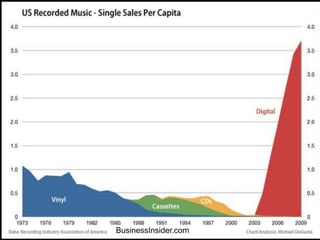
The document discusses the history and evolution of entertainment and information technology from early motion pictures and radio to today's digital streaming media landscape. Key developments include the introduction of personal computers in 1977, the public availability of the internet in 1992, and the rise of streaming video starting in 1997. The computer age and Moore's law have enabled powerful portable devices and digital distribution of media via online stores, YouTube, and streaming services like Netflix and Hulu. However, online piracy and the increasing demands of internet video traffic pose challenges for the entertainment industry and network infrastructure.