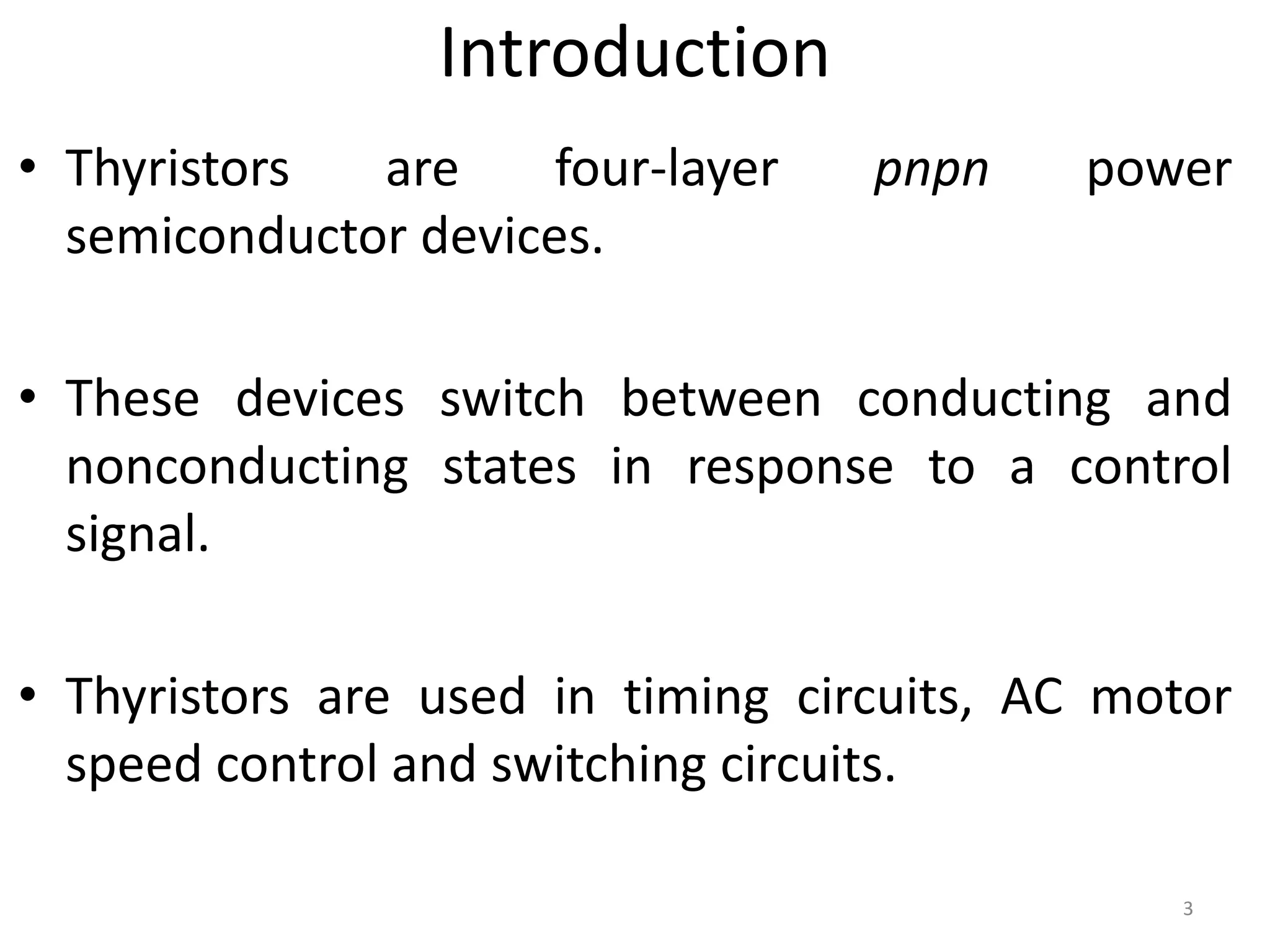
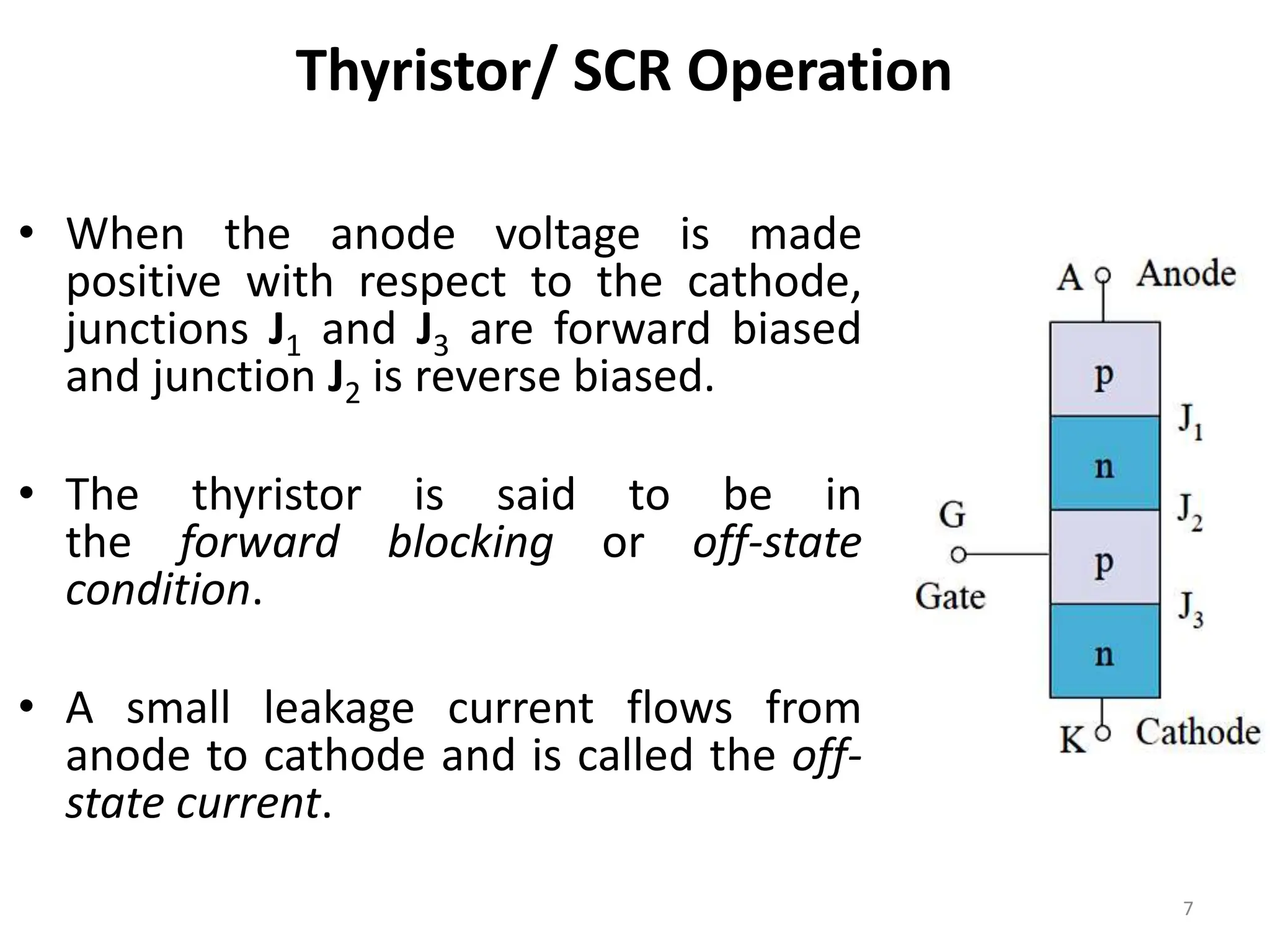
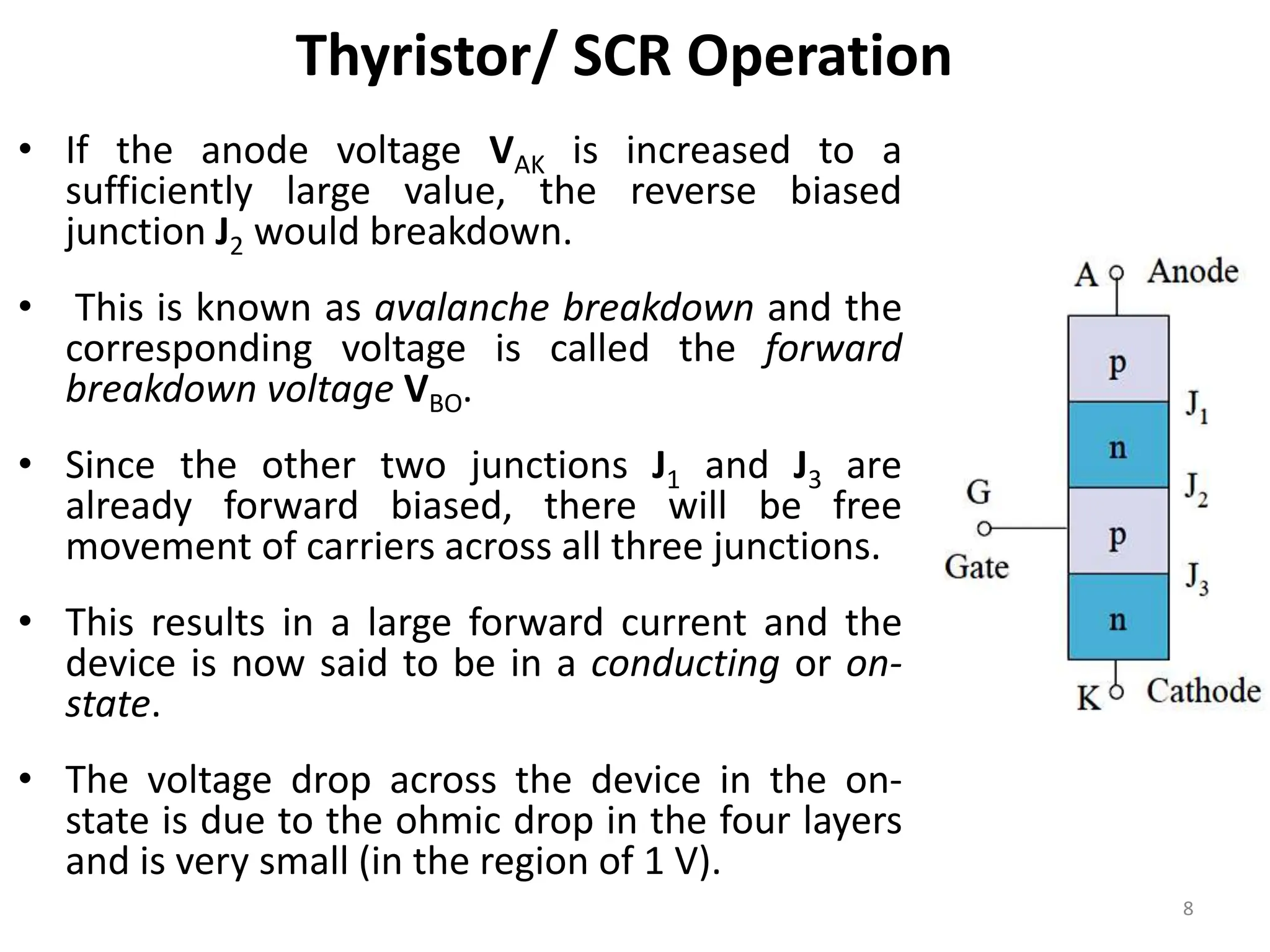
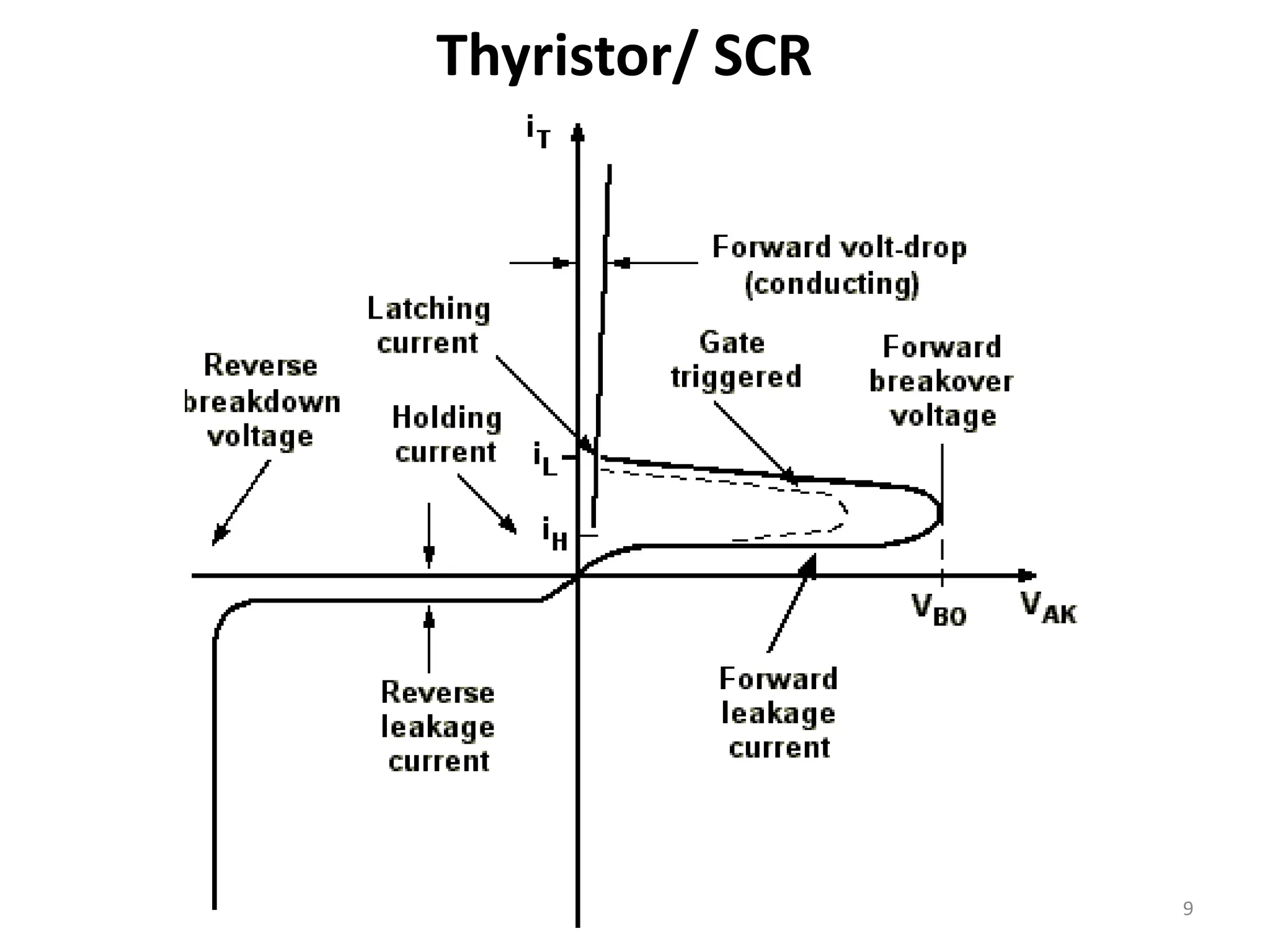
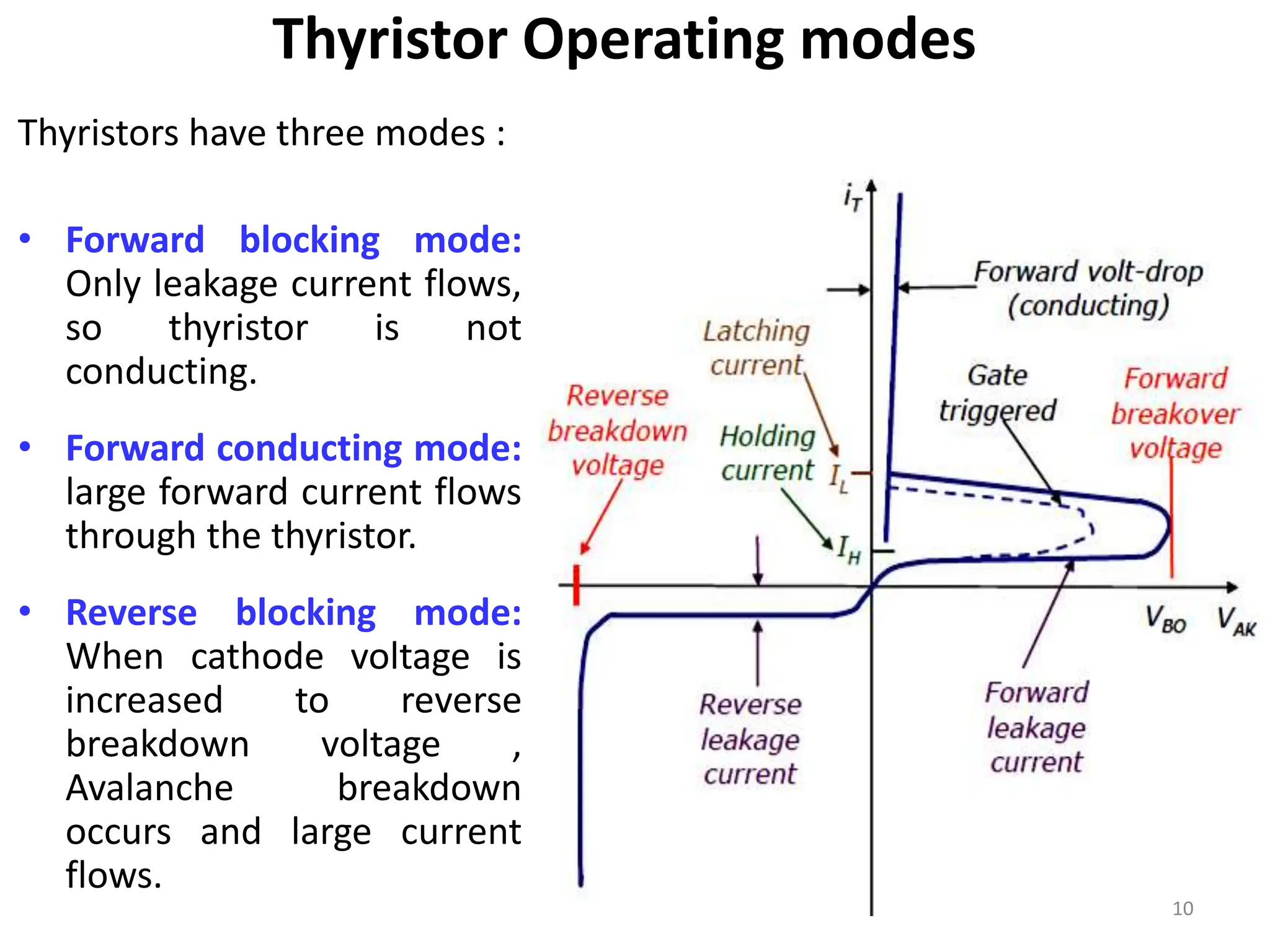
