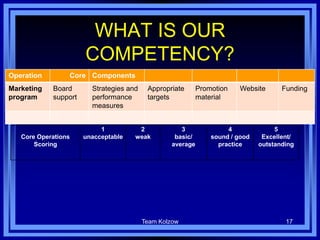
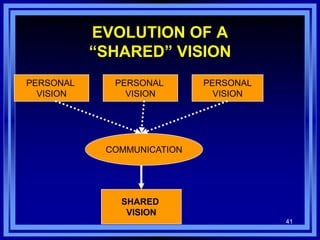
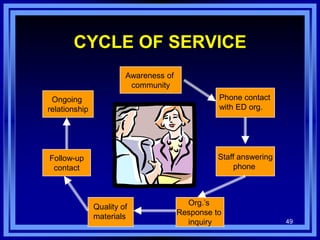
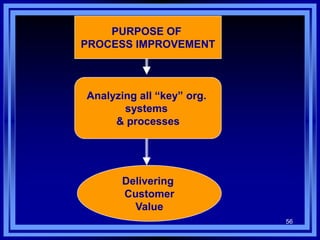
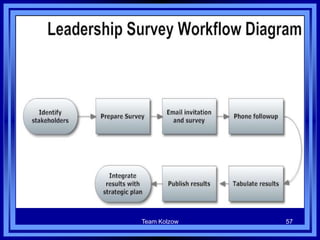
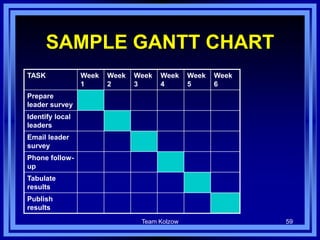
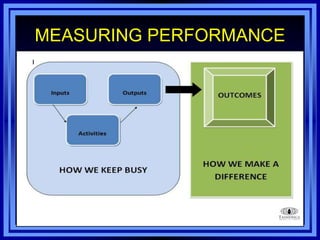
This document discusses managing development organizations for excellence. It covers identifying an organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats through a SWOT analysis. Key aspects of organizational excellence include having a clear mission and vision that is shared by leadership and staff. The document emphasizes the importance of the board of directors in setting policies and priorities to guide the organization. Overall, the document provides guidance on assessing an organization and establishing goals and strategies to achieve excellence.