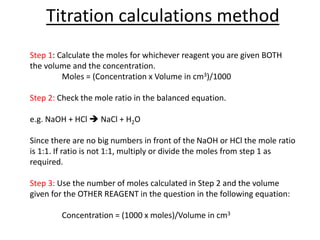
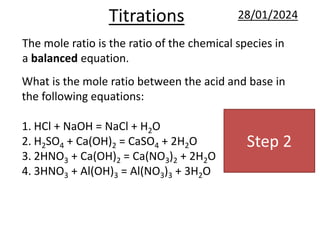
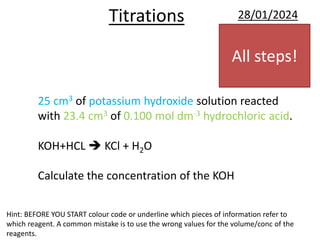
This document provides information and examples related to titration calculations. It defines key terms like indicators, acids, alkalis and salts. It also outlines the step-by-step method for carrying out titration calculations, including determining moles of reagents from concentration and volume, identifying mole ratios from balanced equations, and calculating concentration from moles and volume. Several fully worked examples demonstrate how to apply this method to calculate unknown concentrations.