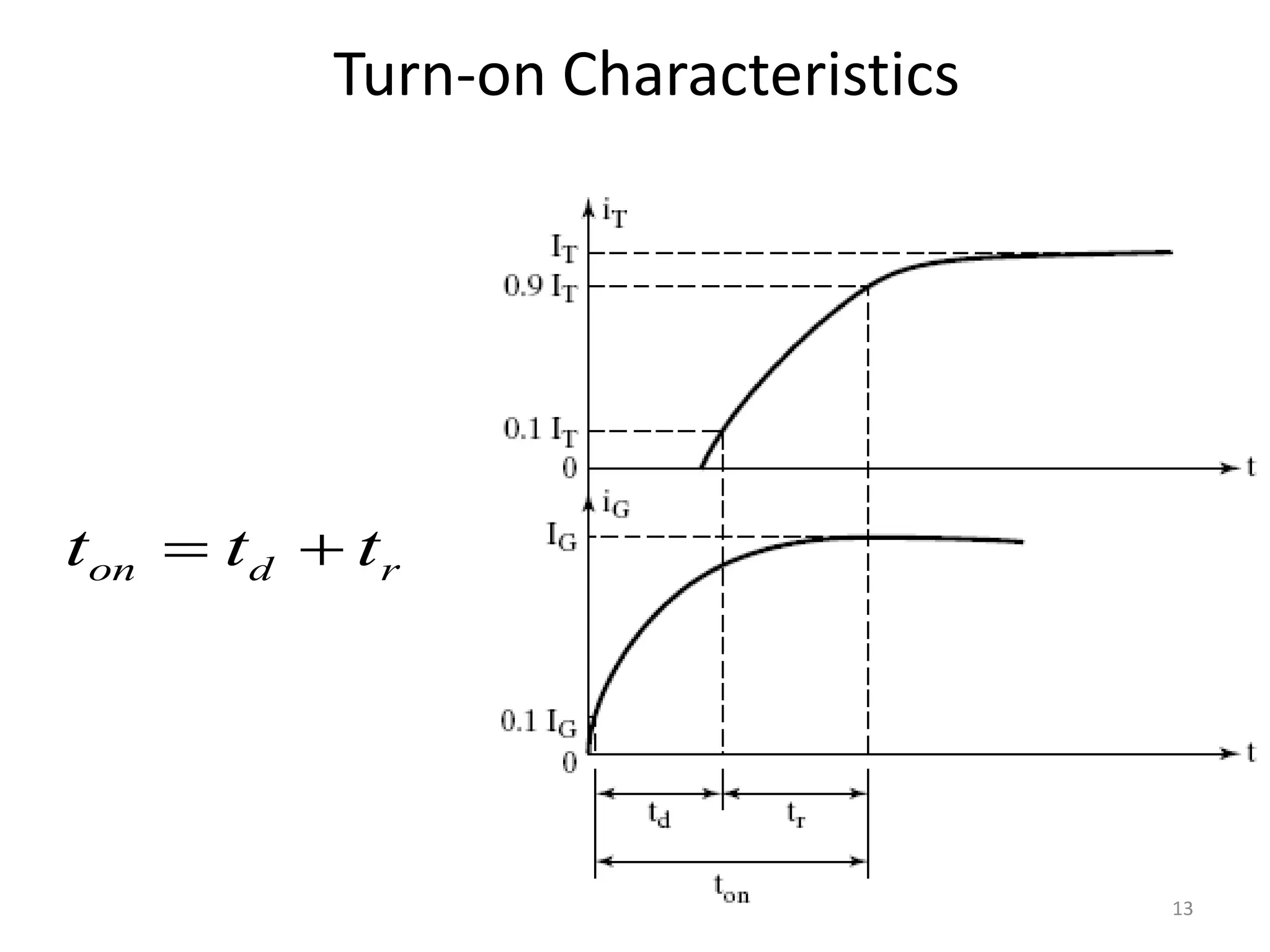
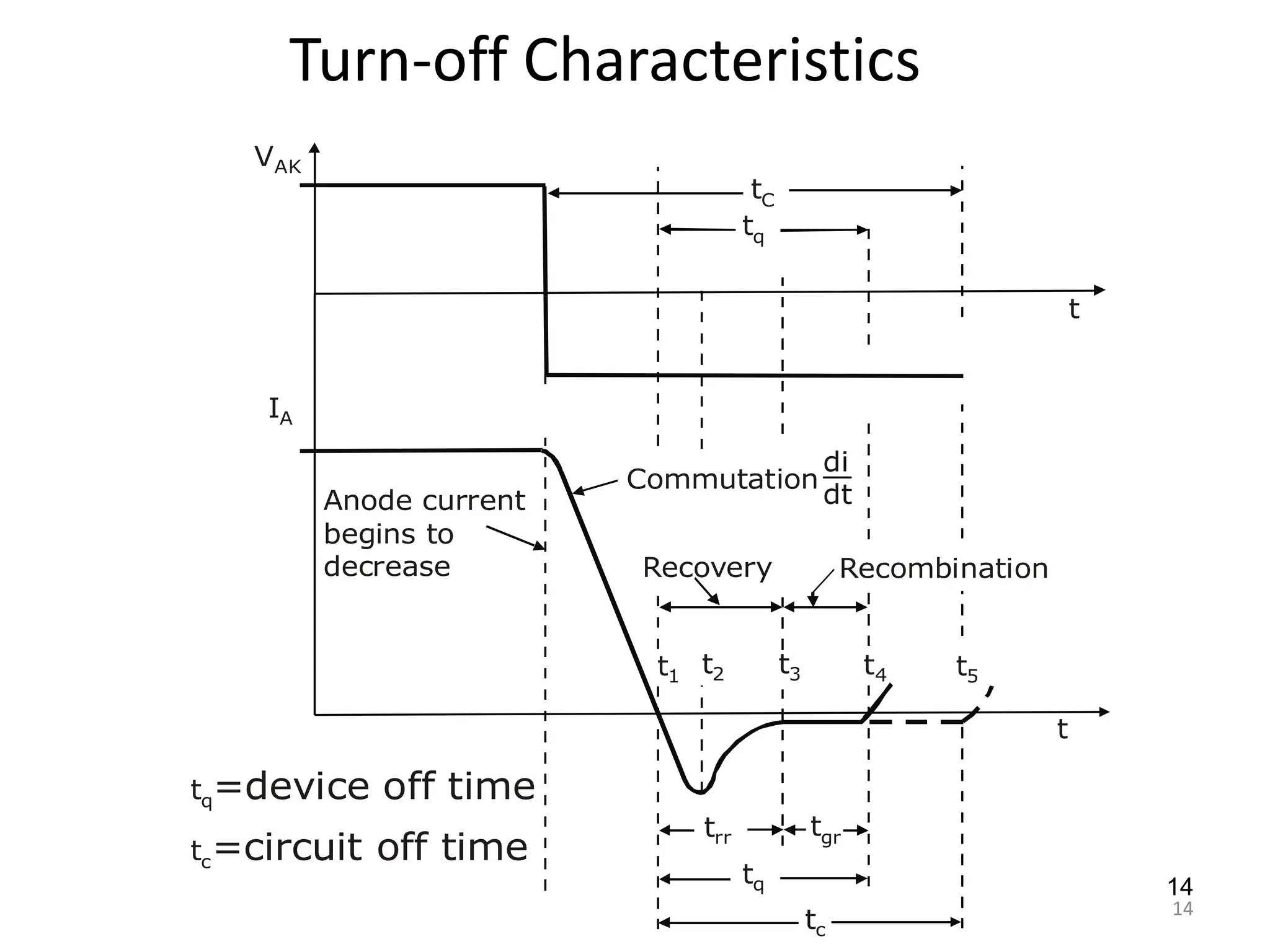
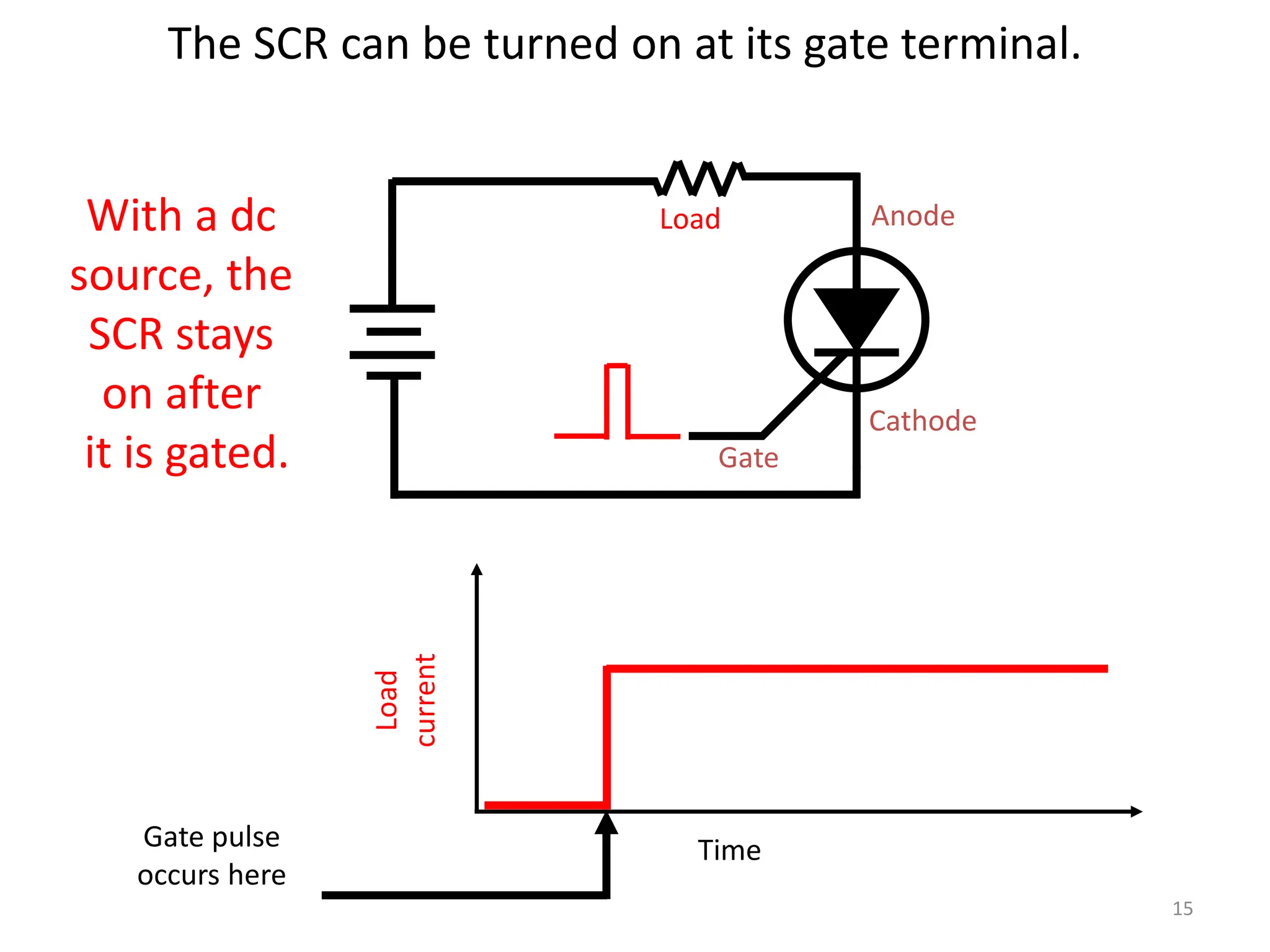
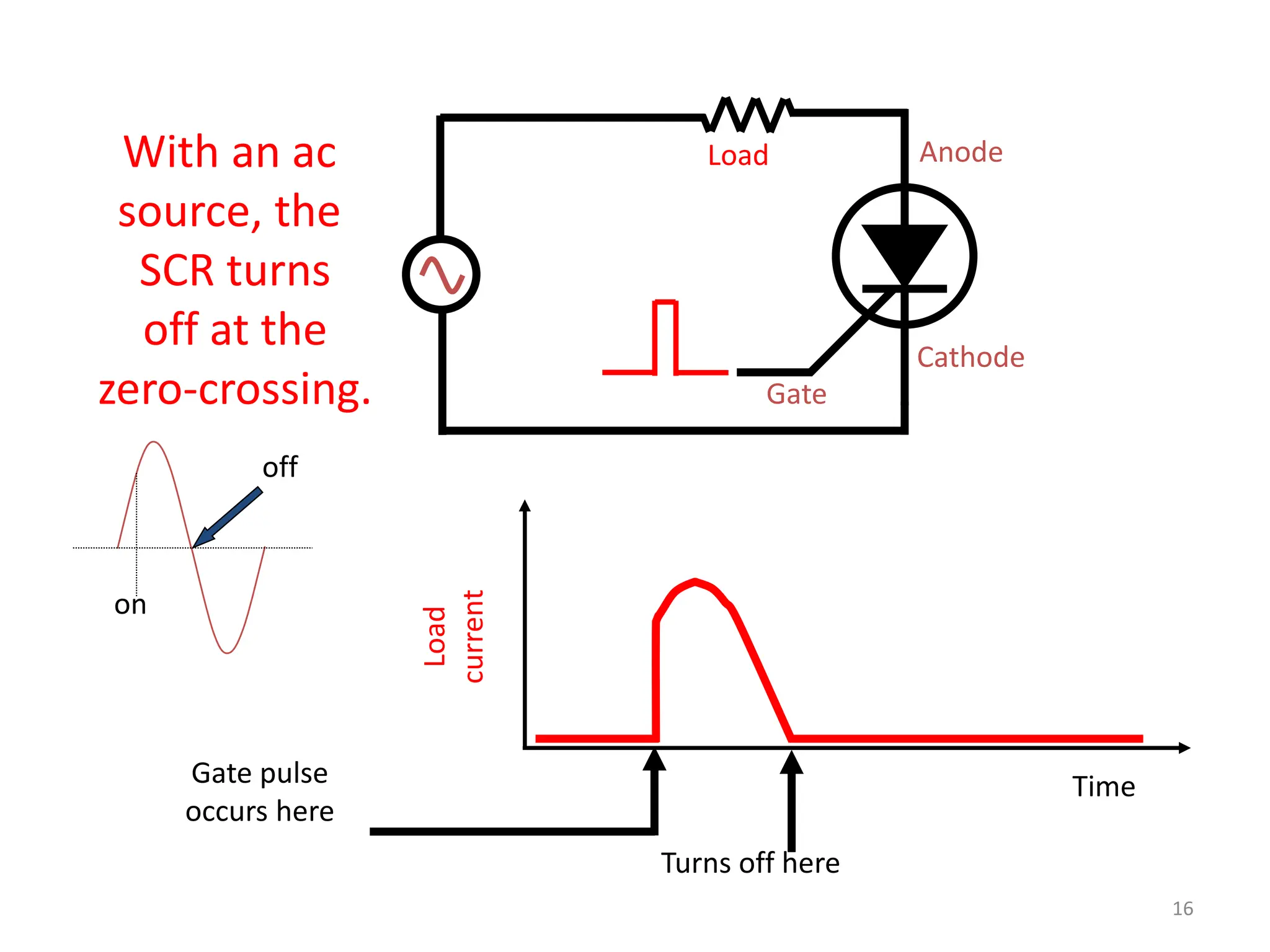
