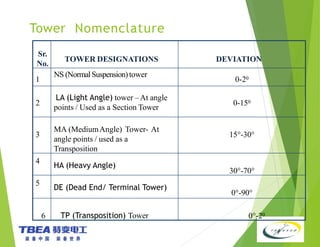
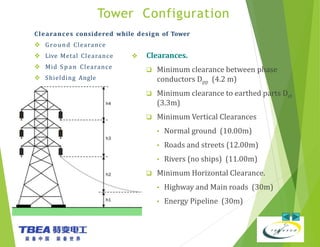
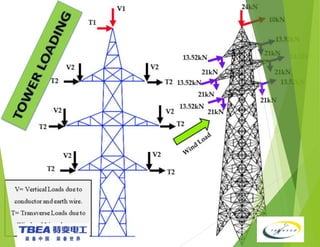
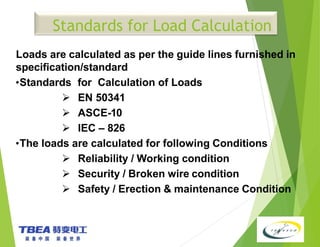
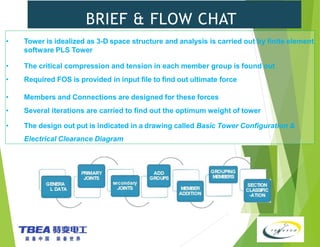
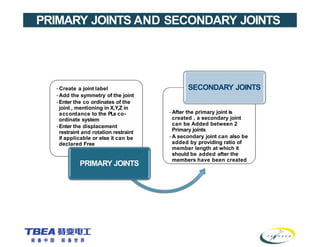
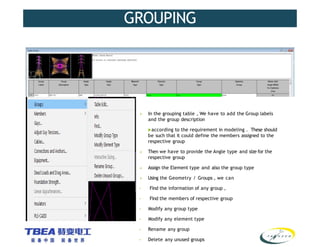
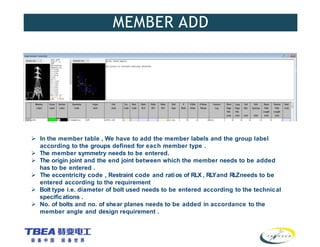
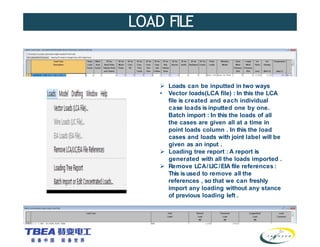
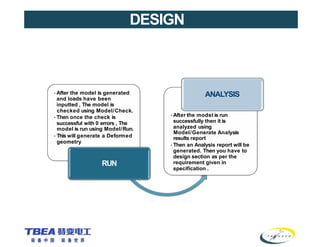
The document details the technical specifications for the construction of a 136 km long, 400 kV double circuit transmission line from Chalinze to Mkuranga in Tanzania, utilizing advanced tower design methodologies. It outlines design requirements such as voltage ratings, environmental considerations, tower components, and loading analysis necessary for the successful erection of the transmission line infrastructure. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of adhering to specific standards and calculations to ensure safe and reliable operation under various conditions.