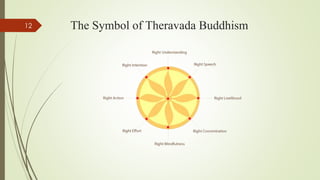
Theravada Buddhism, known as the 'doctrine of the elders,' is one of the three major sects of Buddhism that emerged in India and is prominent in Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia. It emphasizes the use of Pali as a sacred language and the Pali Buddhist canon (Tipitaka) as its highest authority, with an estimated 100 million adherents worldwide, particularly in Southeast Asia. Recently, Theravada Buddhism has gained traction in the Western world, bringing the total number of Theravadins to over 150 million globally.