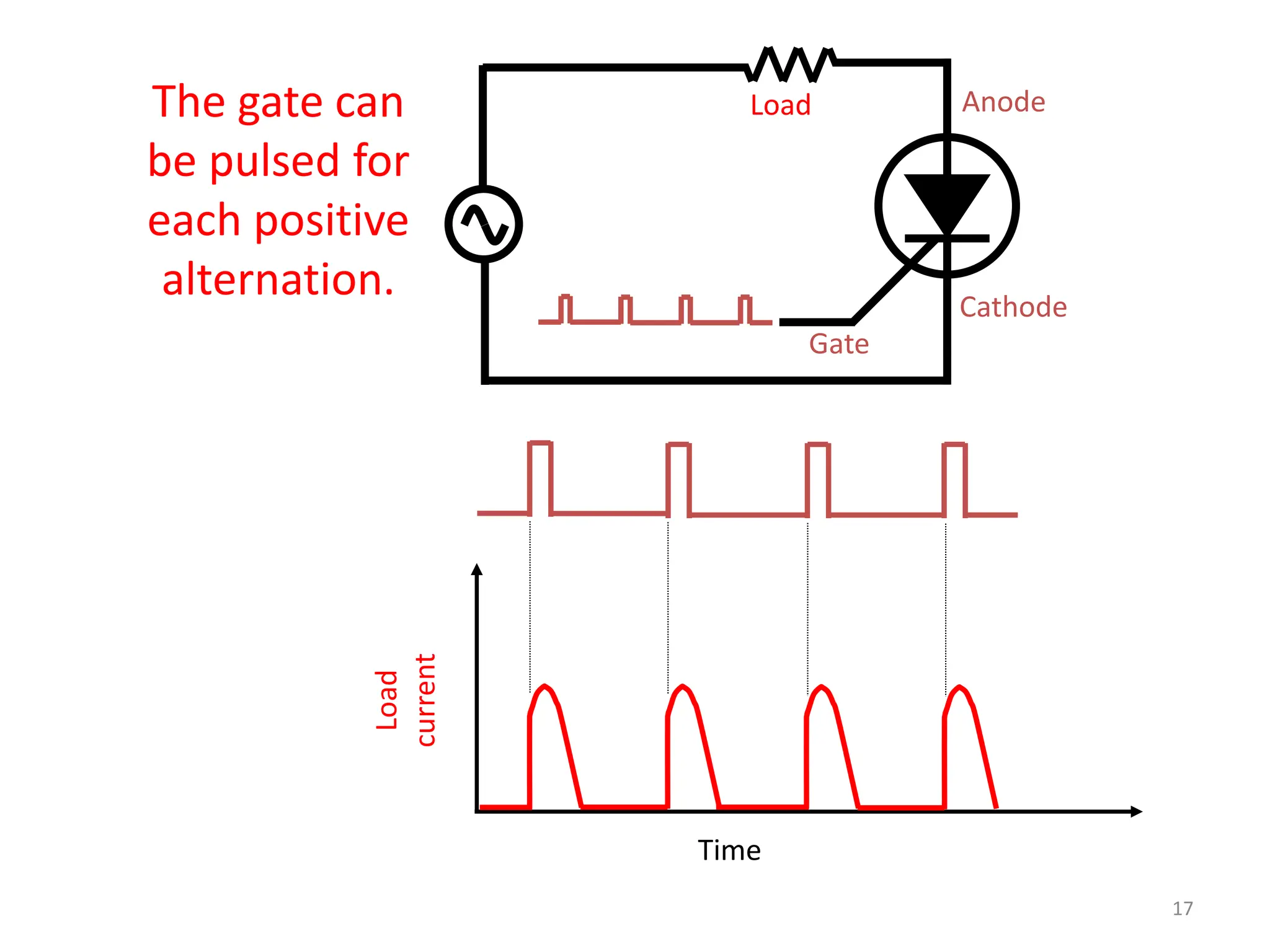
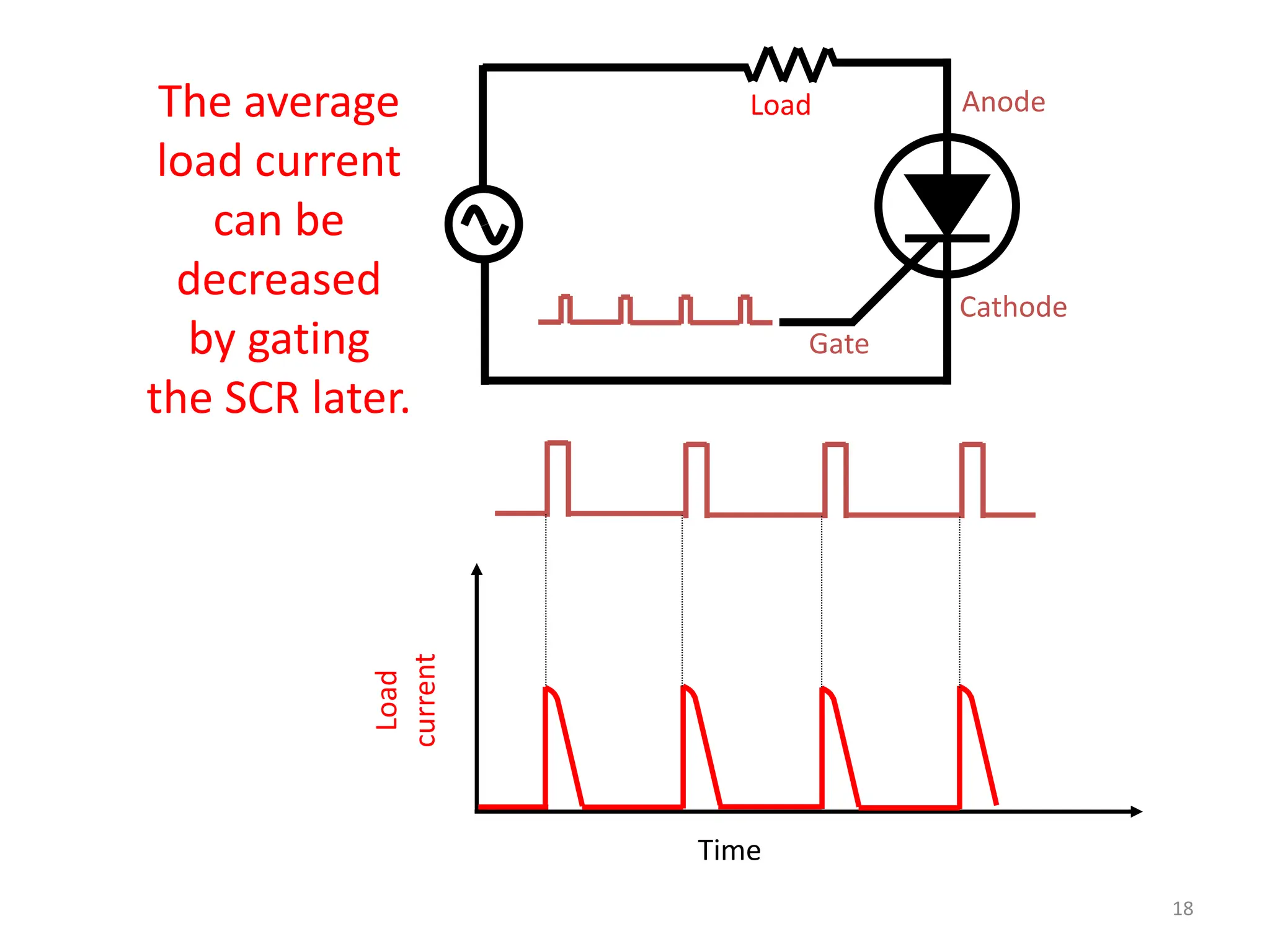
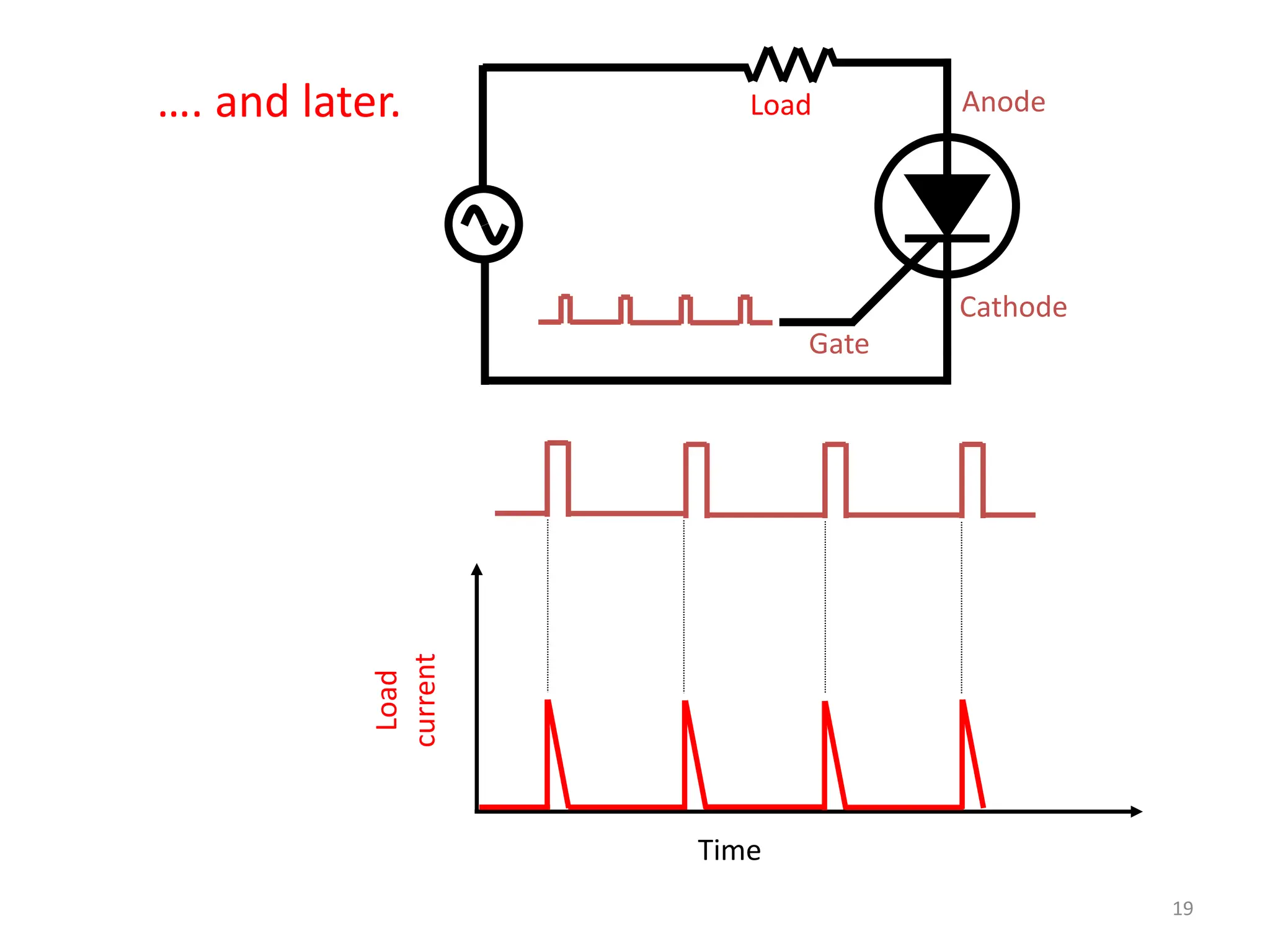
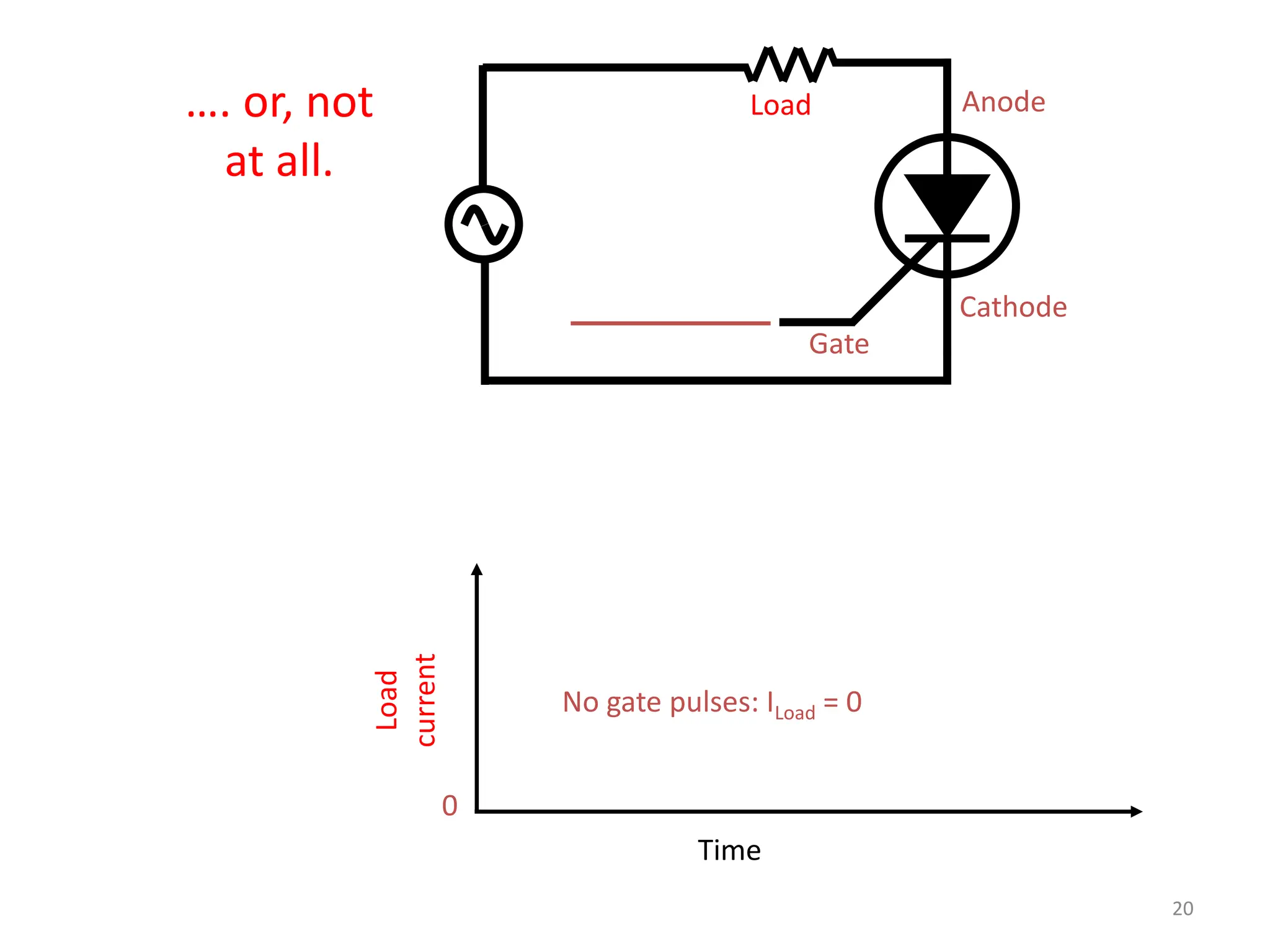
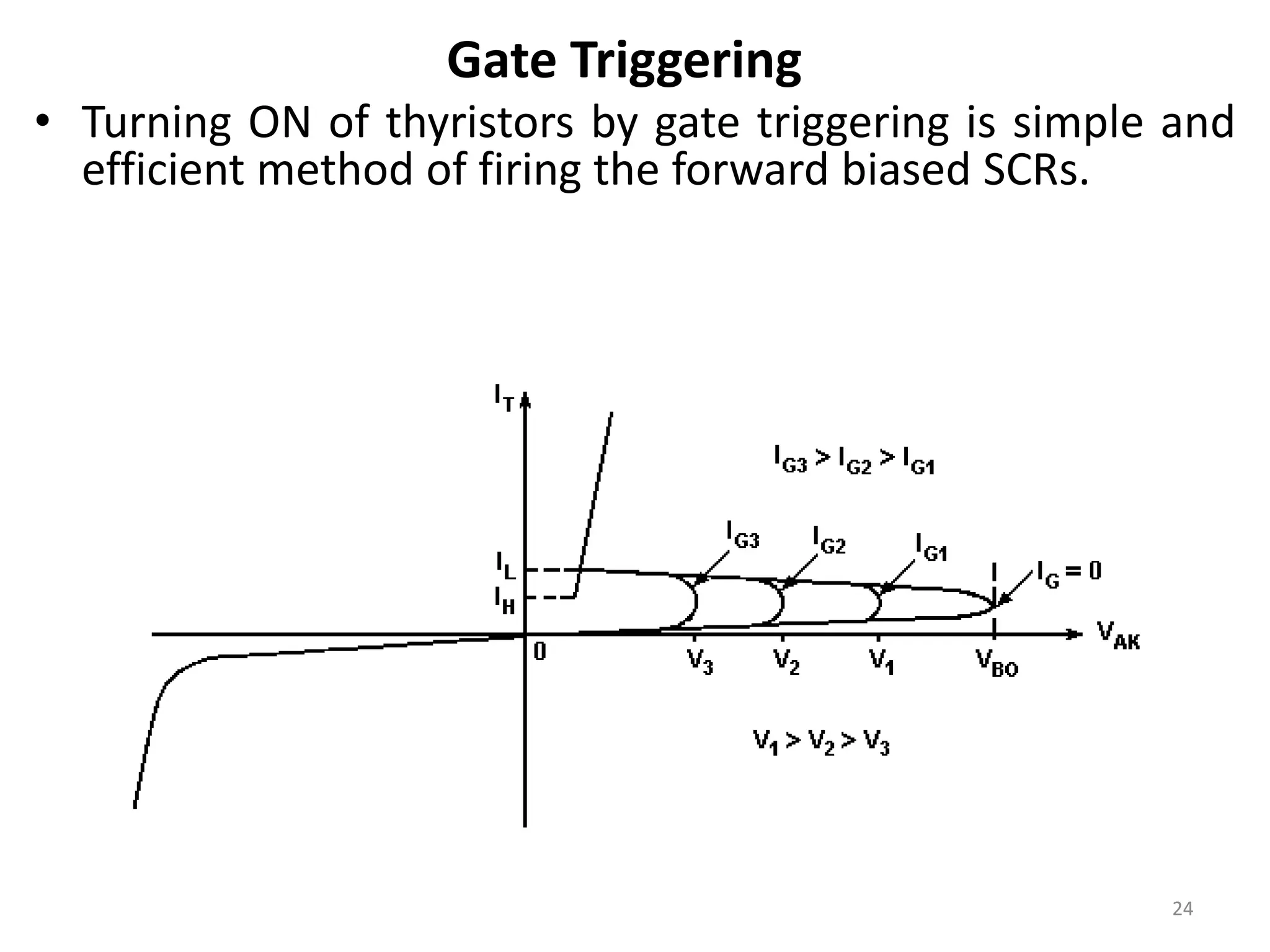
