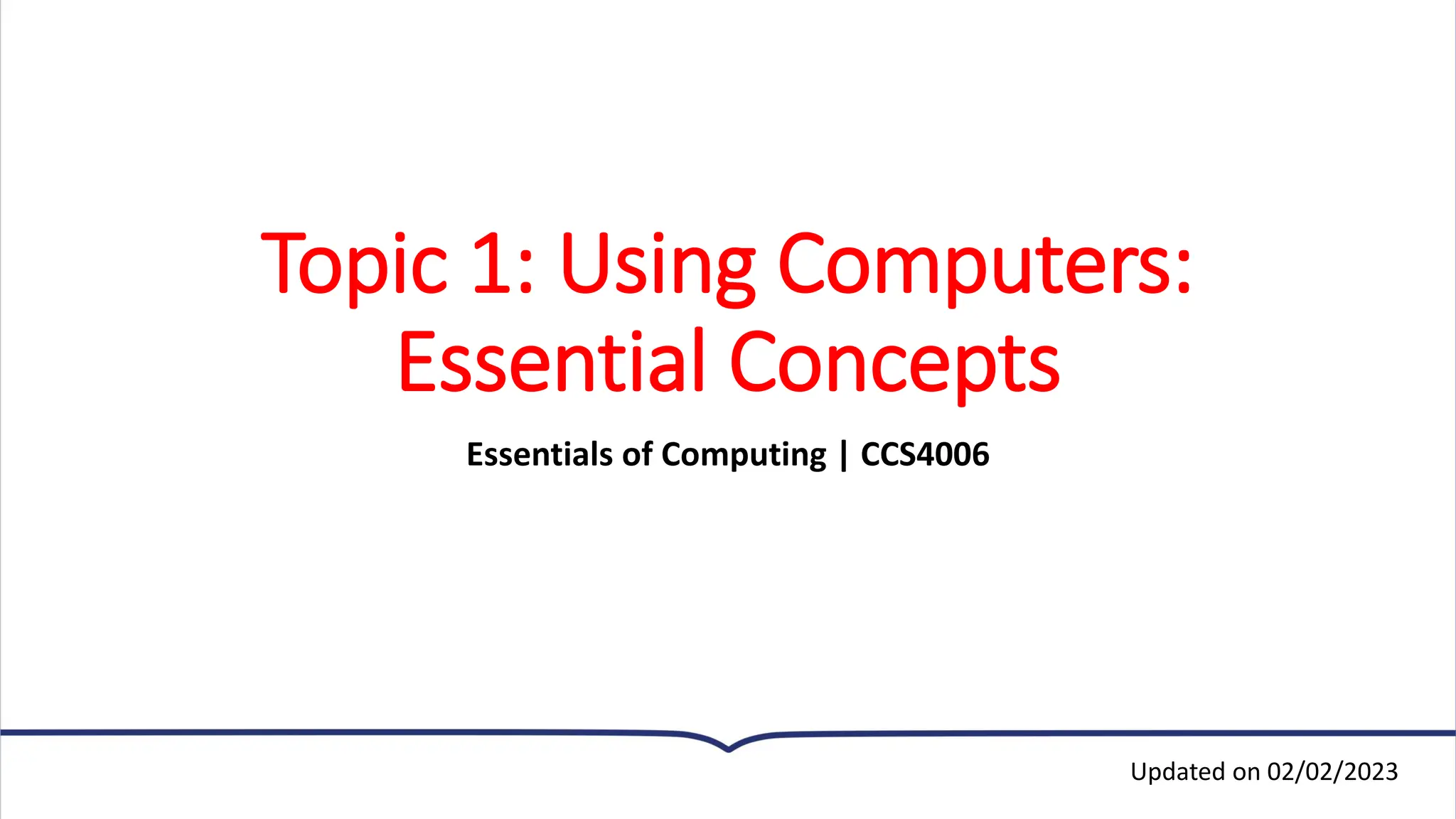
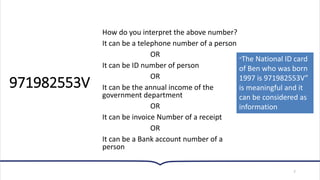
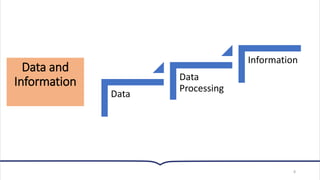
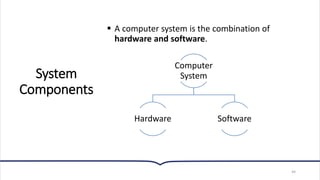
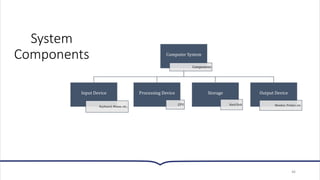
This document provides an overview of essential concepts related to using computers. It discusses the definition of a computer, its main functions of accepting data as input, processing that data, and producing and storing output. The document then covers the evolution of computers through five generations from the earliest vacuum tube computers to today's fifth-generation machines capable of artificial intelligence. It also defines different types of computers like supercomputers, mainframes, minicomputers, and microcomputers. Finally, the key components of a computer system including input, processing, storage, and output devices are outlined.