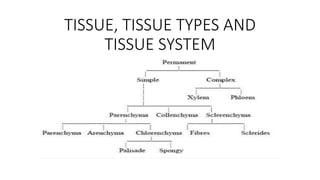
Parenchyma cells form the ground tissue in plants and perform many important functions. They can store starches, fats, oils, and water. Parenchyma cells also transport nutrients throughout the plant and perform photosynthesis using chloroplasts. Additionally, parenchyma cells play roles in gas exchange, protection, buoyancy, healing, and regeneration. Parenchyma cells occur in continuous masses and can be polyhedral, stellate, elongated, or lobed in shape. The mesophyll tissue in leaves contains palisade parenchyma above spongy parenchyma.