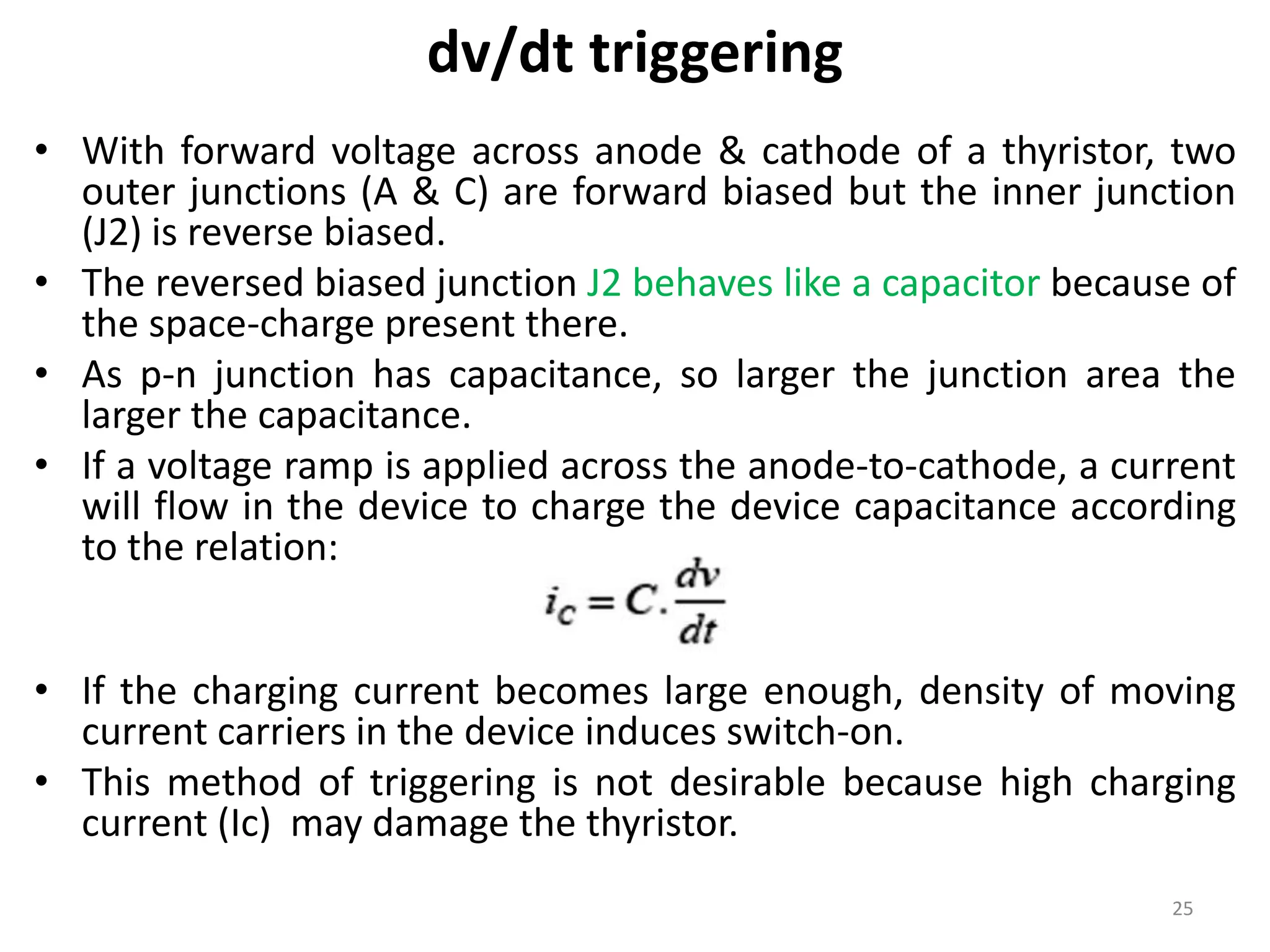
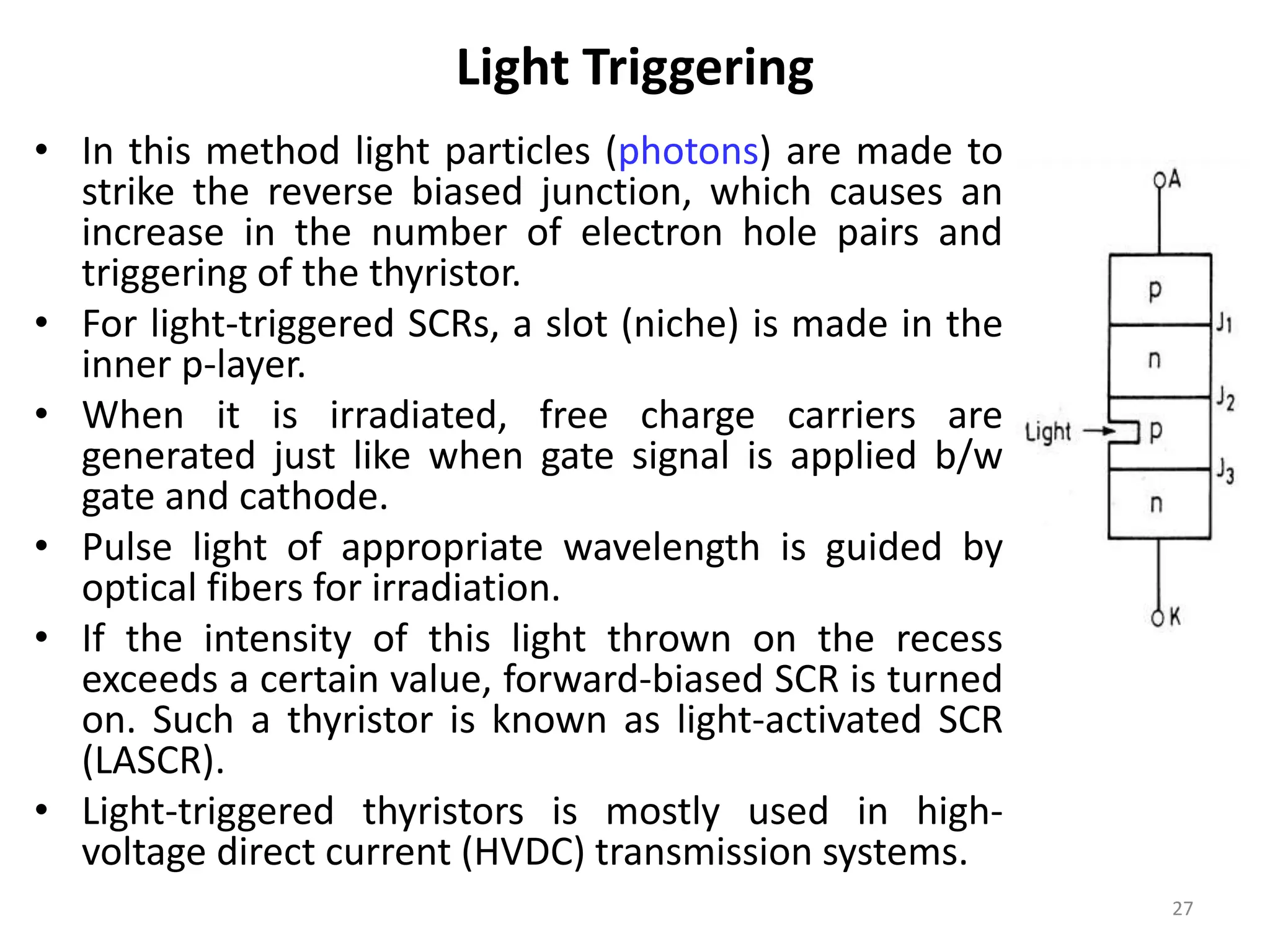
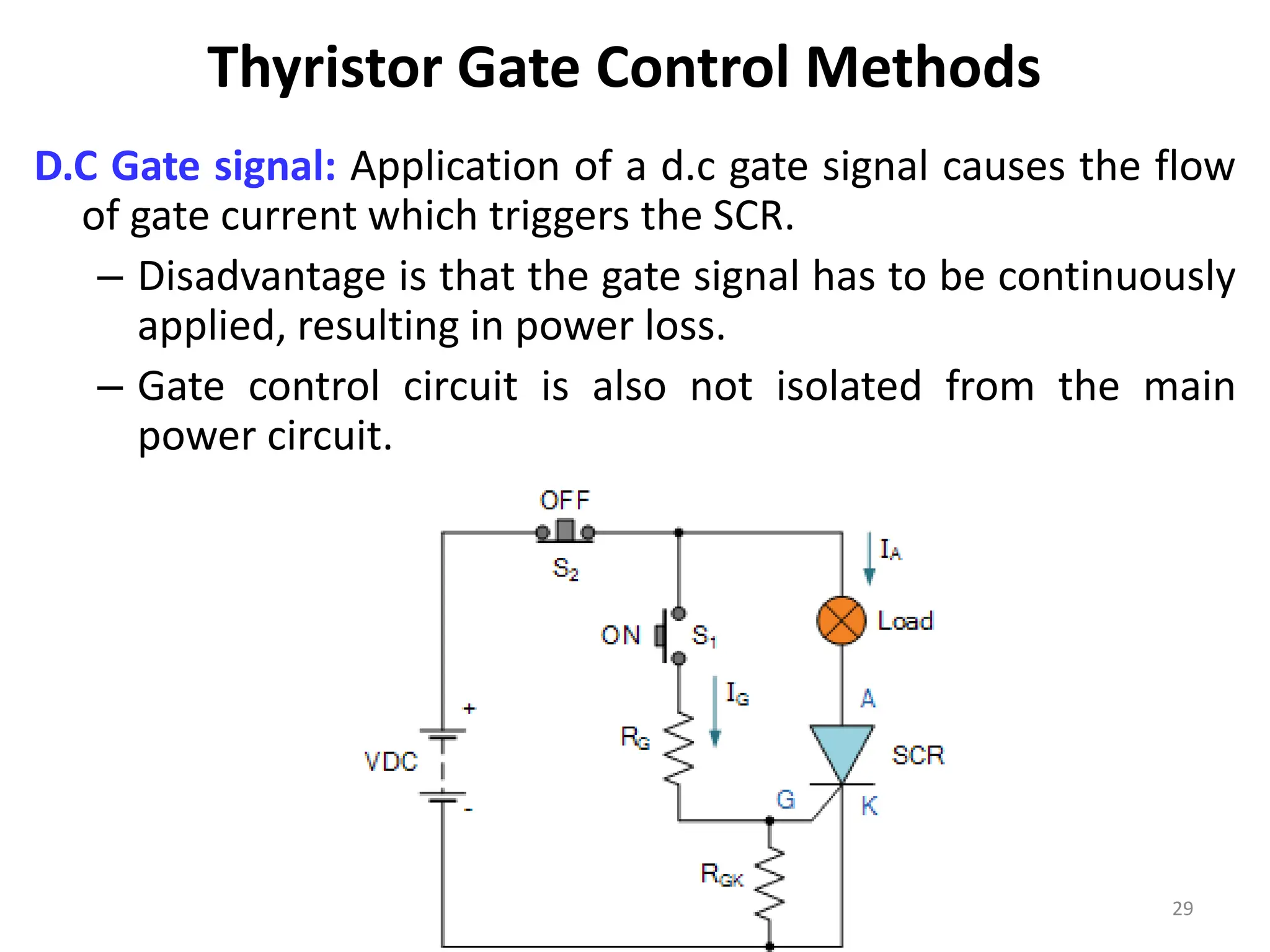
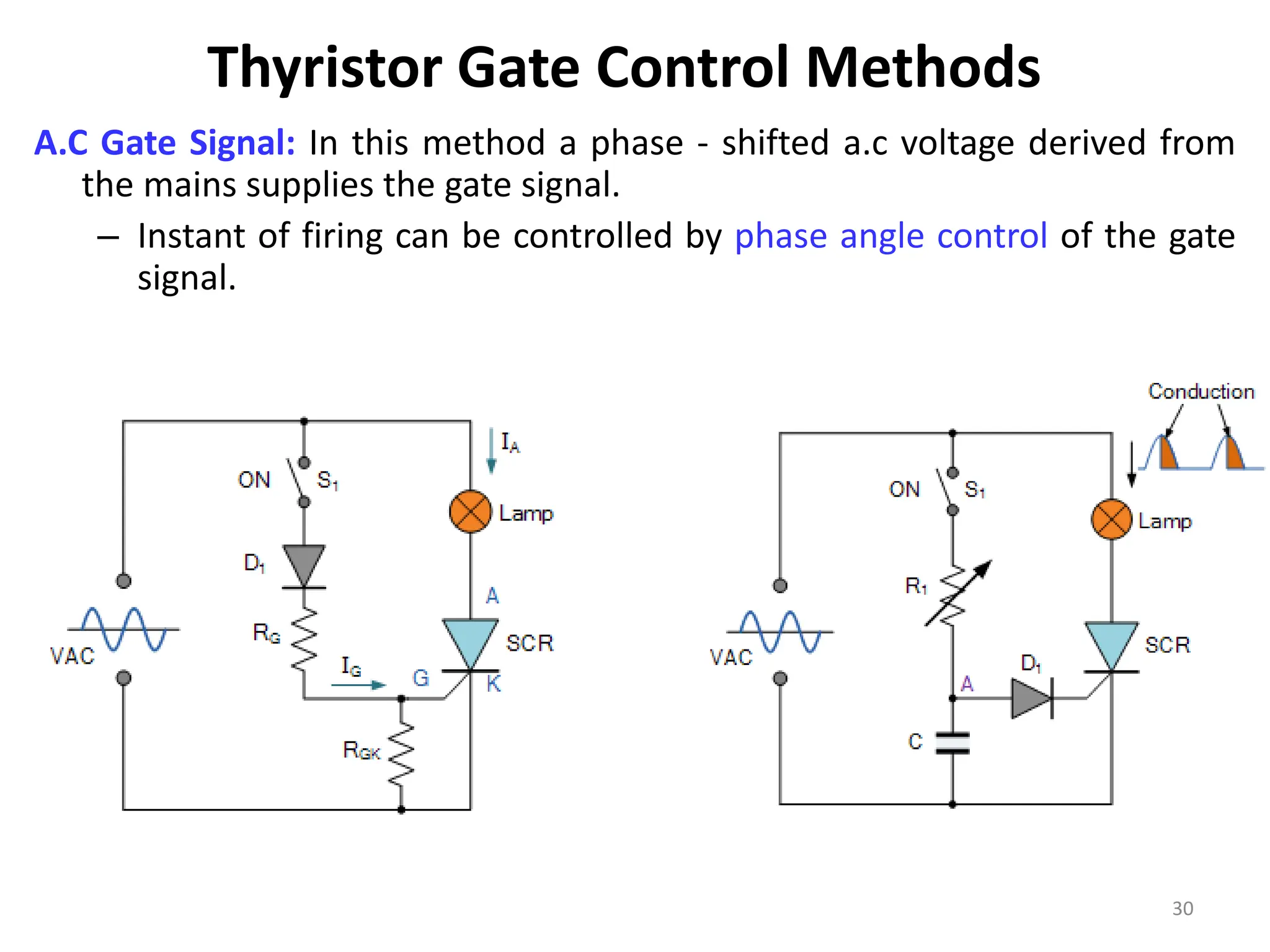
