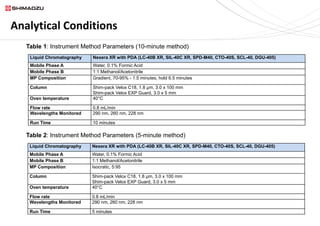
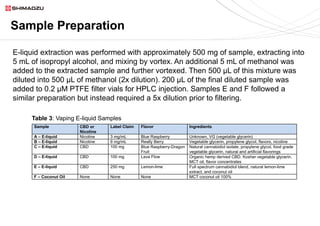
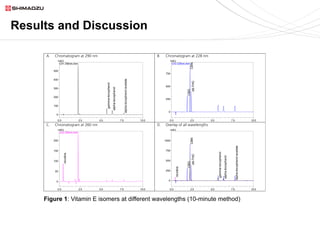
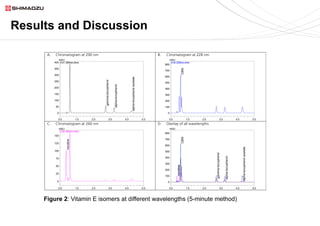
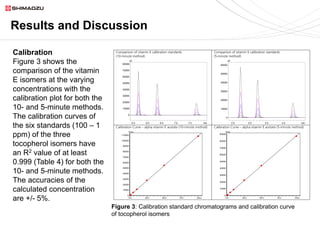
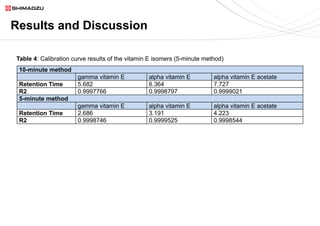
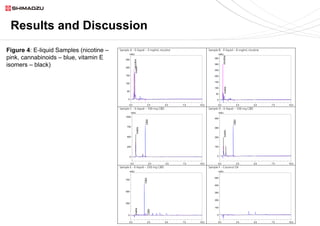
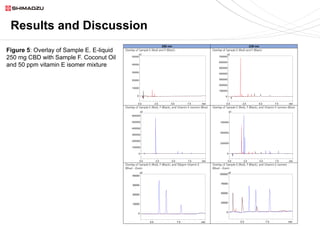
This document describes two UHPLC-PDA methods for analyzing vitamin E (tocopherol) isomers in e-liquid samples. A 10-minute gradient method separates e-liquid matrix, nicotine, cannabinoids, and three vitamin E isomers. A faster 5-minute isocratic method resolves only the vitamin E isomers. Calibration curves for the vitamin E isomers show good linearity (R2 > 0.999) over concentrations of 1-100 ppm. The methods were applied to analyze six e-liquid samples but did not detect any vitamin E. Coconut oil used in one sample was found to contain interfering compounds at lower detection wavelengths.