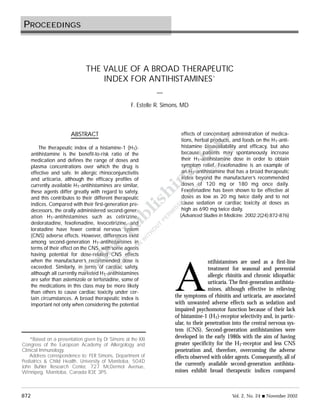
This document discusses the therapeutic index of antihistamines, which is defined as the benefit-to-risk ratio or efficacy-to-safety ratio that determines the range of doses where a drug is effective and safe. While second-generation antihistamines have similar efficacy for allergic rhinitis and urticaria, they differ in their safety profiles and therapeutic indices. Fexofenadine has one of the broadest therapeutic indices, having been shown to be effective at doses as low as 20 mg twice daily and not causing sedation or cardiac toxicity at doses as high as 690 mg twice daily. A broad therapeutic index is important considering potential drug interactions and situations where patients increase their dose in search of


![876 Vol. 2, No. 24 s November 2002
REFERENCES
1. Kaufman DW, Kelly JP, Rosenberg L, Anderson TE, Mitchell
AA. Recent patterns of medication use in the ambulatory
adult population of the United States: the Slone survey.
JAMA. 2002;287(3):337-344.
2. Simons FE, Silver NA, Gu X, Simons KJ. Skin concentrations
of H1-receptor antagonists. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
2001;107(3):526-530.
3. Grant AJ, Danielson L, Rihoux J-P, DeVos C. A comparison
of cetirizine, ebastine, epinastine, fexofenadine, terfena-
dine, and loratadine versus placebo in suppressing the
cutaneous response to histamine. Int Arch Allergy
Immunol.1999;118:339-340.
4. Lee EE, Maibach HI. Treatment of urticaria. An evidence-
based evaluation of antihistamines. Am J Clin Dermatol.
2001;2(1):27-32.
5. Simons FE, Simons KJ. Clinical pharmacology of new hista-
mine H1 receptor antagonists. Clin Pharmacokinet.
1999;36(5):329-352.
6. Van Cauwenberge P, Juniper EF. Comparison of the effica-
cy, safety and quality of life provided by fexofenadine
hydrochloride 120 mg, loratadine 10 mg and placebo
administered once daily for the treatment of seasonal aller-
gic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000;30(6):891-899.
7. Casale TB, Andrade C, Qu R. Safety and efficacy of once-
daily fexofenadine HCl in the treatment of autumn seasonal
allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 1999;20(3):
193-198.
8. Howarth P, Stern M, Roi L, Reynolds R, Bousquet JP. Double-
blind, placebo-controlled study comparing the efficacy and
safety of fexofenadine hydrochloride (120 mg and 180 mg
once-daily) and cetirizine in seasonal allergic rhinitis.
J Allergy Clin Immunol.1999;104(5):927-933.
9. Finn A, Kaplan A, Fretwell R, Qu R, Long J. A double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial of fexofenadine HCl in the treatment
of chronic idiopathic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
1999;104(5):1071-1078.
10. Hindmarch I, Shamsi Z. Antihistamines: models to assess seda-
tive properties, assessment of sedation, safety and other side-
effects. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999;29(suppl 3):133-142.
11. Mann R, Pearce G, Dunn N, Shakir S. Sedation with “non-
sedating” antihistamines: four prescription-event monitoring
studies in general practise. BMJ. 2000;320:1184-1187.
12. Pratt C, Brown A, Rampe D, et al. Cardiovascular safety of
fexofenadine HCl. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999;29(3):212-216.
13. Mason J, Reynolds R, Rao N. The systemic safety of fexofe-
nadine HCl. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999;29(3):163-170.
14. Hindmarch I, Shamsi Z, Kimber S. An evaluation of the
effects of high-dose fexofenadine on the central nervous sys-
tem: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study in healthy vol-
unteers. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002;32(1):133-139.
15. Dogan A, Offord S, Catafau A, et al. Cerebral H1-receptor
pattern at baseline and after a single oral dose of the anti-
histamine fexofenadine [abstract]. Ann Allergy Asthma
Immunol. 2000;86(1):108. Abstract P71.
16. Leurs R, Church MK, Taglialatela M. H1-antihistamines:
inverse agonism, anti-inflammatory actions and cardiac
effects. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002;32(4):489-498.
17. Zareba W, Moss AJ, Rosero SZ, et al. Electrocardiographic
findings in patients with diphenhydramine overdose. Am J
Cardiol. 1997;80(9):1168.
18. Russell T, Stoltz M, Weir S. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacody-
namics, and tolerance of single- and multiple-dose fexofena-
dine hydrochloride in healthy male volunteers. Clin
Pharmacol Ther. 1998;64(6):612-621.
19. Hansten PD, Levy RH. Role of P-glycoprotein and organic
anion transporting polypeptides in drug absorption and dis-
tribution: focus on H1-receptor antagonists. Clin Drug
Invest. 2001;21(8):587-596.
20. Woosley RL. Cardiac actions of antihistamines. Annu Rev
Pharmacol Toxicol.1996;36:233-252.
21. Simons FE. Is antihistamine (H1-receptor antagonist) therapy
useful in clinical asthma? Clin Exp Allergy. 1999;29(suppl
3):98-104.
PROCEEDINGS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/872-876v2-24-150902034915-lva1-app6892/85/THERAPY-INDEX-5-320.jpg)