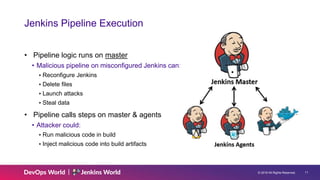
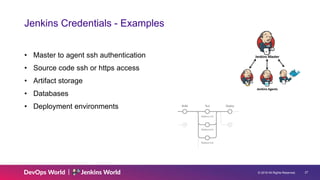
The document discusses Jenkins security principles, such as least privilege and defense in depth, to mitigate risks associated with distributed code execution. It emphasizes securing access to Jenkins components, using credentials effectively, and adhering to best practices like regular updates and monitoring security advisories. Key security measures include proper authentication and authorization methods to protect intellectual property and prevent malicious code execution.