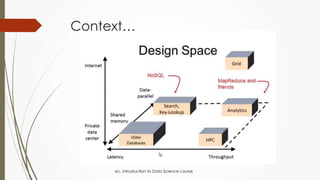
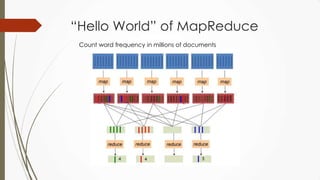
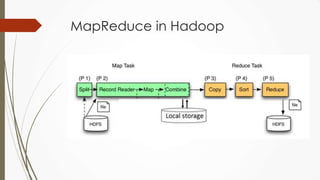
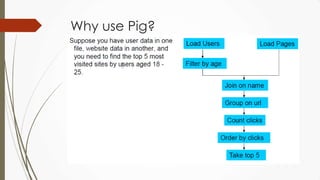
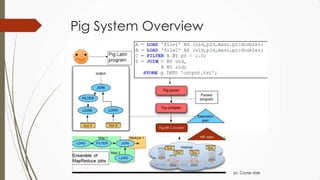
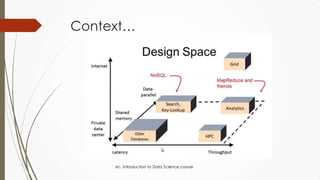
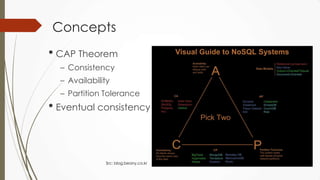
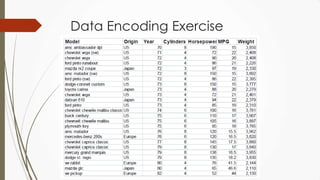
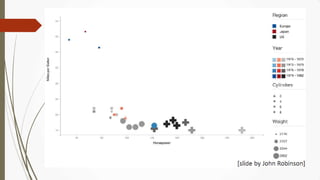
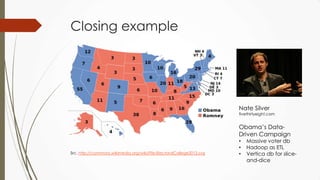
The document outlines a presentation on big data given by Raymond Yu, covering essential topics in data science such as MapReduce, NoSQL databases, and machine learning. It highlights the significance of data volume, velocity, and variety, as well as the methodologies for data extraction and analysis. The talk emphasizes modern tools and techniques used in big data management and visualization, illustrating their practical applications in areas like voter data analysis during political campaigns.