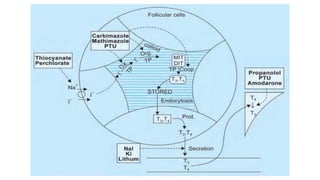
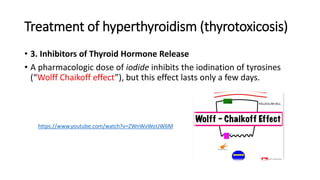
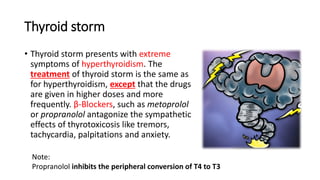
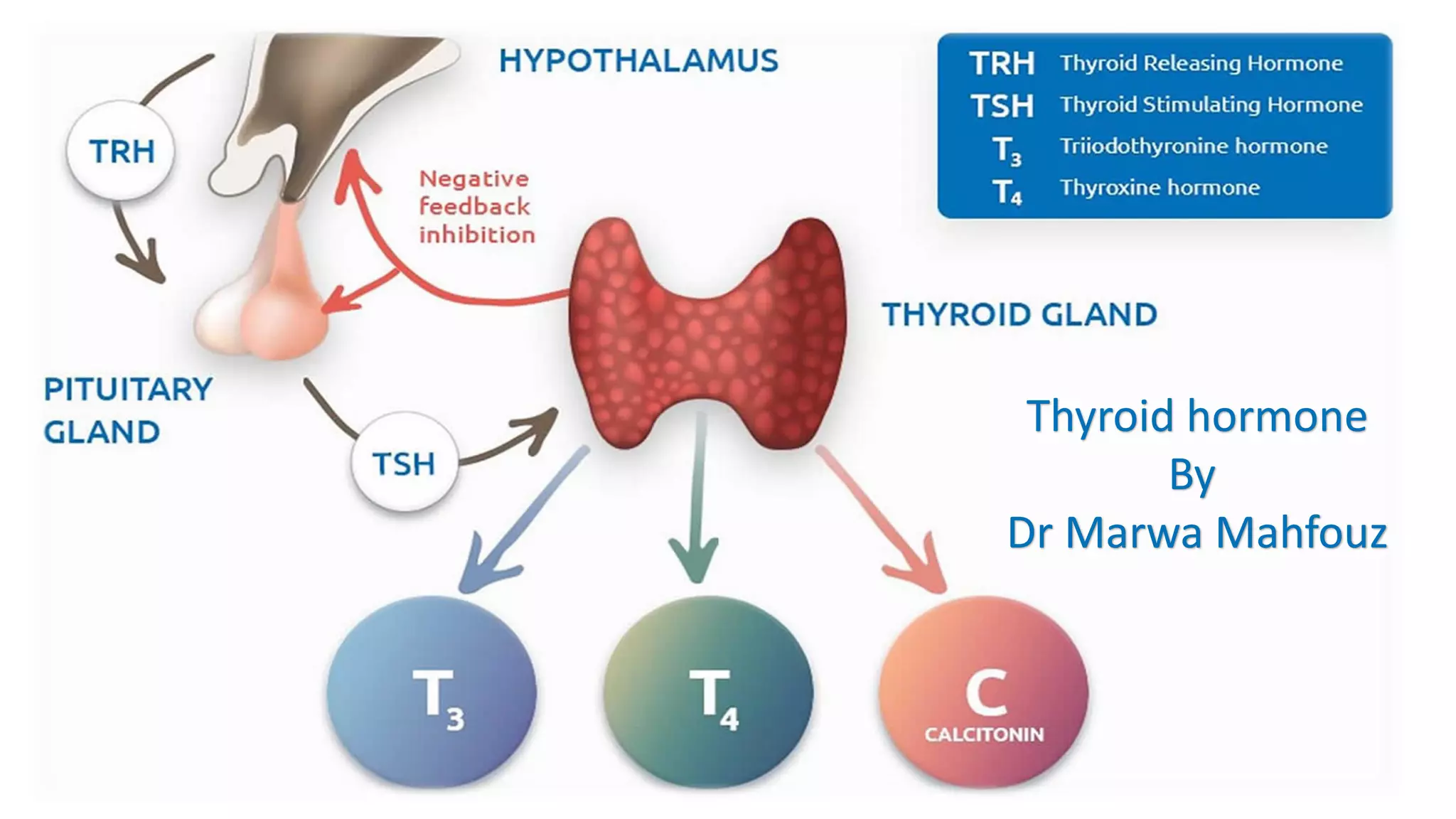
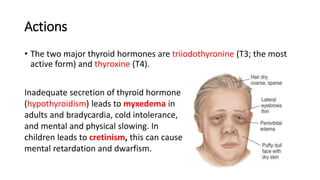
The thyroid gland produces thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) which increase metabolism. Too little hormone causes hypothyroidism with symptoms like bradycardia and weight gain, while too much causes hyperthyroidism with symptoms like tachycardia and weight loss. Hypothyroidism is treated with levothyroxine replacement therapy. Hyperthyroidism treatments include anti-thyroid medications to block hormone synthesis, radioactive iodine ablation of the thyroid gland, or surgery.

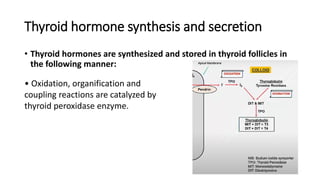
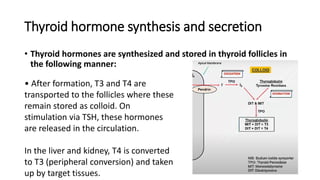
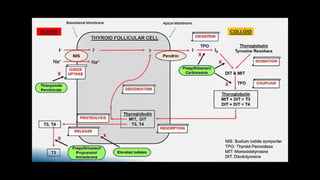



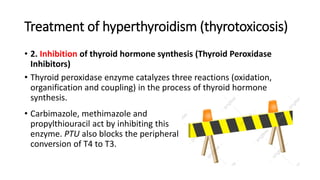
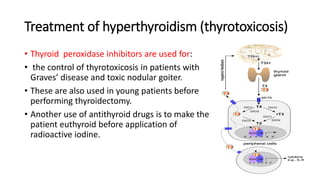
![Treatment of hyperthyroidism (thyrotoxicosis)
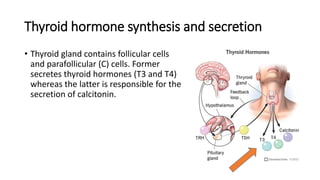
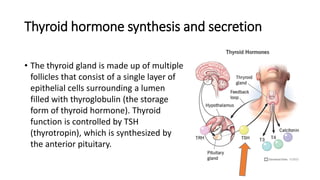
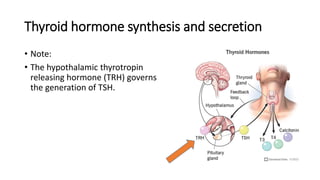
• Grave’s disease, an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid, is
the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. In these situations, TSH
levels are low due to negative feedback. [Note: Feedback inhibition of
TRH occurs with high levels of circulating thyroid hormone, which, in
turn, decreases secretion of TSH.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thyroidhormone-230707193403-fee3dd9b/85/thyroid-hormone-pdf-19-320.jpg)