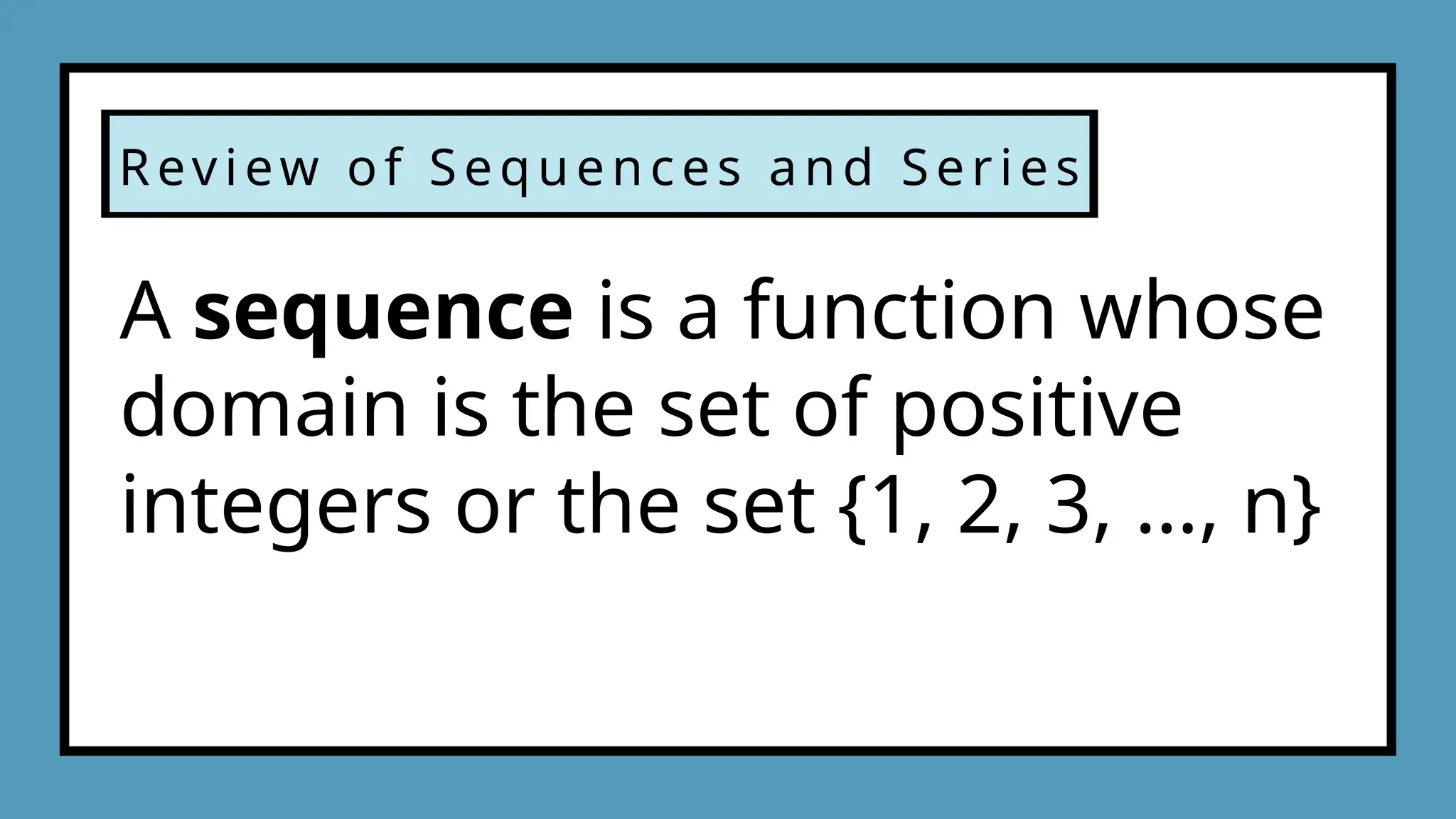
The document focuses on summarizing the concepts of sequences and series, including the differences between them and types of sequences such as Fibonacci, arithmetic, geometric, and harmonic. It explains the use of sigma notation for representing series and includes examples for finding sums and associated series. Additionally, it presents problems related to arithmetic and geometric sequences with practical applications of summation notation.