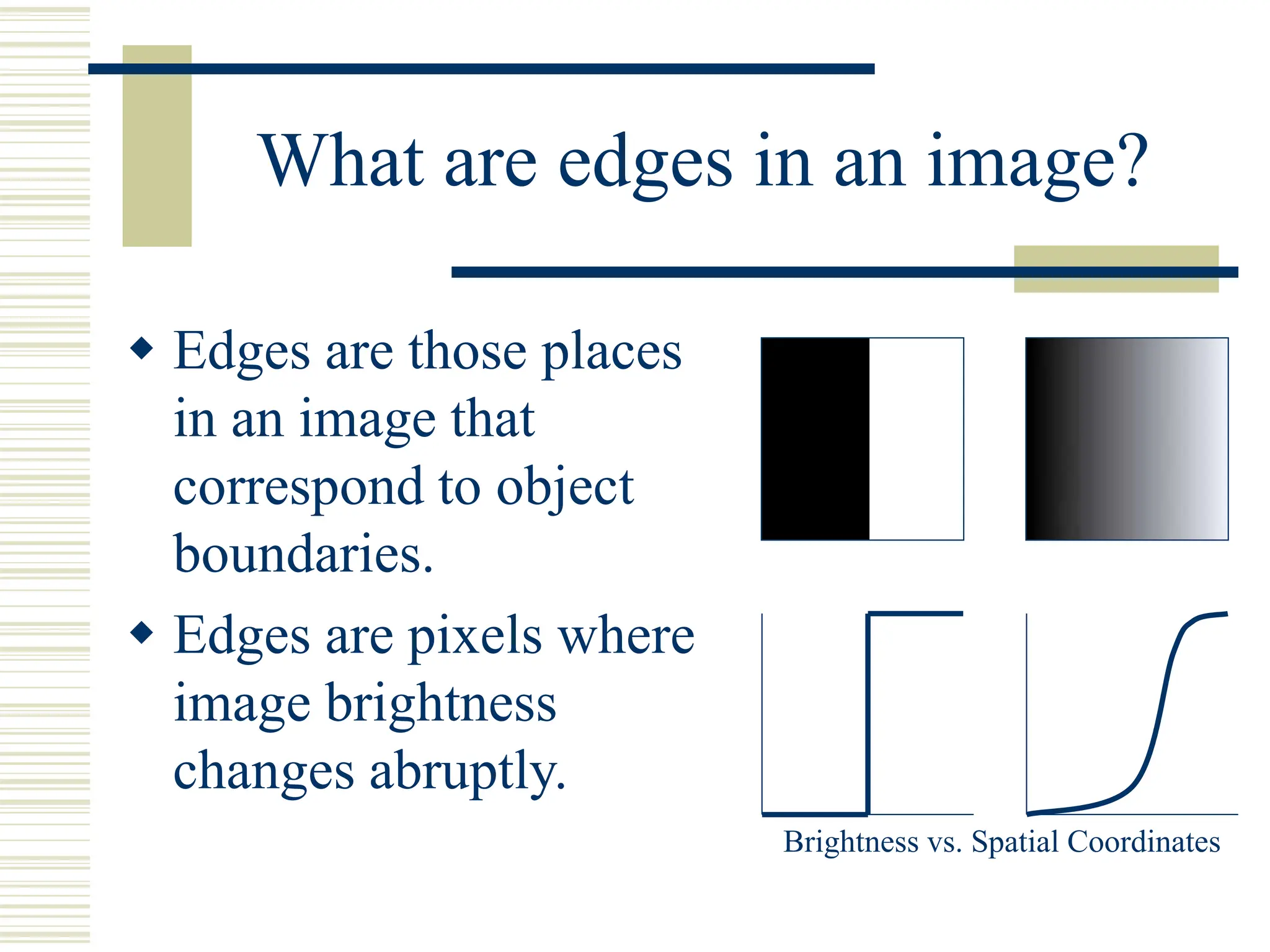
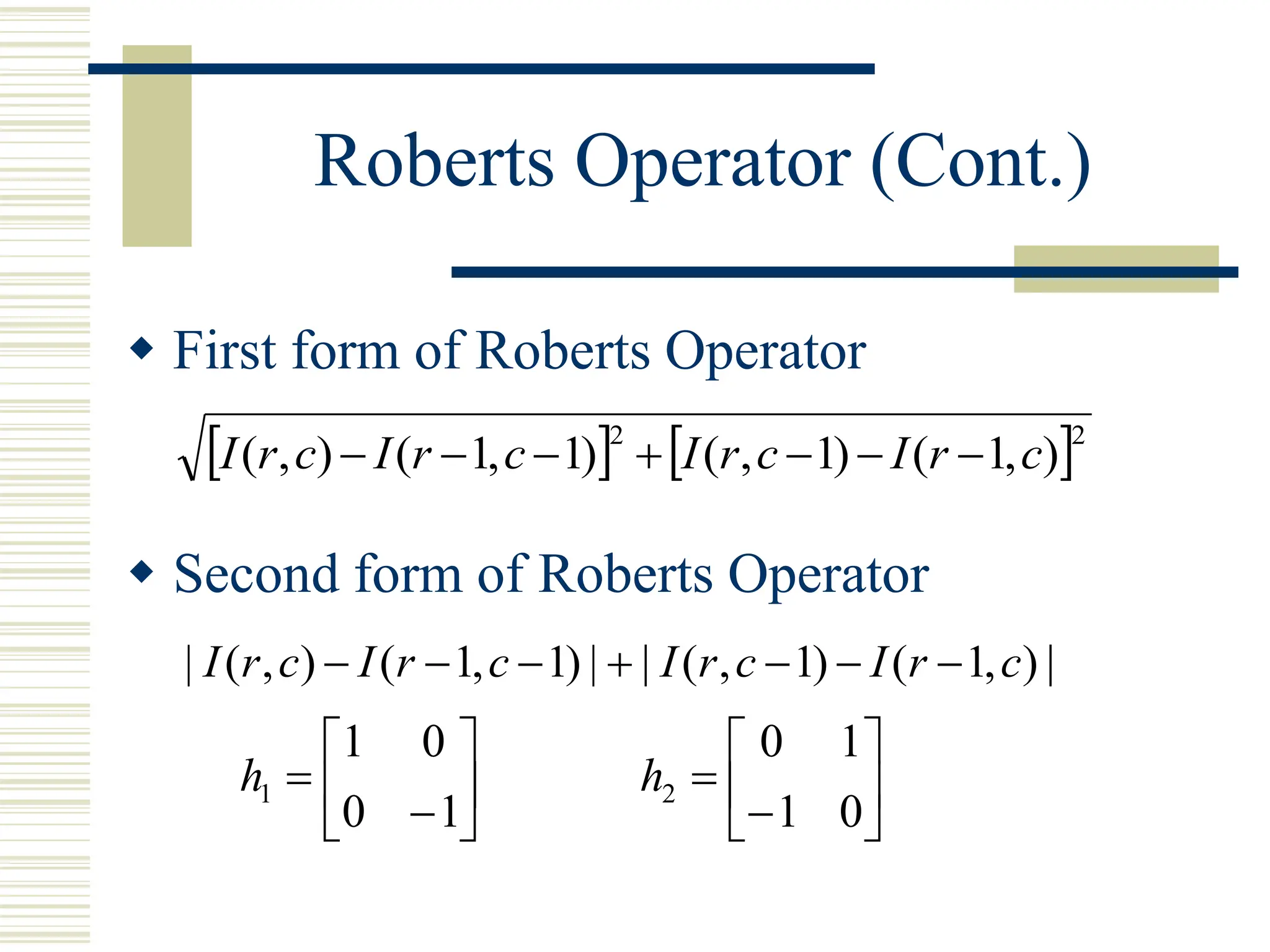
