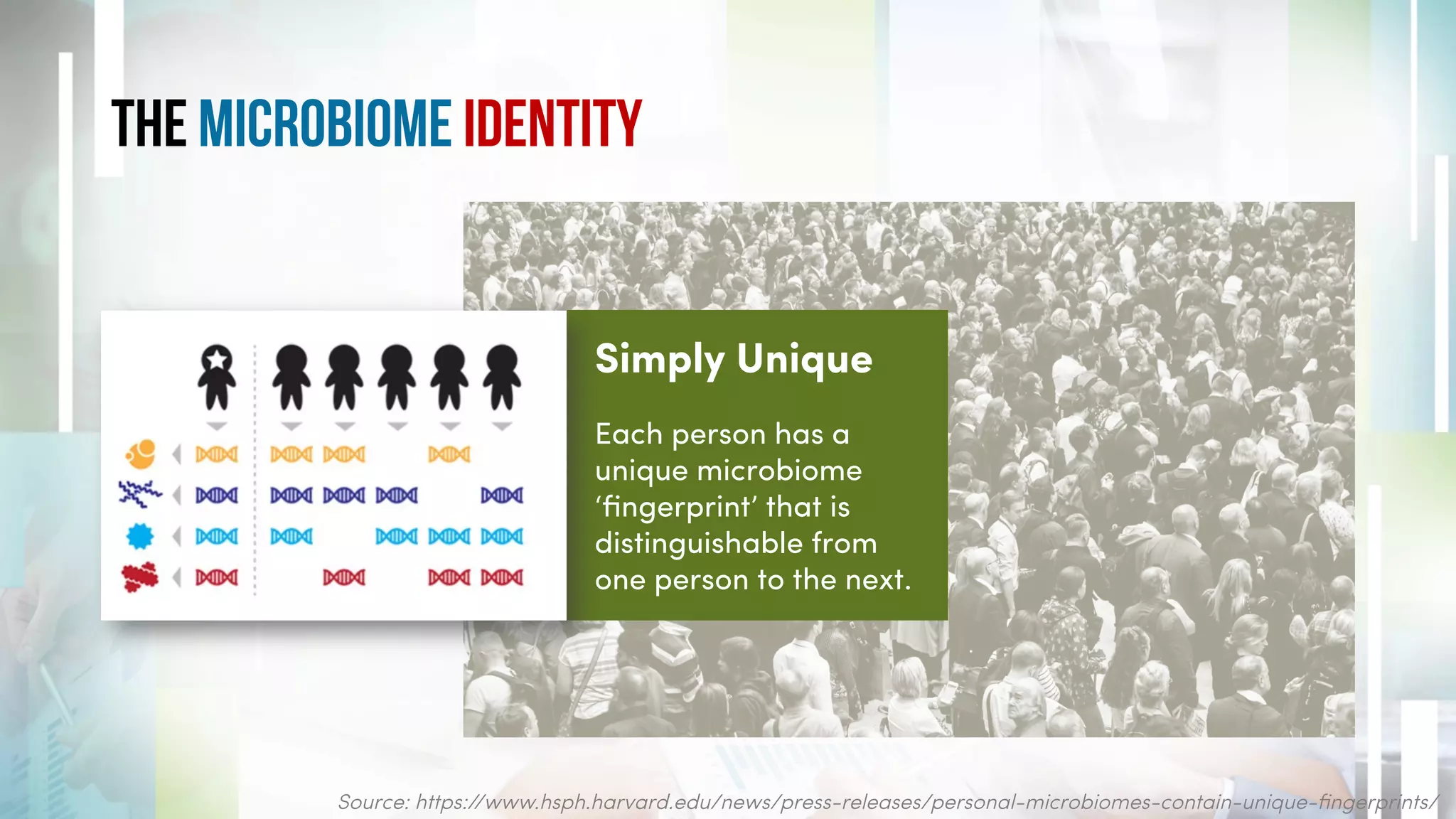
Maintaining a healthy microbiome is crucial for overall health and well-being, influencing digestion, metabolism, and mood. Key strategies include consuming a diet rich in probiotics and prebiotics, exercising regularly, ensuring adequate sleep, and managing stress. Making these lifestyle adjustments can enhance microbial diversity, thus promoting better health outcomes.