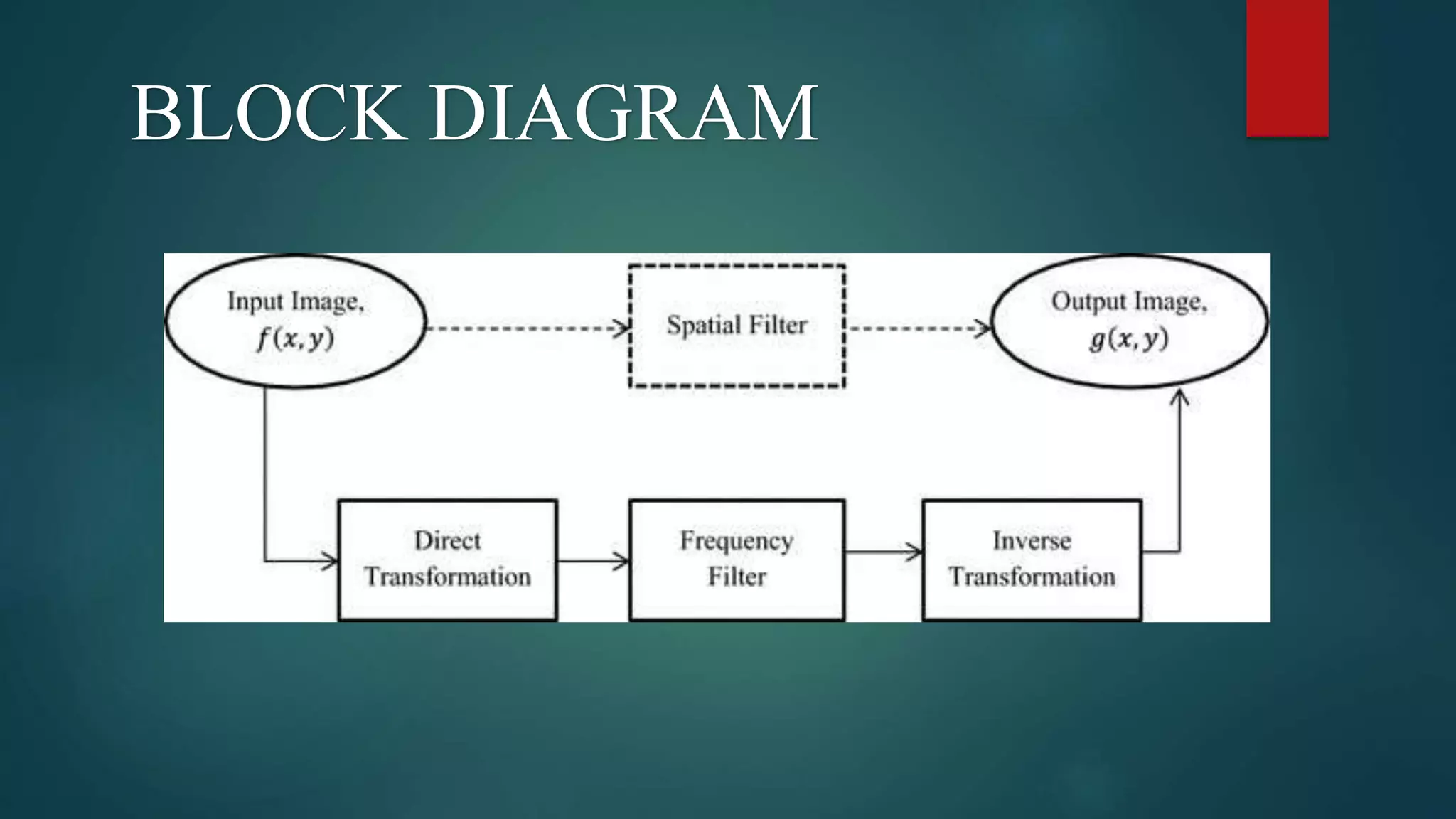
This document summarizes edge detection using the Sobel operator. It begins by defining edges as areas of significant intensity change between objects in an image. There are three main steps to edge detection: image smoothing to remove noise; edge point detection to identify areas of intensity change; and edge localization to precisely locate the edges. The document then explains how the Sobel operator uses two 3x3 kernels to detect horizontal and vertical edges by approximating the image gradient. It provides code to demonstrate Sobel edge detection in MATLAB. The advantages of the Sobel operator are its simplicity and ability to detect edges and their orientations.