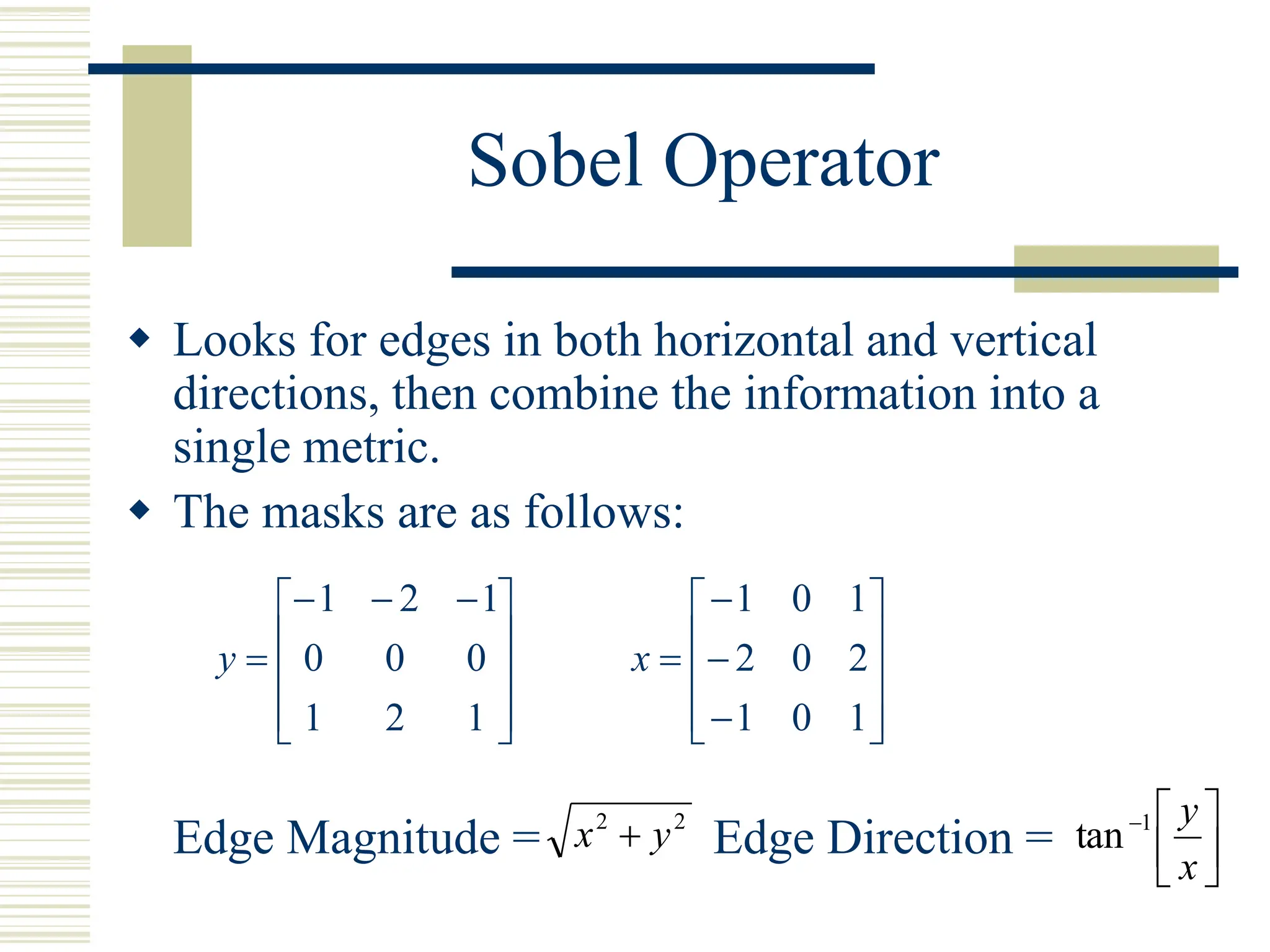
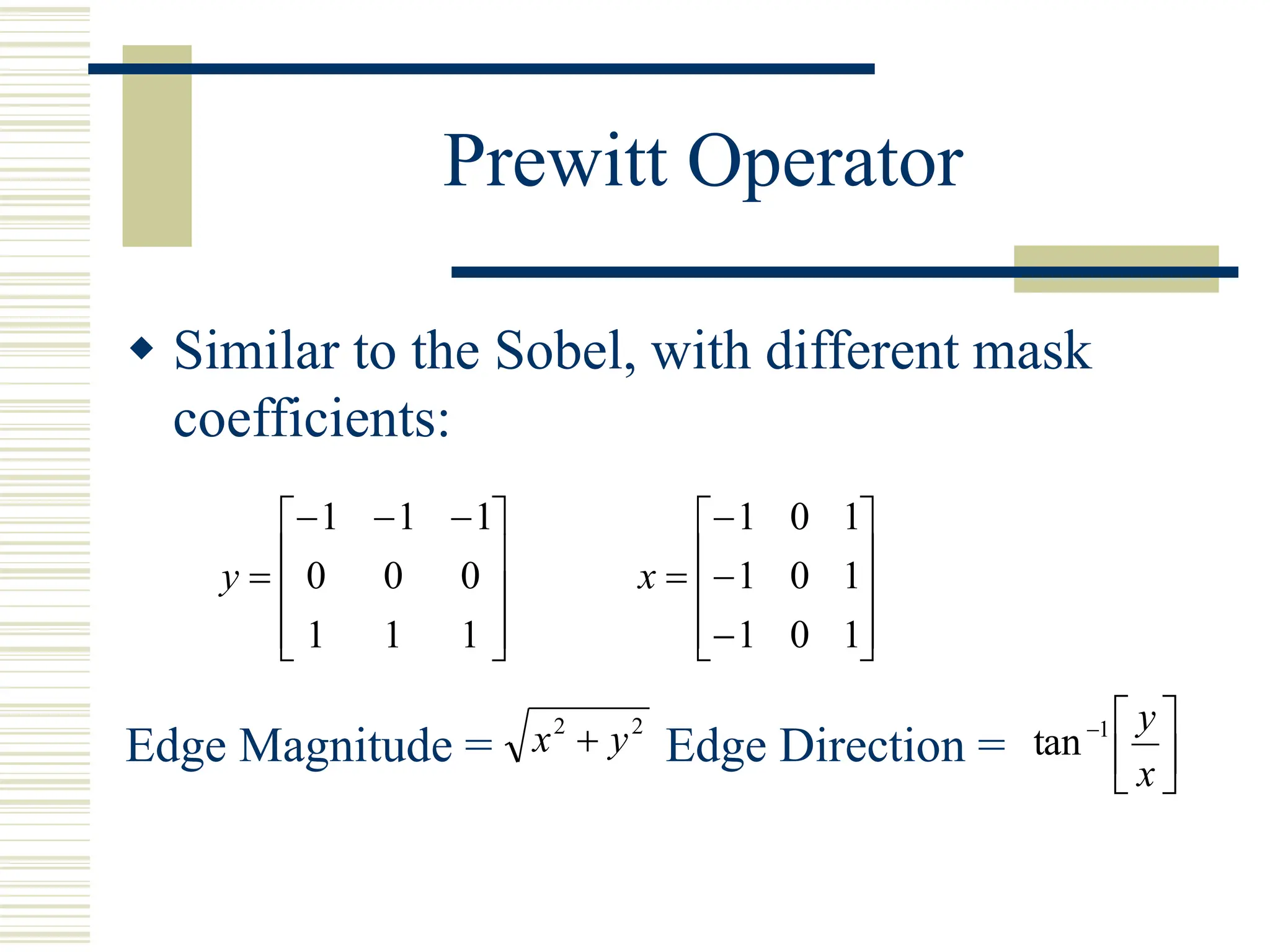
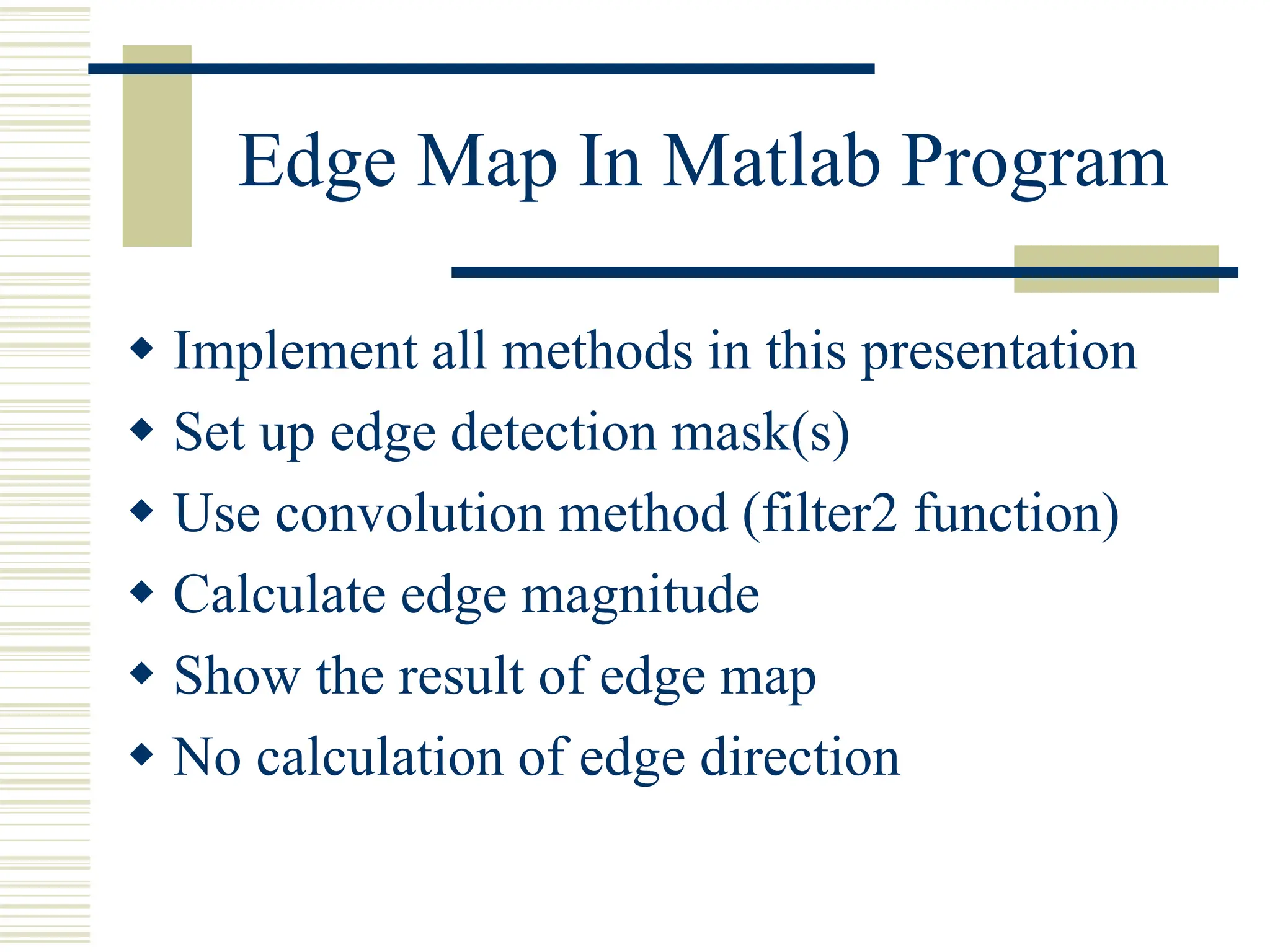
