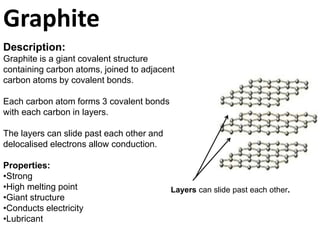
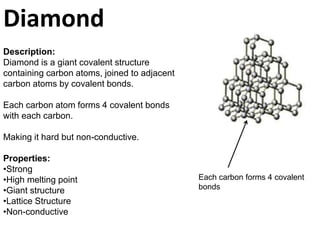
Graphite is a giant covalent structure made of layers of carbon atoms bonded together, allowing the layers to slide past one another. It conducts electricity and is lubricating. Diamond is also a giant covalent carbon structure, but each carbon atom forms four bonds making it very hard but non-conductive. Buckminster fullerenes are hollow carbon cages about 1 nanometer in diameter, stronger than diamond. Carbon nanotubes are flexible carbon tubes about 1 nanometer wide that conduct electricity and are made from half a buckminster fullerene.