This document discusses training and provides details on:
1. It defines training as teaching skills and knowledge to improve capability, productivity, and performance.
2. It lists the importance of training as responding to technology, organizational changes, workforce diversity, and career development.
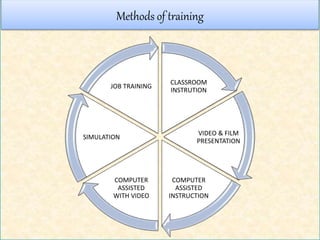
3. It describes different types of training including skills training, retraining, cross-functional training, creativity training, and diversity training.