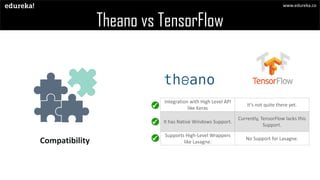
The document compares two scientific computing libraries, Theano and TensorFlow, highlighting their features, performance, and support for various operations. It outlines differences in speed, compatibility with high-level APIs, community support, and code readability. Additionally, the document includes code snippets demonstrating the use of both libraries for training a model.









![Code Readability
import theano
import theano.tensor as T
import numpy
# Again, make 100 points in numpy
x_data = numpy.float32(numpy.random.rand(2, 100))
y_data = numpy.dot([0.100, 0.200], x_data) + 0.3
# Intialise the Theano model
X = T.matrix()
Y = T.vector()
b = theano.shared(numpy.random.uniform(-1, 1), name="b")
W = theano.shared(numpy.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, (1, 2)), name="W")
y = W.dot(X) + b
# Compute the gradients WRT the mean-squared-error for each parameter
cost = T.mean(T.sqr(y - Y))
gradientW = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=W)
gradientB = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=b)
updates = [[W, W - gradientW * 0.5], [b, b - gradientB * 0.5]]
train = theano.function(inputs=[X, Y], outputs=cost, updates=updates, allow_input_downcast=True)
for i in xrange(0, 201):
train(x_data, y_data)
print W.get_value(), b.get_value()
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# Make 100 phony data points in NumPy.
x_data = np.float32(np.random.rand(2, 100)) # Random input
y_data = np.dot([0.100, 0.200], x_data) + 0.300
# Construct a linear model.
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1, 2], -1.0, 1.0))
y = tf.matmul(W, x_data) + b
# Minimize the squared errors.
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - y_data))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5)
train = optimizer.minimize(loss)
# For initializing the variables.
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
# Launch the graph
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
# Fit the plane.
for step in xrange(0, 201):
sess.run(train)
if step % 20 == 0:
print step, sess.run(W), sess.run(b)
# Learns best fit is W: [[0.100 0.200]], b: [0.300]
www.edureka.co](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theano-vs-tensorflow-191023053902/85/Theano-vs-TensorFlow-Edureka-14-320.jpg)
![Code Readability
# TensorFlow
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1, 2], -1.0, 1.0))
y = tf.matmul(W, x_data) + b
# Theano
X = T.matrix()
Y = T.vector()
b = theano.shared(numpy.random.uniform(-1, 1), name="b")
W = theano.shared(numpy.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, (1, 2)), name="W")
y = W.dot(X) + b
www.edureka.co](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theano-vs-tensorflow-191023053902/85/Theano-vs-TensorFlow-Edureka-15-320.jpg)
![Code Readability
# Tensorflow
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - y_data)) # (1)
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5) # (2)
train = optimizer.minimize(loss) # (3)
# Theano
cost = T.mean(T.sqr(y - Y)) # (1)
gradientW = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=W) # (2)
gradientB = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=b) # (2)
updates = [[W, W - gradientW * 0.5], [b, b - gradientB * 0.5]] # (2)
train = theano.function(inputs=[X, Y], outputs=cost, updates=updates, allow_input_downcast=True) # (3)
www.edureka.co](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theano-vs-tensorflow-191023053902/85/Theano-vs-TensorFlow-Edureka-16-320.jpg)



