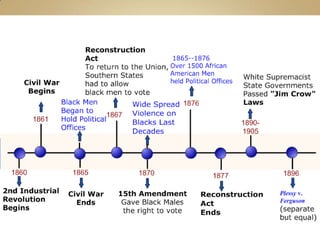
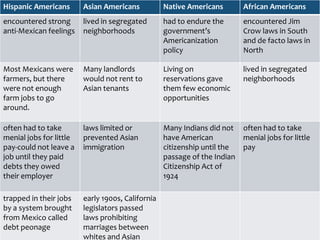
After the Civil War, racial discrimination became institutionalized in the United States with the passage of Jim Crow laws that legalized segregation and denied African Americans basic civil rights. Tactics like literacy tests and poll taxes were used to prevent African Americans from voting. The 1896 Plessy v. Ferguson Supreme Court decision upheld the doctrine of "separate but equal" and allowed racial segregation to continue for nearly 60 years. It took the 1954 Brown v. Board of Education decision to begin overturning legalized segregation.