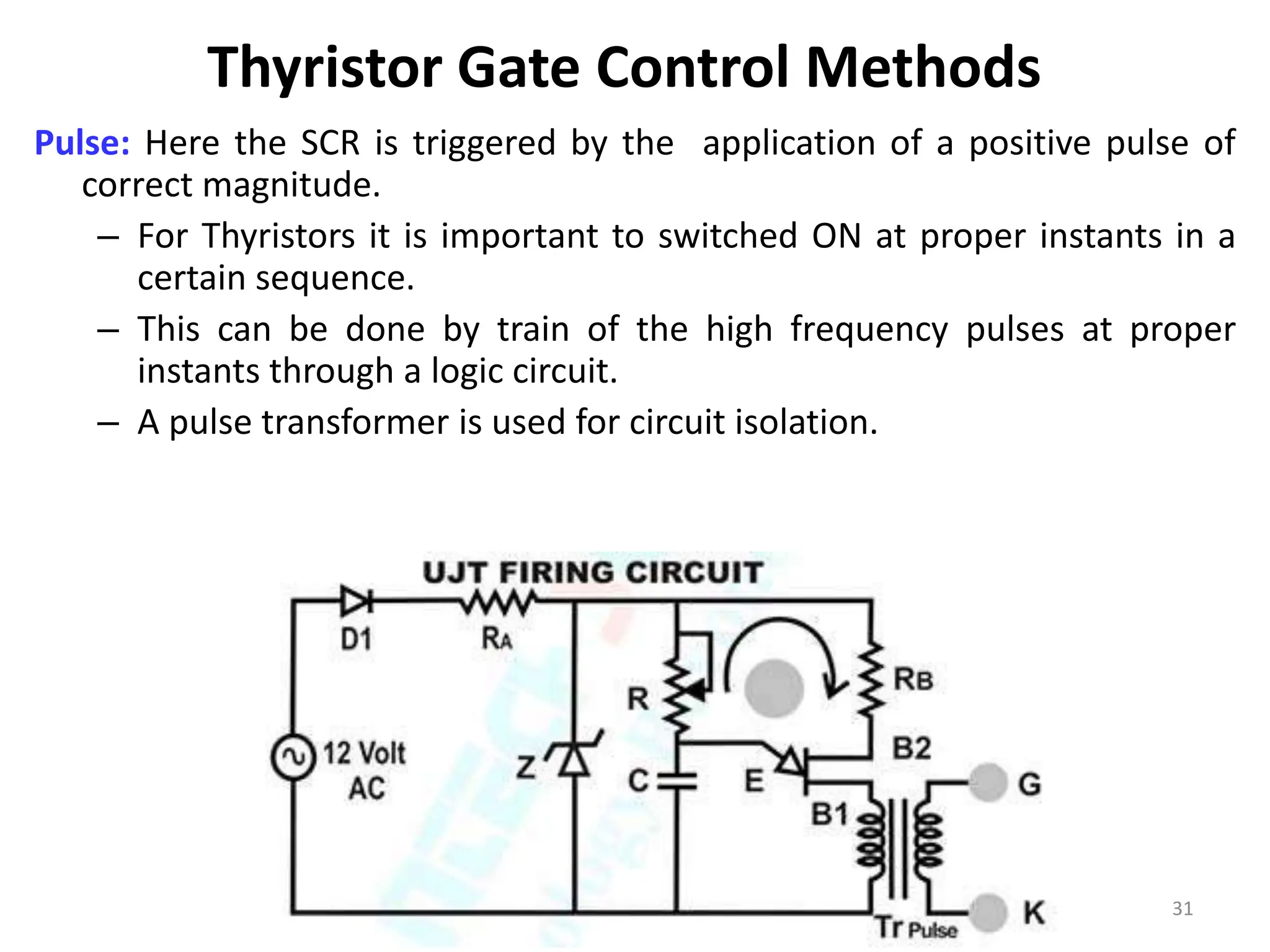
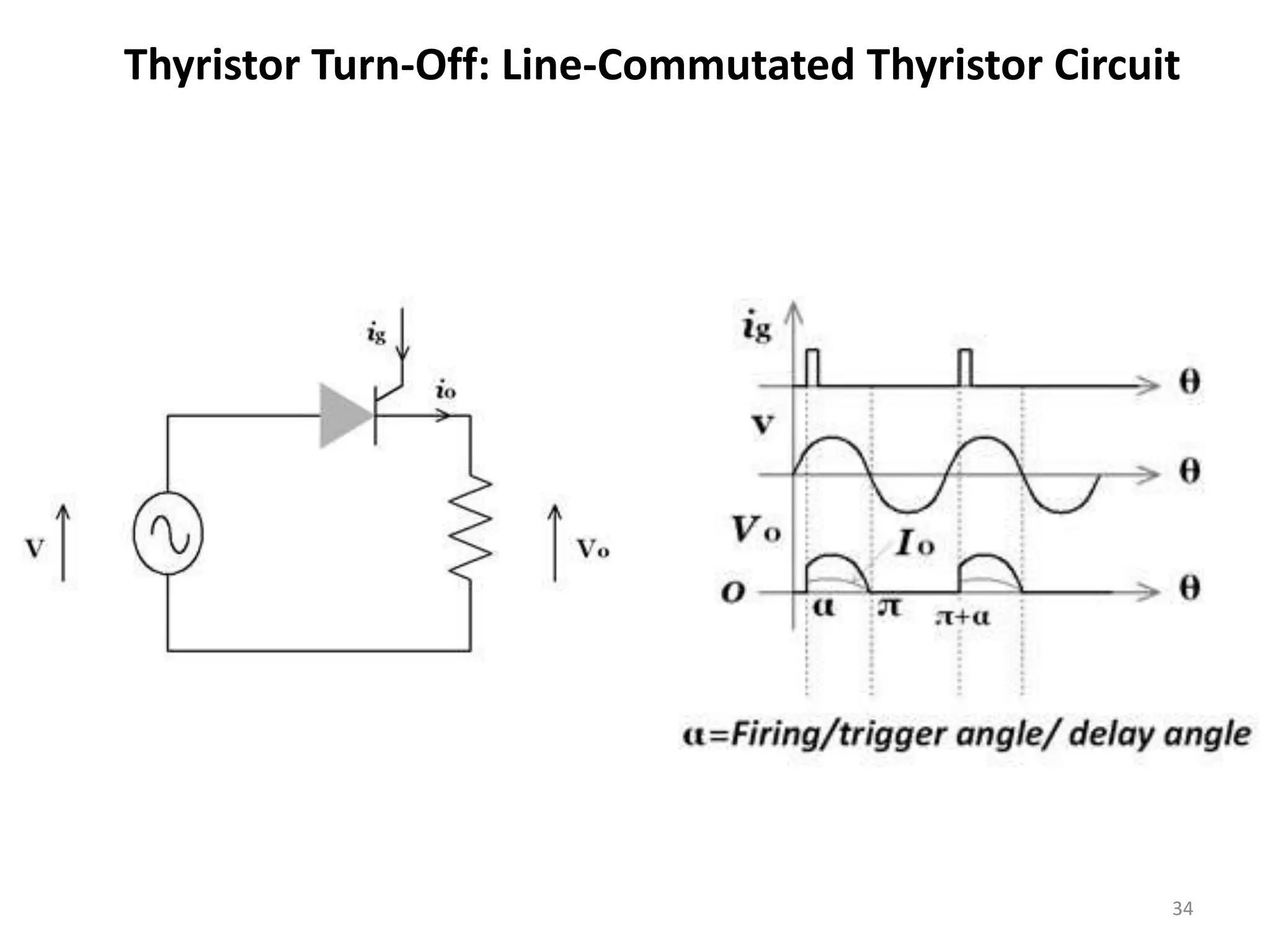
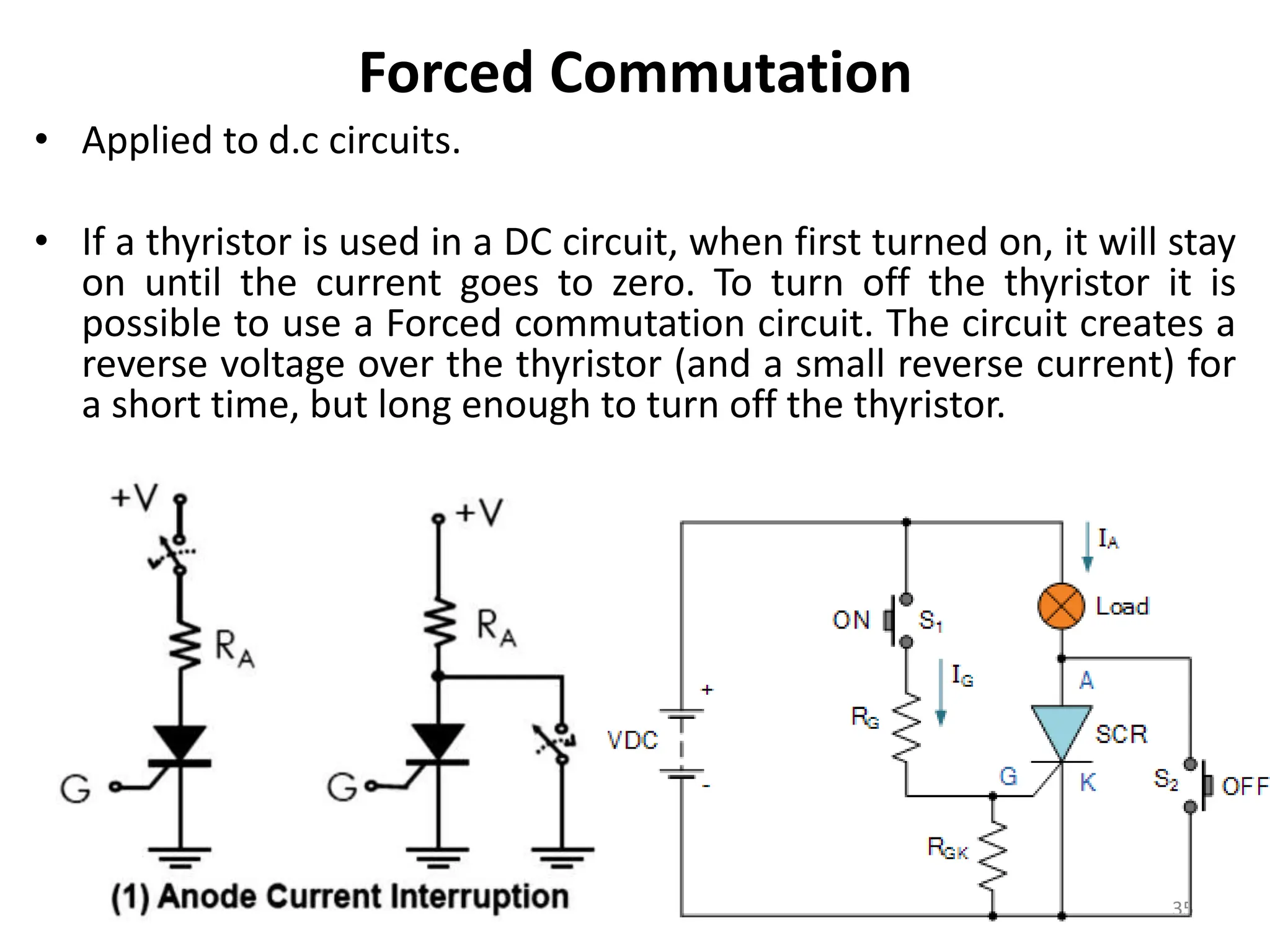
Thyristors are four-layer pnpn power semiconductor devices that switch between conducting and nonconducting states in response to a control signal. They are used in timing circuits, AC motor speed control and switching circuits. Thyristors have lower on-state conduction losses and higher power handling capability compared to transistors, but worse switching performances. Common thyristor devices include SCRs, SCSs, triacs, diacs, PUTs, and GTOs. Thyristors can be turned on through forward voltage triggering, gate triggering, dv/dt triggering, temperature triggering, or light triggering, with gate triggering being the most common method.