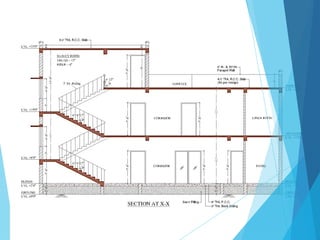
The document provides a detailed overview of building estimation processes, emphasizing the importance of accurate cost projections and the necessary skills for interpreting construction drawings. It outlines the required items for preparing estimates, different types of estimates, and various methodologies for calculating construction costs. Additionally, it includes specific data about a proposed residential building's estimation, including dimensions, materials, and total projected costs.