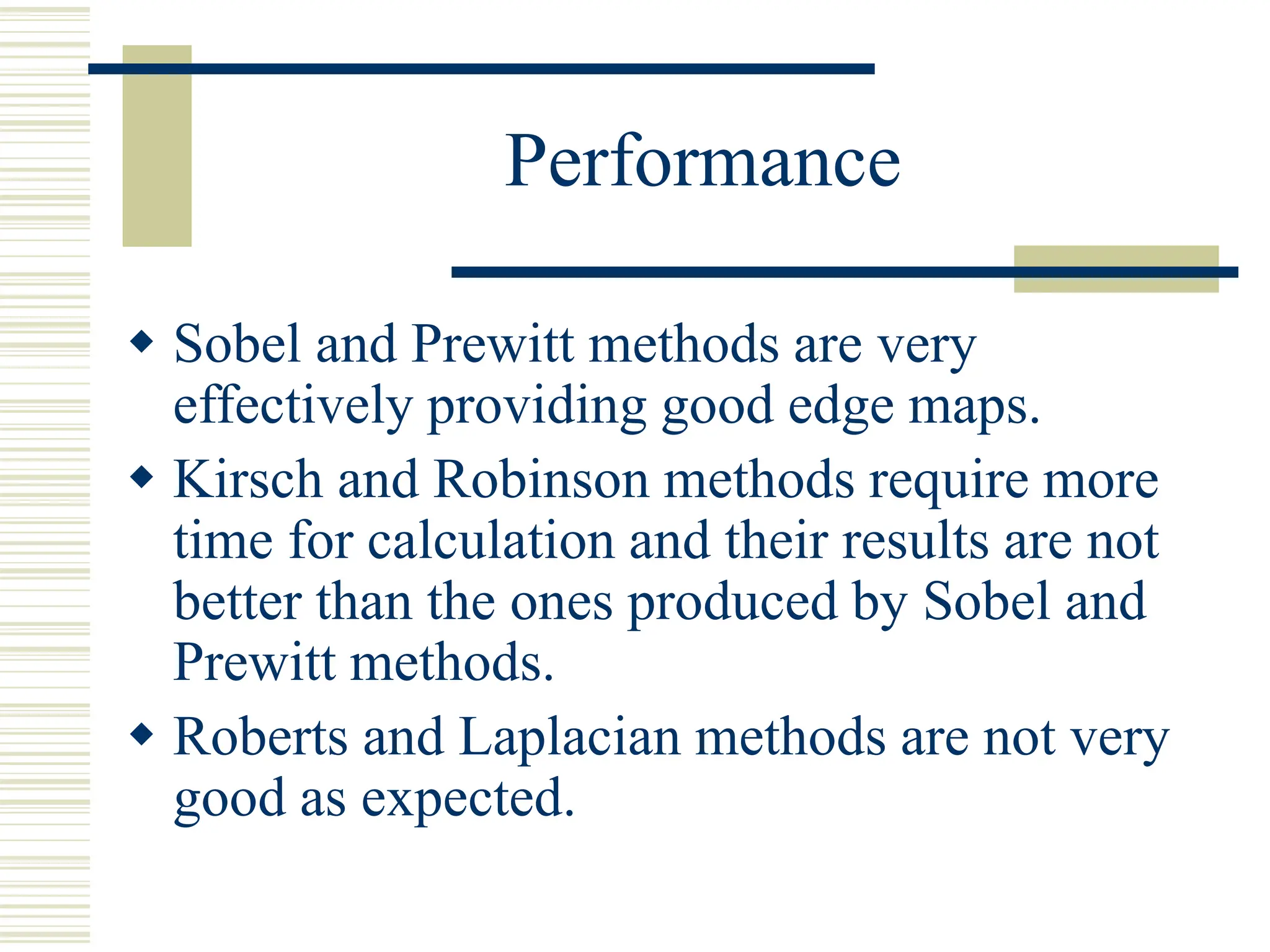
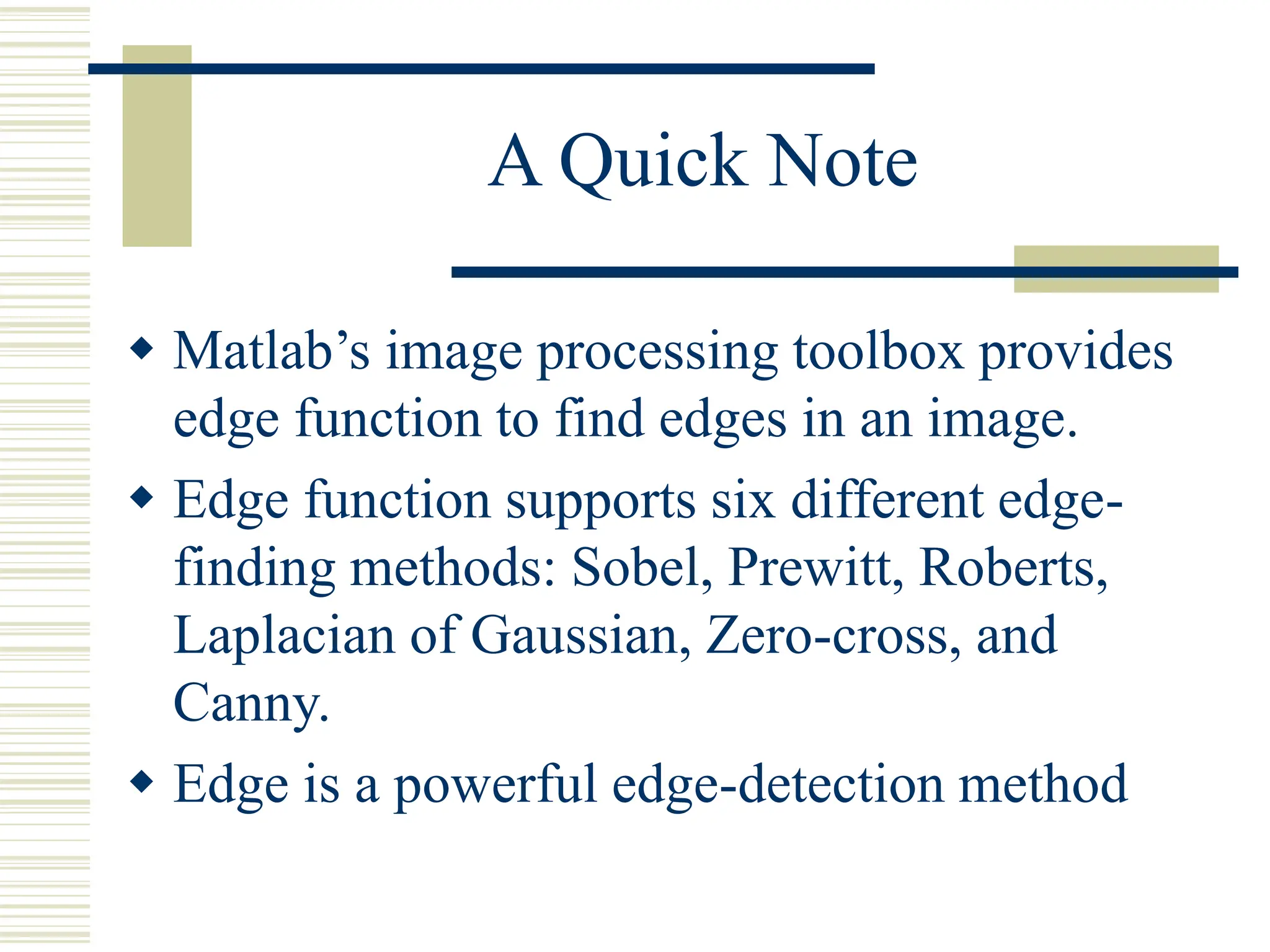
This document discusses various methods for edge detection in images. It describes what edges are and different edge detection approaches, including Roberts, Sobel, Prewitt, Kirsch, Robinson, and Laplacian operators. It also mentions implementing the methods in Matlab using convolution and filtering functions to produce edge maps and compares the performance of the different techniques.